Introduction
The world is not just people, flora and fauna that are on the surface. There are great many of other different organisms that exist in the world, but most people do not see them. The marine world is strange and unique; the organisms that inhabit it may be ranged from the smallest to the biggest in the world according to the size, and from the simplest to the most complex according to the level of the evolutional development. The main purpose of the paper is to present the information about algae, their classification, ancestry and evolution, adaptations and life cycle; moreover, some authors that conducted the research in the sphere will be discussed.
Literature Review
Algae have been researched by a number of scientists. There are great many of different books and other materials on the topic. Juliet Brodie and Jane Lewis (2007) presented a good book on algae where the past and present of the organism is described along with the suppositions about their nearest future based on the scientific conclusions. The other book written by Peter Robert Bell and Alan R. Hemsley (2000) dwells upon the green plant in general, pointing to the most significant points. Such authors as Christer Brönmarkn and Lars-Anders Hansson (2005), and Darryl L. Felder (2009) did not conduct the research specifically on algae, still the information they present about water biology and biodiversity is related to algae in some content.
Algae Classification
There are different types of alga classification and we shall discuss two of them (taxonomic and ecological) to give the general understanding on the types of algae. The taxonomic classification is based on four major considerations: pigmentation, cell wall, storage products, and flagellation, and five major divisions: bacillariophyta (diatoms), chlorophyta (green algae), cyanophyta (blue-green algae), chrysophyta (yellow-green algae), and rhodophyta (red algae) (Hauer and Lamberti 328). Depending from the type, algae possess different characteristics that may influence their place of inhabitant, adaptation qualities and life cycle. Moreover, being one of the parts of the evolutionary chain of higher plants, the type of algae could be the part of the definite land plant.
The ecological classification of algae is based on the principle of the microhabitat they may occupy. Several types of alga maybe separated out while ecological classification, for example, “epilithon is the name given to the benthic algae growing on the rocks, epiphyton grows on plants, epidendron grows on wood, epipelon grows on fine sediment, epipsammon grows on sand, and epizoon grows on aquatic animals” (Hauer and Lamberti 329). As it was mentioned above, it is not the only existing classifications of the algae, as different authors in most cases present their own classifications and it is impossible to mention them all in the paper.
Algae Ancestry and Evolution
Algae are a mixture of complex organisms that came a long evolutional process thanks to which we may see alga in the present forms. To understand the biological essence of algae, we should dwell upon the ancestry diversity and evolution of it. Plastids are the main forms that are considered to be the ancestors of the present existing algae. It is not a surprise that we mentioned this form, as plastids are the most familiar cells of the marine organism (Brodie and Lewis 11). In addition to the information mentioned above, the marine simplest organism are considered to be less researched, as there are great many of different types of such organism, most of them are situated on the depth which is not reached by people, even with the help of modern technologies.
Turning to the question of algae ancestors, it should be mentioned that the evolution of algae is considered from its aquatic habitat. The environmental change is considered to be one of the lading factors of algae evolution. It is proved that algae is extremely ancient form of life and the records of them begin about 3000 million years ago. Following the evolutional chain of algae, it may be concluded that “prokaryotes preceded eukaryotes (perhaps by as much as 1000 million years ago), and that simple unicellular and filamentous algae preceded the pseudoparenchymatous and parenchymatous forms encountered today in the three major divisions of eukaryotic algae: rhodophyta, chlorophyta, and phaeophyta” (Bell and Hemsley 98). It should be mentioned that the algae, as well as the biggest part of the marine organisms are not researched till the end and the information presented above is one of the theories. Still, the theory is supported with the evidence that is scientifically proved and well-reasoned.
It is impossible to avid some facts of importance of algae in the evolutionary chain of the whole mankind. According to Professor Ralph E. Taggart, green algae group served as one of the sources of the evolution of the land plants (Taggart par. 1)
Algae Adaptations and Life Cycle
Before discussing the adaptations and life cycle of algae, it should be mentioned that marine environment is severe and it is impossible to stay there without adaptations. First of all, algae have a strong adaptation to the temperature as depending on the depth, the temperature changes as well as one within the seasons change. Furthermore, algae can adapt to other extreme environmental conditions (Felder 191). Moreover, algae are able to have adaptations to “reduce sinking rate by decreasing density, adjusting size and shape, or having motility organelles” (Brönmark and Hansson 8). Charles D. Amsler is sure that algae should have the adaptations to biological communities, as sometimes algae should possess behavioral, physical or chemical adaptations to survive in the surrounding environment (Amsler 1).
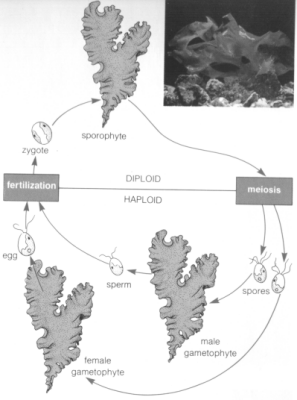
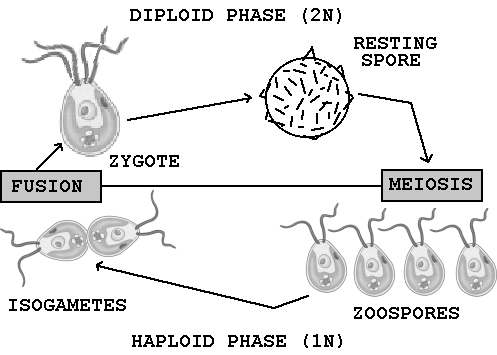
The life cycle of algae will be more convenient to explain looking on the illustrations in Appendix 1 and 2. Appendix 1 present the simplest life cycle of algae, that starts with fusion and coming through diploid and haploid stages. Appendix 2 shows the complex life cycle where algae comes the longer way with multicellular haploid stage that is the dominant in the process (Taggart par. 2).
Conclusion
In conclusion, algae are one of the simplest forms of the marine organisms. While writing the paper we presented the information about algae, their classification, ancestry and evolution, adaptations and life cycle; moreover, some authors that conducted the research in the sphere will be discussed. It was stated that there are great many of different types of algae which influence their characteristics. The ancestry and evolution points are not researched till the end, so it may be one of the aspects of the further conduction of the research. It was also concluded that algae are greatly adaptive organisms and may survive in different environmental conditions, with changing diversity, temperature and biological communities. They are able to use different survival strategies which are disclosed in behavioral, physical or chemical adaptations.
Works Cited
Amsler, Charles D. Algal chemical ecology. New York: Springer, 2008. Print.
Bell, Peter Robert and Alan R. Hemsley. Green plants: their origin and diversity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000. Print.
Brodie, Juliet and Jane Lewis. Unravelling the algae: the past, present, and future of algal systematic. London: CRC Press, 2007. Print.
Brönmark, Christer and Lars-Anders Hansson. The biology of lakes and ponds. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2005. Print.
Felder, Darryl L. Gulf of Mexico Origin, Waters, and Biota: Biodiversity. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 2009. Print.
Hauer, F. Richard and Gary Anthony Lamberti. Methods in stream ecology. New York: Academic Press, 2006. Print.
Taggart, Ralph E. Algae life cycles. Michigan State University. Web.
Appendix 1
Simplest algae life cycle
Appendix 2
Complex algae life cycle, multicellular stage