Executive summary
This report has organised on BMW luxury car that has been suffering from declining sales for the last two years due to recessionary influences and involved to develop successful strategies for recurring this luxury car to an optimistic sales growth within a year by influencing consumer behaviour in the UK. To do so this paper has given central attention on the impact of external influences while it has also enlightened on the consumer behaviour, the paradigm of luxury goods, consumer behaviour model for luxury goods and analysis of BMW luxury cars.
Impact of External Influences
Introduction
This report has been deliberated BMW UK, a luxury automaker with a strong and successful track record of customer satisfaction but due to the global financial crisis, it is passing through a declaiming sales. BMW (2008) mentioned that it has the competence to overcome the situation by 2010 and sustain in the market as a leader in the automotive industry by introducing innovative products with a new strategy, and gives incentives, rewards, reductions, and other facilities. BBC (2010) quoted the statement of Gordon Brown regarding the current situation of the automotive industry and added that BMW (UK) is fighting for the future. In this context, it should adopt new strategies to boost profits; the producer of this report has assumed as a Marketing Manager and kept his effort to identify the external influences on luxury cars of BMW.
Consumer behaviour
Kotler & Armstrong (2009) has labelled marketing as a societal and organisational supervision process that facilitate people to inter-exchange their product and services to satisfy their needs and to create values for the organisations while the essential feature of marketing is the consumer behaviour – the way of appreciating consumers decision-making process and the factors precisely manipulate their buying behaviour. Kotler & Armstrong (2009) has designed the stimuli-response model to analysing the interaction and motivation between the marketer and consumer’s reaction toward that has demonstrated in the following diagram-
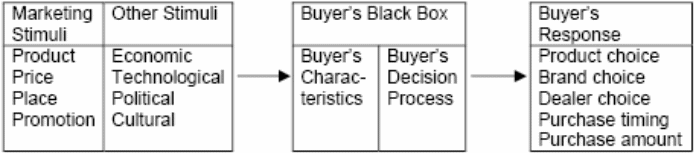
In the above diagram, the external factors such as marketing motivations and other stimulus have transformed within the black box of buyer considering as his responses where the black box organised with two segments presented as the buyer’s characteristics as well as his decision-making process. Taylor (2009) added that the features of the buyers could be further classified as cultural, social, personal, and psychological characteristics that are demonstrated in the following diagram-.
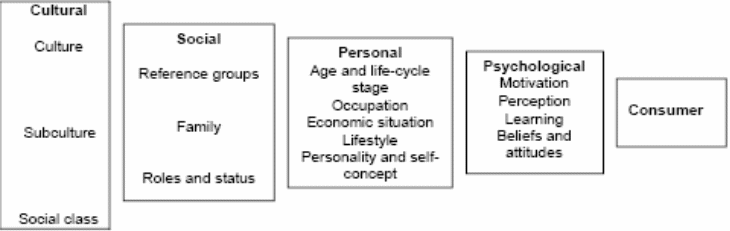
The above models have supposed as a dominant aspect of consumer behaviour the marketers know the significance of the relevant elements within the general framework and would instantaneously focus on the luxurious goods specificities.
Zhengxin (2009) added that the consumption encourages innovation of product and service while the luxury products are more and more turning into essential goods during the general improvement of living standards of people by contributing to the creation of new employment opportunities.
Chua and Zou (2009) argued that from the materialistic perception, distinctions of consumption among the social classes are also imitated in luxurious goods segment while there are strong rapports among consumption, happiness, and income. If the basic needs of people are fulfilled and the increase of income continues, it would bring a significant shock on the stage of happiness, further than this doorstep in excess of consumption can generate other problems as well as a certain degree of attraction to luxurious goods.
Zhengxin (2009) pointed out five different types of consumer behaviour named as unplanned spontaneous consumerism; expansive consumerisms that linked with surplus buying and overloaded consume uninhibited consumerism that is fascination due to greater disposable, consumerism concerned with the brand, and loyal consumerism that fix to a single brand. It has been identified seven mindsets of consumers during their expenditure behaviour these are expenses to get hold of spiritual satisfaction, gratifying the psychological needs; to accentuate individual’s value – it is the point of consumerism that excels needs and turn into identical to be wealthy and famous (Dawber, 2010).
Switching over the mindset is an initiative to renovate money into a tangible means and the comfort consumerism revolve the purchasing function as a way of the drive out self-dissatisfaction. The exploration of innovation turns the purchasing function to the stage of demonstration effect and amassing while lacking interest twist consumerism as a habit of meaningless spending.
Consumer surplus is the variation connecting to the price that a consumer agreed to pay the amount that he has to make payment is also identified as market gain completed by the customer through the course of acquisition. Such variation generates the ground of purchaser profit while the difference between price elasticity and consumer’s mindset has an increasing impact on consumer surplus with accessible time.
The Paradigm of Luxury Goods
Seringhaus (2002) has attempted to delineate the notion of a luxury good as an excellent for which demand goes high to higher further than proportionally with income growth while for necessity good demand does not react with income growth in such way.
Brown & Deaton (1992) and Silverstein & Fiske (2009) added that the luxury goods are assumed to carry out high-income elasticity of demand considering the consumer turns into more affluent; he will be interested in purchasing the luxury goods in a greater extent. At the same time when the customer’s income goes down, demand for luxury goods will decrease as the income elasticity of demand for luxury goods is not steady in relation to income, it possibly will shift to a different levels. Consequently, the luxury good could be converted into a normal good otherwise turn into an inferior good of poles apart income stage, for instance, while a rich consumer discontinues purchasing an escalating quantity of luxury automobiles, that luxury car will turn into an inferior good (Gutierrez, 2006).
Chadel (2009) argued that the paradigm of luxury goods has shifted in this modem era while lots of factors have seriously biased the conceptual framework of the luxury good is at present experiencing huge changes of consumer behaviour, as the recent generations come forward with different novel requirements and desires while the production of luxury goods eager for immolation. That went before with luxury goods were clarified by the exceptional characteristics, qualities and rare features inherent to the product turned into luxury for instance fashion, ornaments, automobiles, and real estate while their exceptional quality, comfort and prestigious properties made them luxury goods.
BCG (2002) added that the luxury is not only allied with the technical characteristics of a good but it is also concerned with the emotional and brand features that generate the sense of prestige or respect belonging to the communities. Stegemann (2006) emphasised that these attributes lead the luxury produces to innovate pragmatic luxury paradigms throughout the process of production to delivery to ensure consumers satisfaction with brand development.
Silverstein & Fiske (2009) pointed out the most influential aspect of modern luxury goods and added that it has shifted from ‘Prestige’ that is concerned with high cost and lower quantity to the direction of ‘Masstige’ that is concerned with high cost and bulk volume purchase. It is essential for the luxury produces that the customers not only purchase for the sake of having possession of precious or hit cost products but also eager to reduce stress and frustration and the luxury marketers needed to address this aspect.
Consumer Behaviour Model for Luxury Goods
Brown & Deaton (1992) emphasised on Engel Curve to modelling consumer behaviour for luxury goods while Engel’s Curve have addressed on luxury as well as necessities. It has assumed that the exponential structure of income -demand function would be represented as –
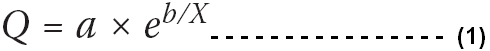
- Where Q = quantity of consumer demand, a dependable variable,
- a = Parameter,
- e = exponential function,
- b = Parameter,
- X = Consumer’s income level, (here is an independent variable)
To resolve the parameters applying ordinary least squares technique, above exponential equation of the Engel curve would be shaped as –
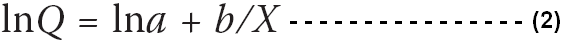
Integrating equation (1) and (2) the income elasticity function for Engel’s Curve would form as follows-
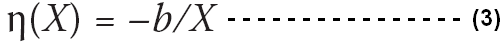
In equation (1) if the parameters a > 0 and at the same time b > 0, then the interaction of income -demand function would match with purchasing inferior goods under Engel curve that has demonstrated consumers income level X ∈ (0;+∞)
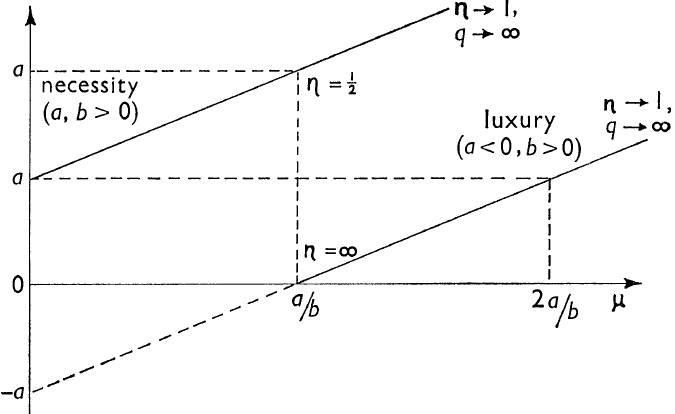
Brown & Deaton (1992) and Syrovátka (2007) added that the exponential function of the Engel’s curve meets the condition a > 0 ∧ b < 0, the transformation of income-demand interaction would sanguinely match the criteria of normal necessary goods as well as luxury goods and those possibilities would be generated from the impending worth of income elasticity function. Customer behaviour respond to the luxury good has demonstrated in the above figure.
Analysis of BMW luxury Cars
Anurit, J. et al (2005) and BBC (2010) reported that BMW (UK) would help the customer to purchase a new car by offering scrap incentive to increase sales. The company provides a clear overview of CRM to identify the best customers and their choice in order to offer best service to retain the loyalty of customers by maximising current and lifetime value of customers. The environment of the automobile industry flattering gradually more complicated and competitive that differentiate the industry with challenges of competitive profit margins and auto dealers are assertively addressing on CRM to draw attention of new customers.
External influences
Rather than the product quality of luxury BMW cars and after sales services, following are the external influences to boost it sales revenue-
National culture
Britain the homeland of modern civilization consists with England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales is full of customs, and traditions while most of them have very extended histories. BMW UK has the opportunity to discover most of customs and traditions by addressing lucrative offer in social events.
Sub-cultures
For BMW UK, the subculture has been poised with black people migrated from Africa while the fastest growing ethnic subculture in UK is the Asian specially Bangladeshis, Indians and Pakistani and the company has the strategy for them with low priced luxury cars.
Family and household influences
For BMW luxury cars family and household influences played a vital role for its historical growth and the company is eager to inspire this belongings.
Opinion leaders
BMW’s media policy has engaged to maintaining advertising in both print and electronic media opinion leader are recurrently influencing others customers behaviours. BMW UK is eager to get in touch with opinion leaders so far they can. It is essential for BMW to enlist these talents to assist them extend their efforts for the company.
Reference groups
The real individuals and group who has conceived on the BMW luxury cars with significant evidence self-evaluations, ambition, and behaviour has treated as reference and BMW use their opinions as reference. The company has considered its reference groups are significant to convey advertising messages those move towards the reference group for further influence (BMW, 2009).
Income and social class
The income and social classes of BMW luxury car purchasers and their standard of living prolong to getting better, which is correlated with roles of females in the workplace and they are achieving high-paying jobs and escalating higher. Consumer demand for BMW luxury car depends on capability and enthusiasm to purchasing and relaxing standard of living, as they tend to spend money for securities and comforts.
Recommendation
- BMW should develop more efficient database to collect and retrieve data about the customers and dealers to take steps to ensure prompt the services to the customers.
- The call centre of the BMW needs to be virtual and dynamic to respond to the demand and enquiry of the customers to overcome existing few dilemma in CRM issues at
- BMW necessitates to building a team of employee with strong interpersonal skills to deal with the customers to convince them more vigorously;
- The marketing and communication of BMW could do with target properly, so that the right person gets the right massage,
- BMW would build a philosophy where the dealer not only focuses on profit but also on the long-term relationship with the consumers.
- BMW should consider the CRM strategies of competitors to acquire a comprehensive and consistent view of every customer,
- BMW should integrate other related software for customer relationship management, procedure for sales, complaints management, campaign management, after-sales service, and facilitate the sharing of knowledge.
Conclusion
As a leader of luxurious automobile, BMW is continuously emphasising on how to expand its competitive perimeter by learning from their customers and renovating that gathered knowledge into victorious marketing strategies for their future growth to overcome the impact of global financial crisis. BMW’s strapping CRM strategy and proper analysis of customer behaviour would contribute the company to boost its sales and increase profit
Recommended Positioning Strategy
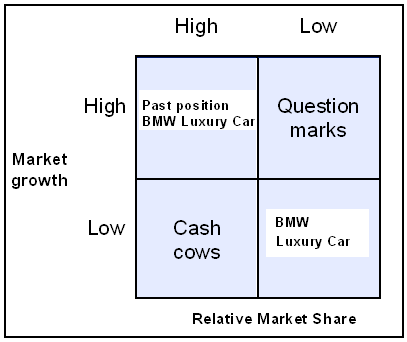
Position of BMW Luxury Car in BCG Matrix
Before attempt to develop the board of BMW Luxury car considering both online and offline positioning messages and images, it is essential to assess the position of BMW in the BCG matrix, as it is a portfolio planning process to measure the market condition of the brand in terms of relative market growth rate and relative market share.
Star
Before global financial crisis, BMW Luxury car occupied this section but for the changing of purchasing power this brand failed to reach expected market growth and share. The aim of the stakeholders is to regain its position by changing customer behaviour or increasing market demand;
Cash cow
On the other hand, the brand of BMW Luxury car is in the high risk to fall their position in terms of growth rate and market share business of the competitors as this product is in dog section. In this context, the decision-maker of this brand intend to upgrade its position in this segment within very short time as it indicates high market share in low market growth.
Dog
It is very unfortunate that the brand of BMW Luxury car occupies this sector at this moment because this part indicates low- growth with low- share of its business. In addition, the companies require large investment for further improvement as it has to increase budget for all sectors. However, the board of directors are monitoring the position in order to find out possible ways to overcome from economic meltdown though it is very difficult for other automobile manufacturers to capture star position in such economic distortion.
Question mark
Many competitors of BMW Luxury car occupied the position of Question mark in global financial crisis as they experienced favourable growth rate in region of the world.
Positioning strategy for BMW Luxury Car
According to the view of Johnson, Seholes & Whittington (2006), positioning is a significant feature of an offering’s strategy, which demonstrates its main advantages with regard to competitive offerings. By applying positioning strategy, the marketer of BMW Luxury Car will try to build an image or occupy a distinctive place in target customer’s mind through its quality, speed, price, and durability product, brand, and so on. However, some important stages of BMW Luxury Car’s overall positioning strategy are –
Positioning map
The following table illustrates the positioning map of BMW Luxury Car, which will help the marketer to recognize the perception of target clients towards the brand of BMW Luxury Car in terms of other competitors, for example –
Table 1: Evaluation of competitive positioning of BMW Luxury Car. Source: Self generated.
Selection of a positioning strategy
As the sales revenue has decreased, the brand of BMW Luxury Car should choose a perfect positioning strategy, which will include possible competitive advantages of the firm, comparing them with the value position of other car manufacturing companies. However, the marketer of the BMW Luxury Car should concentrate more on the product and service differentiation by delivering globally standard automobiles at comparatively reasonable prices in order to develop customer demand. After reducing the price of this luxury brand, it should take a look on the sales growth to measure the development of this strategy. As the purchasing power of the customer has reduced, BMW should provide detail information about the value proposition, which refers to the full positioning of its brand or the complete mix of benefits. However, BMW should give more attention on the number of differentiating issues to promote about the incorporation of various characteristics, such as, significant, distinctive, superior, communicable, defensive, affordable, and lucrative and so on. Considering the benefits of this luxury brand and the price of the products, BMW Luxury Car brand should select following positioning strategy in order to change the mind of customers.
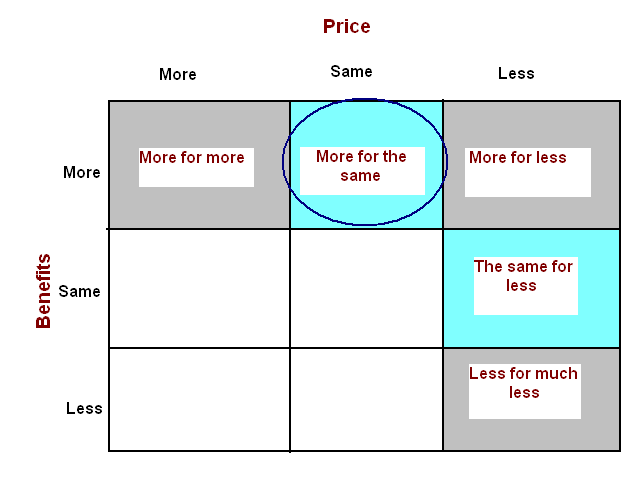
According to the figure 12, it should pursue “more for the same” value proposition strategy in order to build a stronger fight with other luxurious car brands in terms of offering high quality motor vehicles at reasonable cost.
Building a positioning statement
The aim of this strategy is to provide a statement, which will summarizes the brand positioning of BMW Luxury Car while it has been developing a number of adoptive and effectual positioning statements in different periods of time, for instance, development of brand positioning statement as “The Ultimate Driving Machine” or “A Company of Ideas.”
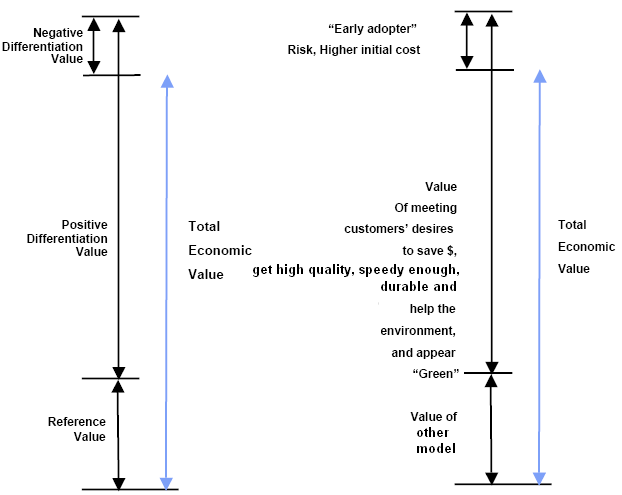
Economic Value for the Customer model
It has already mentioned that BMW offer low cost luxurious car for the customer but it failed to capture market of the developing countries. In this context, the marketer of this product can consider the EVC model of Toyota, as this model examines the economic value that a purchaser calculates while purchasing the product. According to the view of Capon & Berthiaume (2007, p.41), this value investigation follows a measurement scale from negative differentiation to positive differentiation value as well as reference value –
Purchase decision map
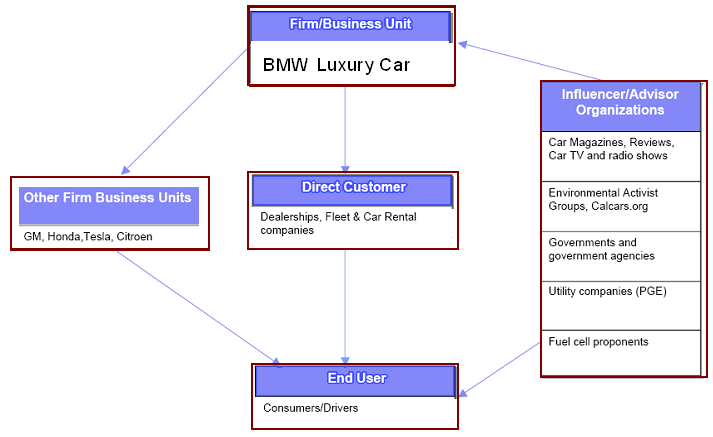
Information
BMW Luxury Car has already integrated SAP/ERP in order to maintain the close relationship with customers because the environment of the automobile industry becoming more complicated and competitive. By taking help of these software, the marketer regularly contact with the old customers to provide latest information of the offerings but it never contact with new customer, as it has to follow Data Protection Acts.
Evaluation
It is important to mention that the overall customers measures alternatives in terms of model specifications, affordability, accessibility, and emotional variables because the market is competitive where most of the companies offer similar products. According to the annual report 2009 of BMW, the buyers of this luxury brands mostly focus on technical, monetary, engines, models or style, and other functional features of a car.
Choice
The marketer of BMW Luxury car always value customers because the select any product considering the outcome of functional, economic, and emotional reactions of buying decision.
Post- purchase
In order to satisfy the customers, BMW Luxury Car should develop post-purchase services otherwise, the customers will lose their confidence on the products. For instance, this brand guarantees replacement and repair facilities within a particular timeframe but practically the marketer ask for mileage used within the duration and disagree while provide any service after sales. However, most of the previous customers were highly satisfied with the service of the BMW Luxury car and the post purchase service, which has positive influence on the target market of this brand.
Recognition
The research and development teams should more concentrate on the market risk as the position of the company in BCG matrix has fallen for the global financial downturn. In addition, many other factors influenced the customers while a customer would like to purchase a car, for example, changes in life style for social or economical problems, high price of fuel, and environmental issues (like global worming) and so on.
Key Recommendations
- As the global automotive market is getting more and more competitive, the brand of BMW Luxury Car should consider the positioning strategies of the competitors to set up own positioning strategy;
- It should reduce the price of the products in order to capture the international market like high-density areas. The rational for this recommendation is that most of the people of Asian countries lave not enough money to purchase luxurious car, so they search alternative products like Toyota, Ford motors and so on;
- In addition, BMW should identify the nature of instability of global automotive market to implement realistic positioning strategies and it can apply adequate forecasting methods to predict uncertainties of the market;
- The marketers of this brand should predict the market condition before introduce a new product as it would not be a realistic decision to take high risk without consider purchasing power of the customers;
- It should increase the expenditures for the R&D than the previous years to survey the market as this process will help the company to increase total sales;
- As total sales revenue of BMW is decreasing, it should boost the budget for overall marketing issues;
- It should also increase the budget for promotional activities;
- It should follow Ansoff’s strategies in order to enter in to a new market;
- It should more responsive in meeting customer demand according to their choice;
- Finally, BMW should provide special offer for loyal customers.
Critical Reflection
How I reached in this view
To arrive at my views on the customer’s behaviour towards the BMW luxury car, I have adopted PEEL (Project for Enhancing Effective Learning) process, which is an action research program. I have preferred the process to steps forward the receiving of teaching and learning of customer behaviour by means of encouraging my teachers. To discover and measure how far I learnt my lessons at classroom and interacting those outcomes with my own reflection on the concerned lecture at my individual groups or team. Within the PEEL process, I have organised the network of self-ruling voluntary groups that played a responsibility of interdependent innovator where my teachers supported regularly to reflect on practice under different problem areas applying the gained wisdom from their lectures at classroom.
My reflection
Among my independent voluntary groups, I have lectured on the paradigms of consumer behaviour and their adoption on BMW luxury car. While my first lecture pointed out consumer behaviour as the way of realising consumer’s decision-making process and the factors precisely manipulate their buying behaviour.
In my first lecture, I have explained five different types of consumer behaviour named as unplanned spontaneous consumerism; expansive consumerisms that linked with surplus buying and overloaded consume uninhibited consumerism that is fascination due to greater disposable, consumerism concerned with brand, and loyal consumerism that fix to a single brand.
My second lecture with my peer group concerned with the adoption of theories of customer behaviour on a particular company for a case study approach. In this regards, I have selected BMW luxury car and mainly focused learning outcomes of the customer behaviour module that successful lead to the action of successful marketer to influence customer’s decision-making process. From the very beginning of the module, I have the intention to experiencing and gaining effective problem solver, which aroused in case of the successful marketing manager.
Reflection of my learning on future work
However, as a professional marketing manager, I will work hard to motivate my customer’s decision-making process by applying different theoretical approach and time-to-time; I will evaluate the customer’s behavioural respond to my product to compare the achievements at sales growth.
I am pleased to share some of my feelings on the future of consumer behaviour paradigms. In very particular, I will be moving ahead towards the implications of information technology and its impartiality to analysing the customer behaviour and I must argue for online customer behaviour rather than traditional customer behaviour and suggest for more integrated CRM software for future corporate world.
Reference List
Anurit, J. et al (2005) Consumer Behaviour of Luxury Automobiles: A Comparative Study between Thai and UK Customers’ Perceptions. Web.
BCG (2002) Trading Up: The New Luxury and Why We Need It. Web.
BMW. (2009) Annual report 2009 of BMW. Web.
Brown, A. & Deaton, A. (1992) Surveys in Applied Economics: Models of Consumer Behaviour. The Economic Journal, Vol. 82.328.
Capon, N. & Berthiaume, R. (2007) Toyota Marketing Strategy for Plug-in Hybrids. Web.
Chadel, R. (2009) Does Internet really matter for the luxury goods industry? Web.
Chua, R. Y.J. & Zou, X. (2009) Effects of Exposure to Luxury Goods on Cognition and Decision Making. Web.
Dawber, A. (2010) BMW Profits Put Luxury Car Sector In The Fast Lane. Web.
Gutierrez, C. C. (2006) Consumer Attraction To Luxury Brand Products: Social Affiliation In Terror Management Theory. Web.
Johnson, G., Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2006) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases. 8th ed. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G. (2009) Principles of Marketing. 13th ed. Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Seringhaus, F. H. R. (2002) Cross-cultural exploration of Global Brands and the Internet. Web.
Silverstein, M. & Fiske, N. (2009) Trading Up to New Luxury. Web.
Stegemann, N. (2006) Unique Brand Extension Challenges For Luxury Brands. Journal of Business & Economics Research, Vol- 4, No10. Web.
Syrovátka, P (2007) Exponential model of the Engel curve. Web.
Taylor, P. (2009) Luxury or Necessity? The Public Makes a U-Turn. Web.
Zhengxin, S. (2009) Consumer concepts, behaviour and culture. Web.