In recent years, digital technologies have raised a lot and in a number of fields, they are doing well. With the growth of digital technologies, a number of trends and things are changed now. Wireless technology is one of the upcoming technology in the market which allows portability and connectivity from anywhere. A wireless sensor network is a wireless network consists of distributed autonomous devices with the combination of sensors used for controlling and monitoring physical or environmental conditions, e.g. temperature, sound, pressure, vibration, motion at different points. Area monitoring is one of the common applications of WSN; environmental monitoring is also one of the best aspects of a wireless sensor network. A number of researchers on the wireless network, sensor devices have enabled the development of low cost, low power, and efficient systems for different domains. Usually, in a wireless network, nodes are connected directly with the monitoring station communication load quickly drains the network power resources. Sensor networks are one of the special cases of ad hoc networks. LIFL is designing strategies for updating energy-efficient connected active sensors in order to extend the network life. Three areas require solutions: area coverage, request spreading, and data aggregation.
Area coverage if a sensor node is dropped randomly on target it must monitor, in this case, the area dominating set perform a dual function i.e. extend the network’s monitoring capability and activity schedule. A simple localized protocol is used for the dynamical selection of the area dominating the set. With the aid of protocol monitoring capability is close to 1 if the threshold is less than 1/ (1+√5) of sensor area radius. Some researchers have a proper solution that empowers every node to know its neighboring node position before a monitoring decision is made. The main problem in this whole scenario is that prior knowledge about all sensors, which enhances significant communication overhead one sensor starts to die between communications. Area dominating sets works with the aid of protocols.
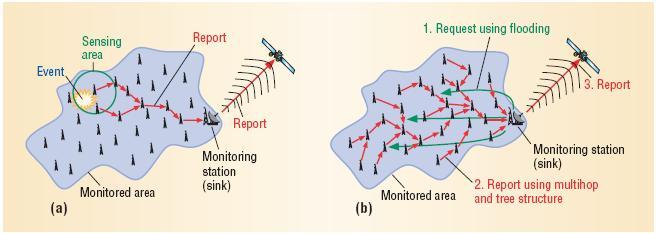
Request spreading. Wireless network usually uses broadcasting for finding routes in order to discriminate requests and data and is based on energy-efficient broadcast protocols. The basic protocol is blind flooding, which is used to generate redundant transmission and leads to packet collision over the MAC network layer. Researches proposed a number of protocols in order to reduce retransmission while ensuring that every node receives a broadcast message. Fixed transmission range protocols save energy by reducing the number of sensors that take part in broadcasting. An energy-efficient solution requires using this network requires more nodes than a fixed transmission solution.
Data aggregation. When the sensor receives a message, it must acknowledge by reporting its measurement. It only responds with important information like average value or extreme energy. The spanning method is also used to reduce message retransmission. For a particular request, a node can wait for multiple replies from all nodes in the tree before replying to the data fusion.
The wireless network is considered best but there are some flaws in this area. WSN widely uses an algorithm and implicit assumption is always made that a design or protocol is independent of WSN and there is no variability in this application, this assumption is clearly false. WSN relies on global co-ordination is necessary, not all application requires global coordination protocol literature does not consider numerous design choices which leave complexity and depth in literature. There are three undefined questions: specific application which needs to be deployed over a large network, Why the various design choices not listed to make the various networking or related issues travel in real applications, what are the basis of evaluation new protocols when parameter space is not justified against specific applications.
Works Cited
Jean Carle and David Simplot-Ryl. (2004) Energy Efficient Area monitoring for wireless sensor network. Web.