Research Question
The research question underpinning a scholarly study plays a critical role in defining what data should be collected from both primary and secondary sources and establishes the path to be taken in an investigation. Bernard (2013) explained that a properly structured research question makes it possible to achieve the research goal and objectives. The following primary research question will guide this project:
What are the critical challenges in managing human resources in the current business environment?
Synopsis of the Central Research Problem
According to Azanza, Moriano, and Molero (2013), managing human resources in the modern business environment is becoming increasingly complex because of a number of factors. For example, talented employees can easily move from one firm to another. The investment of much time may be required to train and equip every worker with the right skills for the workplace. A qualified employee who is lost to a rival firm will transfer acquired skills to the new employer. Workers will potentially realize their importance within a firm as well as the employer’s motivation to retain them. Thus, employees may become demanding, especially when they know that they can always find opportunities in other companies.
This state of affairs may force a firm to come up with various monetary and non-monetary policies to ensure that competent talents are not lost to rival firms. Another emerging problem involves the constant use of social media in the workplace, especially the addictive platforms Facebook and YouTube. The number of workers who cannot resist the temptation to visit Facebook while at work is increasing at an alarming rate (Hana, 2015). The problem was thought to affect primarily young employees below age 30. However, that is no longer the case. Bryman and Bell (2015) showed that even middle-aged and some senior employees cannot resist the temptation to visit social networking sites when they are on the clock.
The problem that this study focuses on is suitable for research at a master’s level of study. A human resource manager equipped with master’s-level education is expected to understand such challenges and find effective ways of dealing with them. Human resource managers were not faced with these emerging issues as recently as about two decades ago, and because the problem is relatively new, it is not possible for current management to emulate the approach of previously effective managers. Thus, this research promises to provide an important foundation for today’s human resource managers to develop a greater understanding of the challenges currently arising in their workplace.
As Kirkman and Harris (2017) observed, managing people is not easy. As such, the concept of leadership has gained popularity with an eye to ensuring that managers can exert influence rather than attempting to force employees to take a given action. However, in some cases, this approach may require a manager to embrace the concepts of both a leader and a manager to achieve specific goals. A master’s-level student should understand how to achieve this delicate balance within the organizational setting. The problem under discussion was also considered suitable because it requires critical research. As an emerging problem, the discovery of some contentious issues may be likely as scholars are seeking common ground for solving the identified problem. Thus, critical thinking will also be necessary.
It is important to look at the academic issues that underpin the research question. Managing human resources has always been a challenge from the time the concept of management initially emerged. However, issues such as addiction to social media and the ease of moving from one job to another are relatively new. Although academicians in the field of human resource management have been focusing on these issues, Cunningham (2016) acknowledged the fact that a significant gap remains in the literature.
The nature of social media, while meant to ensure that family and friends remain connected even when physically located in different geographic locations, is evolving. It is common to find that even when friends are in the same room, they continue to access social media platforms such as Facebook and YouTube. This can be taken to mean that these sites have broadened their scope, transitioning from mere communication platforms to taking on the additional role of entertainment sites.
The dynamic nature of social media platforms poses unique challenges to human resource managers, calling for further research. As Bratton and Gold (2017) observed, the desire is always present to create an enabling work environment for employees where they are not under constant supervision by the managers. However, such freedom can be abused when employees spend much of their time on activities that are not related to their job description. Establishing the delicate balance between freedom and adequate supervision is an academic issue that demands further research.
Thinking Ahead
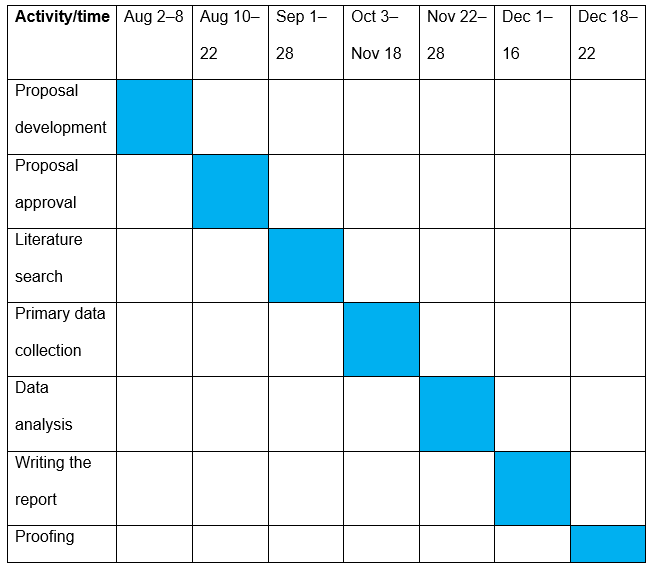
It is critical to develop a time frame for the various activities to be conducted in this study. As Billinghurst, Clark, and Lee (2015) observed, in every academic research endeavor, planning is critical. The report must be ready within the time frame set by the school. The first step to develop the proposal, which involves outlining what must be achieved in the study and how the research objectives will be realized. The next step will be the approval of the proposal.
This requires the assigned professor to go through the document and approve it before the process moves on to the next step. At this point in the proceedings, the professor can make any necessary suggestions toward improvement. When the proposal has been approved, the next step will be to collect and review relevant literature. According to Kloppenborg (2015), every research should introduce new knowledge in a given field. Duplicating information that already exists through previous studies renders a piece of research meaningless. Therefore, the student should begin this phase by reviewing what other scholars have discovered. In addition, the process of the literature review creates a foundation upon which a given study will be based while also enabling a researcher to identify gaps in the literature.
The next step is to conduct primary data collection. Identified research gaps must be addressed through collection and analysis of primary data from sampled participants who have the relevant information needed in the study. Bernard (2013) explained that a researcher must have a careful plan for how to identify the pertinent population and then develop an appropriate sample that is manageable within the time frame available for the study.
Ethical consideration should be observed when collecting data from these respondents, as will be discussed in the sections that follow. The next step is to analyze the primary data collected. Analysis should be conducted based on the research question and objectives. The outcome of the analysis should provide an effective answer to the research question. The next step is to write the report. After reviewing the related literature and analyzing the primary data, the researcher will be equipped with the necessary information to facilitate report writing. The final stage is proofing to eliminate any grammatical mistakes. Table 1 shows the time line for each activity.
Locating Literature
Shahzad, Farrukh, Ahmed, Lin, and Kanwal (2018) focused on the role and relevance of transformational leadership in the banking sector. Employees working in the banking sector play a critical role in a country’s economy. It is important to ensure that they remain loyal to their employer and to the bank’s customers to avoid cases of fraud. The authors’ main findings show that a transformational leadership style is critical in influencing employees positively and minimizing cases where they are tempted to engage in unlawful activities.
In this study, the researchers used a quantitative method to answer their research questions. They were able to determine the number of respondents who felt that this style of leadership is effective when managing employees in the banking sector. The main strength of this approach is that it makes it possible to determine a specific number of respondents who support a given argument. However, the method also precludes understanding the varying views of different participants.
Szierbowski-Seibel (2018) focused on the impact of strategic human resource management on the performance of employees. The findings of the study showed that many firms are embracing the concept of strategic human resource management. However, it is advisable to determine the impact of this approach on the performance of workers as its main aim. Every time a firm introduces a new policy, it is always advisable to determine its relevance.
The researchers used a qualitative method to establish the relevance of strategic human resource management in Europe, parts of Asia, and in North America. The strength of the method chosen is that it facilitates evaluating an issue qualitatively without having to rely on statistical figures. A researcher can answer critical questions based on varying characteristics of the issue being investigated. However, the method’s main weakness is that it does not support mathematical analysis. Thus, identifying the level of acceptance of this leadership method is not possible.
Vong, Ngan, and Lo (2018) focused on determining how the organizational climate minimizes job-related stress within an organization. In their findings, the researchers revealed that in a greatly stressful job environment, employees’ desire to quit is always strong. However, losing a highly skilled employee can present a major loss to a company. In responding to this potential problem, it may be advisable for a firm to create a positive organizational climate that can convince employees to stay despite the possible stress that may be associated with their jobs.
The researchers used a quantitative method in their study, which made it possible for them to determine the number of respondents who agreed with the claim that a positive workplace environment can make employees want to stay even in the face of job stress. However, this method did not accommodate the specific views of the respondents. The following is a list of other sources useful for the study:
- Azanza, G., Moriano, A., & Molero, F. (2013). Authentic leadership and organisational culture as drivers of employees’ job satisfaction. Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 29(21), 45–50.
- Bernard, H. (2013). Social research methods: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: SAGE Publications.
- Billinghurst, M., Clark, A., & Lee, G. (2015). A survey of augmented reality. Foundations and Trends in Human–Computer Interaction, 8(2), 73–272.
- Bratton, J., & Gold, J. (2017). Human resource management: Theory and practice (6th ed.). London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Bryman, A., & Bell, E. (2015). Business research methods (4th ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
- Cunningham, J. (2016). Strategic human resource management in the public arena. London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Hana, U. (2015). Competitive advantage achievement through innovation and knowledge. Journal of Competitiveness, 5(1), 82–96.
- Kirkman, B., & Harris, T. (2017). 3D team leadership: A new approach for complex teams. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Kloppenborg, T. (2015). Contemporary project management: Organise, plan, perform (3rd ed.). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
- Wilton, N. (2016). An introduction to human resource management. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE Publications.
The Philosophy of Social Research and the Approach
Determining the appropriate research philosophy and approach is critical to ensure that the researcher makes the right assumptions when conducting a study. Wilton (2016) explained that the chosen research philosophy should be aligned with the research approach to guarantee harmony in data collection and analysis. In this section, the researcher will discuss these two aspects of research methodology.
Research Philosophy
Ren, Fang, and Yang (2017) defined research philosophy as “a belief about the way in which data about a phenomenon should be gathered, analyzed, and used” (p. 110). This tool defines the assumptions that should be made when investigating an issue of interest. A researcher can choose any of four (positivism, pragmatism, realism, or interpretivism) research philosophies based on the nature of the research question.
It is important to understand the tenets of each of the four before explaining why one was selected as the most appropriate for the study. Pragmatism holds the view that a concept can only be acceptable if it can support actions (Busse, 2017). This view propounds that the world can be interpreted in different ways based on factors such as personal experience, knowledge, and available instruments. The ability to ensure that the interpretation made can support an action is important.
Positivism holds the view that knowledge can only be factual if gained through observation (Bernard, 2013). In this case, the primary role of a researcher is limited to data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The researcher is not allowed to influence the participants in any way. In comparison, realism takes the view that knowledge is independent of the human mind, and that the scientific method is the only way of coming to understand the truth (Bratton & Gold, 2017). Interpretivism, on the other hand, holds that reality can only be gained through shared meaning (Talat & Chang, 2017). As such, a researcher is likely to be directly involved with subjects when collecting data from them.
The most appropriate philosophy in this study, based on the research question, is pragmatism. When investigating critical challenges that human resource managers face in the modern workplace environment, it is essential to be pragmatic. A researcher must understand that different ways of interpreting the world are possible. A manager in one organization may consider it extremely difficult to control employees’ addiction to Facebook, while another in a different firm may find it easy to address such problems based on the organizational culture and other factors.
For example, a firm that restricts workers from using personal electronic gadgets such as phones, iPads, and laptops may not have to deal with the problem of Facebook addiction. Similarly, a firm that has a conducive workplace environment and is capable of paying its employees the best salary in the industry may not have to worry about the potential loss of its talented employees. The fact that different firms can deal with these two major problems in the realm of modern-day human resource management does not mean that these issues do not affect other firms. Thus, the philosophy of pragmatism was considered the most appropriate of the four alternatives.
The chosen philosophy offers both weaknesses and strengths. One of the main strengths of this method is that it makes it possible to use mixed methods, allowing the researcher to draw on the strengths of both qualitative and quantitative research methods. Unlike interpretivism, which requires a researcher to get involved with the participants to understand the truth, simple observation or a survey method can be employed.
The limited time available for the study makes a survey one of the most appropriate methods of data collection. The main limitation of the philosophy comes into play when the approach includes interpretation of a phenomenon that does not take into account the understanding of a person having a different cultural practice. For instance, it is acceptable for an employee in Japan to work for 11 to 13 hours a day (Wu & Shie, 2017). However, most employees in Europe and the United States prefer working an eight-hour day. A concept that one group of people may view as normal and acceptable may be strange to another group. Such facts must be taken into consideration in conducting research.
Research Method
After selecting an appropriate research philosophy, the next step is to determine the appropriate method of investigation. The method chosen must accommodate principles and assumptions of the selected research philosophy. A researcher can choose qualitative, quantitative, or mixed method research based on the goal to be achieved by the end of the study. Qualitative research is an explorative investigation that focuses on understanding the reasons why a phenomenon has occurred in a particular manner (Bernard, 2013), providing opinions, reasons, and motivations behind the phenomenon under consideration.
Using this method of research requires formulating semi-structured or open-ended questions to allow respondents to give their opinions and explanations of the matter being studied. In comparison, quantitative research involves statistical analysis of a specific issue to determine the number of people (respondents) who agree with a predetermined concept or argument (Bernard, 2013).
In most cases, this method is used to quantify behavior, attitude, opinion, or any other variable in a study and may take various forms such as surveys (online, paper, mobile, or kiosk surveys), interviews (face-to-face or telephone interviews), online polls, or systematic observation.
The choice is often based on the availability of the respondents for interviewing, the geographical location of the participants, time available for the study, and the financial capacity of the researcher, among other factors. In this study, it will be necessary to use a mixed research method, which will enable integrating facets of both qualitative and quantitative studies. This means that it will be possible to explain why each of the identified factors is a challenge to modern-day human resource managers and the extent to which they affect the management process. However, the main limitation of this method is that it is time-consuming in terms of employing both qualitative and quantitative methods.
The Samples
Challenges associated with managing human resources are not unique to firms in the United Arab Emirates but affect companies worldwide (Wong, 2017), meaning that the desired population for the study comprises individuals working in human resource management. Thus, potentially millions of people can qualify to be part of the study as long as their job description entails managing or supervising human resources. The inclusion criteria for individuals who will take part in the study include being over 21 years of age and working in a managerial position in a firm having over 50 employees. Because of the limited time available for this project, it is not possible to collect data from the entire population but is appropriate to identify a manageable sample of respondents who meet the set inclusion criteria for the investigation.
The study will include a sample of 150 participants. These individuals must be working in the department of human resource management in organizations within the city of Dubai. The chosen sample size was considered appropriate, given that some participants may fail to provide input for various reasons. The desirable number is 100 respondents. An extra 50 participants would help ensure that any who fail to respond can be effectively replaced; thus, the sample size will not fall below the desired minimum. The set characteristics for the sample size allow for participants to have the right information about the topic under investigation. Individuals working in the human resource department understand the challenges associated with managing human resources and are familiar with the current trends in this aspect of management.
According to Hana (2015), it is crucial to define an effective way of reaching out to the selected participants. Because the research focuses on an issue that directly affects companies in this country, it will be necessary to select specific firms to take part in the investigations. As Bernard (2013) advised, when planning to collect data from employees of a particular company, it is prudent to start by seeking permission from the relevant authorities. The sample will be accessed through the guidance of the top management unit of each company involved in the study.
Ethical Considerations
When conducting research, it is necessary to observe ethical concerns. This study raises various such concerns that should be discussed to ensure that the principles and policies of the University of Leicester regarding research ethics are observed. One of the main ethical issues is diversity in the workplace environment. According to Wu, Sun, Zhang, and Wang (2016), some of the challenges that human resource managers face in the workplace arise because of cultural differences among employees. For example, a Muslim manager working in a firm dominated by Christians may face numerous challenges because of religious differences.
As Hao, Hao, and Wang (2016) explained, it is important for human resource management scholars to promote integration within a firm. Every study should play a role in creating an environment where people understand and appreciate the existing diversity.
One problem in this study is that the investigation may evoke emotions related to cultural differences, meaning the issue must be addressed with the intent that the research will exert a positive impact on firms taking part in the study. To deal with this ethical concern, the researcher will design questions in a way that avoids evoking emotions related to cultural differences. In the case that culture is a factor that affects the management process, then it should be discussed with an eye to promoting investigation. The focus of the question should be on how employees from different backgrounds can be influenced to work as a unit regardless of cultural barriers that may exist.
According to Wilton (2016), employees in various firms in the Middle East have complained of mistreatment by their supervisors for differing reasons. In this paper, the focus is to understand the challenges that managers experience when trying to lead their employees to achieve organizational goals. Some respondents may not be in a senior managerial position and would likely prefer answering questions regarding the challenges they meet as junior employees under their managers or supervisors.
In this case, participants might come to believe that the research is biased. However, instead of examining factors that affect junior employees, the study focuses on issues that affect human resource managers. The view that the study is biased in favor of managers should be addressed before data collection from the sampled respondents begins. The researcher should explain to the participants the scope of the study along with the reasons why the study’s focus is on managers, assuring the latter that other studies are already focusing on the plight of junior employees who have highly demanding managers in the region and in other parts of the world.
Other than the ethical issues arising from the research question, Bernard (2013) noted that a researcher has a responsibility to observe ethics when collecting data from respondents. First, the security of the respondents should be given priority. Some issues tend to be controversial, and holding a view that is contrary to that of the majority may expose an individual to victimization. It is unfair to cause a respondent to be subject to harm after he or she agrees to provide a personal or expert opinion. To address this issue, all respondents will be assigned codes for the purpose of identification instead of using actual names.
Hiding the identity of respondents is an ethical requirement because it eliminates the possibility of third parties tracing them (Hana, 2015). Participants will be informed about the need to hide their real identity, and no participant will know his or her assigned code. This strategy will ensure that not even the participants will be able to identify themselves in the results.
It is ethically required that a researcher acquire permission from every participant before including him or her in the study. As explained previously, before accessing employees of the selected companies, the researcher will seek permission from top managers. After the requisite approval is given, it remains important to obtain the approval of the individual employee. The goal of the study should be explained, including the employees’ role in the data collection process. Participants will be reminded of the fact that their participation is on a voluntary basis and that they can withdraw from the study at will without any consequences. These steps will be taken to ensure that participants engage in this study without feeling coerced in any way.
Bernard (2013) noted that participants may have fundamental concerns that they want addressed before taking part in a study. For example, the issue may involve their availability or inability to take part in face-to-face interviews because of personal concerns. Responding to these concerns to the greatest possible extent is advisable as a sign of care on the part of the researcher, who should take such issues seriously. If the participant is unable to participate in a face-to-face interview for any reason, then other avenues such as phone interviews or sending questionnaires through personal e-mail may be considered. The goal will be to ensure that participants are sufficiently comfortable to participate in the study.
The University of Leicester expects that every student developing a dissertation should observe specific ethical considerations. The researcher will ensure that these rules and regulations are respected throughout the investigation. First, the researcher will see to it that the project reaches its conclusion by the deadline set by the institution. This means that primary and secondary data collection, data analysis, writing the report, and proofing must be completed within the established time frame. Second, the researcher will avoid any form of plagiarism and related malpractice in this study. The report will be written from scratch.
The goal will be to introduce new knowledge in this field of study. Duplication of existing information will defeat the purpose of the research. Any information obtained from other secondary sources will be cited appropriately using American Psychological Association (APA) format. The assigned professor may issue specific instructions to help enhance the ethics in this study. The researcher will ensure that such guidance is followed strictly to heighten the study’s success.
Techniques
The right research techniques can facilitate collecting data from various sources. After developing a plan for data collection and defining all ethical considerations that should be observed, the next step is to determine the appropriate research techniques to be used in data collection. Bernard (2013) explained that when selecting an appropriate technique, it is important to take various factors into consideration. These include the nature of the research question, the time available for the research, and the availability of participants. In this project, the researcher will use desk research, interviews, and a survey as applicable techniques for data collection in this case. The appropriateness of these research methods is supported by the relevant literature as discussed under each technique.
Desk Research
Desk research is one of the most popular techniques for collecting data (Hana, 2015). In conducting a research study, it is always appropriate to collect secondary data. A researcher must start by understanding what other scholars have discovered as part of the process of identifying an existing research gap. In this project, desk research will form the basis of the collection of secondary sources.
Traditionally, a student is expected to visit the school library to access the necessary books and journal articles. However, the emergence of electronic databases is transforming the way that secondary sources of data are accessed. Instead of visiting a physical library facility, it is easy for a researcher to visit the online libraries where most of the needed materials are available. A number of reasons make the technique appropriate for this study as discussed in the following paragraphs.
One of the main reasons why this approach was considered appropriate is the effort made by the University of Leicester to ensure that all relevant materials students may need are available in the online library. Books and journal articles deemed essential to this research can be found online through the digital library. Another benefit of this technique is that it avoids a common problem in physical libraries where a book is unavailable because another student has already taken it. All the materials are always obtainable at all times when needed. The school library also offers some of the latest books and journals, making it feasible to understand the current state of the issue under investigation.
It is necessary to note the strengths and weaknesses of the chosen technique. Besides the benefits already mentioned, it is also important to note that desk research is simple and requires a minimal time investment to locate the needed materials. Unlike in a school library where it is necessary to search for materials physically, an online search only needs the use of key words to obtain information about a particular book or journal article.
According to Bernard (2013), desk research also offers the researcher access to numerous databases. When the needed material is not available in the school’s online library, it remains possible to visit other online databases. Furthermore, this kind of search only takes a few seconds, considerably simplifying the process of secondary data collection.
However, it is also important to keep in mind some of the weaknesses that may be present in the process of desk research when locating secondary sources through online platforms. According to Hana (2015), one of the biggest challenges of desk research is that while this method allows access to numerous materials, not all information found will be relevant to the study, a problem that often affects young researchers. Once a key word is used, a voluminous list of books and journal articles is likely to result, requiring the keen eye of an expert to select specific sources that will be relevant to the study.
Interviews
Interviewing will be the first technique to be used to collect primary data in this study. This process involves asking specific questions of the respondents in a face-to-face setting or via telephone. The researcher will request the sampled individuals to take part in a face-to-face interview.
A questionnaire will be prepared to ensure that the interview questions are standardized. The interview will take place in the respondents’ place of work or another safe location that is convenient for both the researcher and the interviewee. For those who are not available for a face-to-face interview, the researcher will organize phone interviews. The same questions will be used in both cases. A main reason why this technique is appropriate for the study is the need to create a personal relationship with the respondents. The physical interaction of the researcher and the participant will emphasize the importance of the study and help the participants to feel more committed to the study.
The chosen technique has strengths and weaknesses that should be considered. The main advantage of this technique is that it increases the chances of obtaining responses. The fact that a researcher will follow up with every participant increases the likelihood that all selected participants will answer the questions set for the research. According to Bernard (2013), face-to-face interviews minimize the cases where a participant deliberately provides misleading answers.
The researcher will also be able to read a participant’s body language and facial expressions during an in-person interview, making it easy to understand his or her attitude toward every given question. Another benefit of interviews is that this technique will help in determining those who will take part in the study and those who will not. If a respondent fails to appear on the agreed-upon date, a quick decision can be made to replace the individual early enough to ensure that the right sample size is realized.
The technique poses a number of challenges that cannot be ignored. One of the greatest is the intensely time-consuming nature of the process, both for the researcher and for the participant. For example, having to travel from one physical location to another to conduct interviews takes time and incurs some financial cost. As a result, if this is the main method of collecting primary data, only a few people can be interviewed because of the limited time frame of this academic project.
If a respondent agrees to take part in a telephone interview, the researcher will have to make the calls, which also involve some financial cost. According to Bryman and Bell (2015), in the case of a telephone interview, it may not be easy to ascertain the identity of the person at the other end of the telephone, which means that a participant can let someone else who lacks the desired qualifications take part in the interview.
Survey
A survey will be used to facilitate data collection from a large number of respondents. Unlike interviews, where the researcher engages respondents in a question-and-answer session, a survey involves distributing questionnaires to the participants physically or electronically and allowing them to answer the questions in their own time. Respondents are then expected to send back the answered questionnaire for analysis.
The researcher intends to use online methods to deliver questionnaires to the respondents using the e-mail address each respondent provides, requesting them to answer the questions and then return their replies within a week. This technique is appropriate for the study because it will ensure that primary data is collected from the sampled respondents within a short time. Respondents will be provided ample time to go through the questions before supplying the appropriate answers.
The chosen techniques possess inherent strengths and weaknesses. According to Bryman and Bell (2015), one of the biggest advantages of surveys is that this approach is not time-consuming. Once the questionnaires are prepared and sent to the participants electronically, the researcher must simply wait for them to be sent back. It is also less costly compared to interviews. After making a phone call to the respondents to confirm the receipt of the forms, a researcher will only have to make a final call to each to thank them for their participation.
The biggest disadvantage of this method is that sometimes a respondent may hand over the questionnaire form to another, possibly unqualified, person to fill in the answers. The ample time allowed may also create room for participants to fabricate answers, especially in the case of a sensitive issue (Hana, 2015). In addition, some respondents may fail to deliver the completed questionnaire within the set duration.
Data Analysis
The final stage after primary data collection involves analyzing the data. This process transforms raw data into meaningful information that can help in drawing conclusions and making recommendations. In this study, the researcher will use a mixed methods approach to analyze the primary data. Data obtained from structured questions will be coded for mathematical analysis. Using SPSS or an Excel spreadsheet, the researcher will determine the degree to which each factor affects human resource management. Data analyzed quantitatively will be presented using charts and graphs to facilitate the process of interpretation (Bryman & Bell, 2015).
A qualitative method will be used to understand why a given issue is considered a problem. For example, if Facebook addiction is identified as a major issue in modern-day human resource management, a key point of interest will be to explain why it is a problem and what various stakeholders can do to ensure that the issue is addressed. The mixed method approach in data analysis is expected to provide a comprehensive understanding of the issue under investigation.
References
Busse, R. (2017). Value diversity and performance in small groups: Empirical evidence from Chinese management students in Germany. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 8(2), 114-128.
Hao, Y., Hao, J., & Wang, X. (2016). The relationship between organizational justice and job satisfaction: Evidence from China. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 7(2), 115-128.
Ren, T., Fang, R., & Yang, Z. (2017). The impact of pay-for-performance perception and pay level satisfaction on employee work attitudes and extra-role behaviors: An investigation of moderating effects. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 8(2), 94-113.
Shahzad, I.M., Farrukh, M., Ahmed, N.O., Lin, L., & Kanwal, N. (2018). The role of transformational leadership style, organizational structure and job characteristics in developing psychological empowerment among banking professionals. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 9(2), 107-122.
Szierbowski-Seibel, K. (2018). Strategic human resource management and its impact on performance – do Chinese organizations adopt appropriate HRM policies. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 9(2), 62-76.
Talat, U., & Chang, K. (2017). Employee imagination and implications for entrepreneurs: Inspiration from Chinese business enterprises. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 8(2), 129-152.
Vong, L.T., Ngan, H.F., & Lo, P.C. (2018). Does organizational climate moderate the relationship between job stress and intent to stay: Evidence from Macau SAR China. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 9(1), 2-20.
Wong, Y. (2017). Affective commitment, loyalty to supervisor and guanxi: Chinese employees in joint ventures and reformed state-owned enterprises. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 8(2), 77-93.
Wu, M., Sun, X., Zhang, D., & Wang, C. (2016). Moderated mediation model of relationship between perceived organizational justice and counterproductive work behaviour. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 7(2), 64-81.
Wu, X., & Shie, A. (2017). The relationship between customer orientation, emotional labour and job burnout. Journal of Chinese Human Resource Management, 8(2), 54-76.