Introduction
The US healthcare system needs to be liberated to meet universal health coverage. Existing policies aid in leveraging any underlying challenges in the country’s care system. For instance, Medicaid and Medicare are popular insurance options implemented to help US citizens afford medical bills (Rock, 2022).
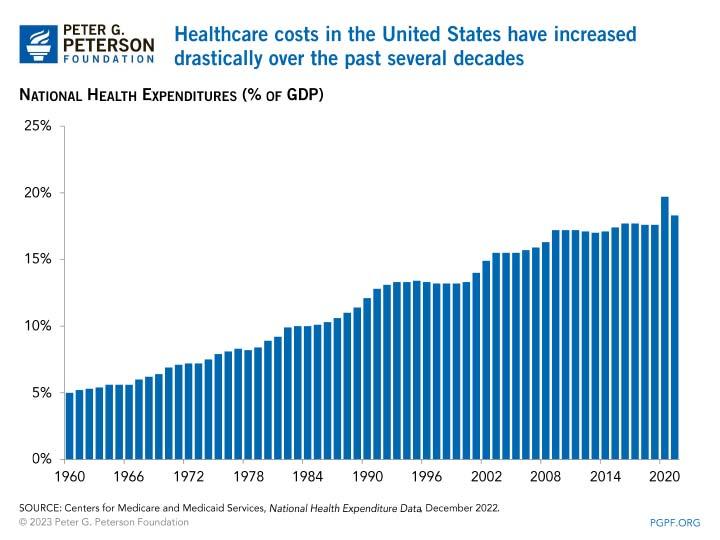
Healthcare coverage has been collaboratively offered in the country, with both public and private organizations developing holistic approaches that allow rational metrics to be undertaken regarding healthcare. About 60% of US citizens believe that healthcare coverage in the country is average, while the remaining portion says the system is the best and above average (Younger, 2018). It is important to note that the US government does not offer health benefits to its citizens or foreigners, which means that any time a person receives care, there must be a payment. Figure 1 shows high national expenditure on healthcare in the United States.
Literature Review
Access to Health
Healthcare access in the US is challenged by the inability to have insurance, social determinants, discrimination, and staffing shortages. According to Ameringer et al. (2018), healthcare disparities exist within the entire management spectrum of US financial, geographic, cultural, and social challenges. That shows the country does not have a seamless transition in healthcare access due to existing barriers and discrepancies.
First, when it comes to insurance, the coverage often makes it difficult for all members to access health services due to the inability to pay for medical bills that may be high depending on the health problem. That has led to health consequences, such as people missing appointments and fearing being detained in hospitals due to a lack of financial capability (WHO, 2023). Additionally, insufficient coverage leads to skipping critical care processes and procedures, where many families may not receive screening, dental care, and pediatric visits due to the problem.
The other barrier to access is staffing shortages, where the healthcare system could be short of many professionals in care facilities. Rock (2022) says there is a significant lack of physicians and nurses in critical care dimensions such as advanced nursing practice (APN) and specialized doctors in chronic diseases. The insufficiency causes a healthcare access gap that may lead to liabilities such as increased mortality. Discrimination is a key barrier where immigrants and foreigners report not getting appropriate care services (Khanna et al., 2020). That may be due to language barriers, racial disparities, or fear that they might be judged for their underlying problems, such as a patient seeking mental health care at an asylum.
Discrimination can be solved to ensure that healthcare in the US does not become a nightmare for many who may not be able to afford it. The US government must introduce universal health coverage to care for members belonging to less fortunate groups, such as people experiencing poverty, immigrants, veterans, and others with chronic conditions (HHS, 2023; Khanna et al., 2020). Overcoming the barriers must involve collaborative care practice, government efforts, and communal associations that target all citizens without discrimination.
Cost to the Average Working Adults
The US healthcare cost may not be affordable to the average working adult due to economic constraints, responsibilities, and unsustainable work-related issues. According to Beasley (2023), more than 40% of American adults report difficulty paying for healthcare services because they are underpaid, have many responsibilities, and have low disposable income. Employer-sponsored insurance has not changed the reality and experience of healthcare affordability since healthcare costs are high and are characterized by inflation, expensive resources, and economic constraints in the country (HHS, 2023). The problem is evident since people are forced to skip needed care due to costs, which risks the entire population as an increase in patient mortalities may be high and adverse impacts such as long-term exacerbations.
The challenge cannot be overlooked since the number of people wishing to be treated is increasing daily, and the government cannot reduce the price of medication and equipment used to provide these services. Working adults allege that they are underinsured, prompting them to supplement their medical payments from their pockets (Quinones, 2021; Rajkumar, 2020). The irony is that these employees complain they are being deducted large amounts of money to meet the high monthly premiums.
Age-Restricted Care
Part of the problems experienced in healthcare as far as the US is concerned is age restriction, which is translated as discrimination. “In the American health care system, age shapes patients’ options. Most people over 65 are eligible for Medicare, which is inaccessible to almost everyone under 65” (Persad et al., 2019, para. 1).
With that information, there is discrimination regarding who can access health insurance. Younger people are left in the coverage, which calls for interventions to save future generations from short life expectancy brought about by healthcare challenges (Lazovich, 2018). Additionally, the restriction is extended regarding specific clinical interventions for older adults, such as in vitro fertilization and transplants.
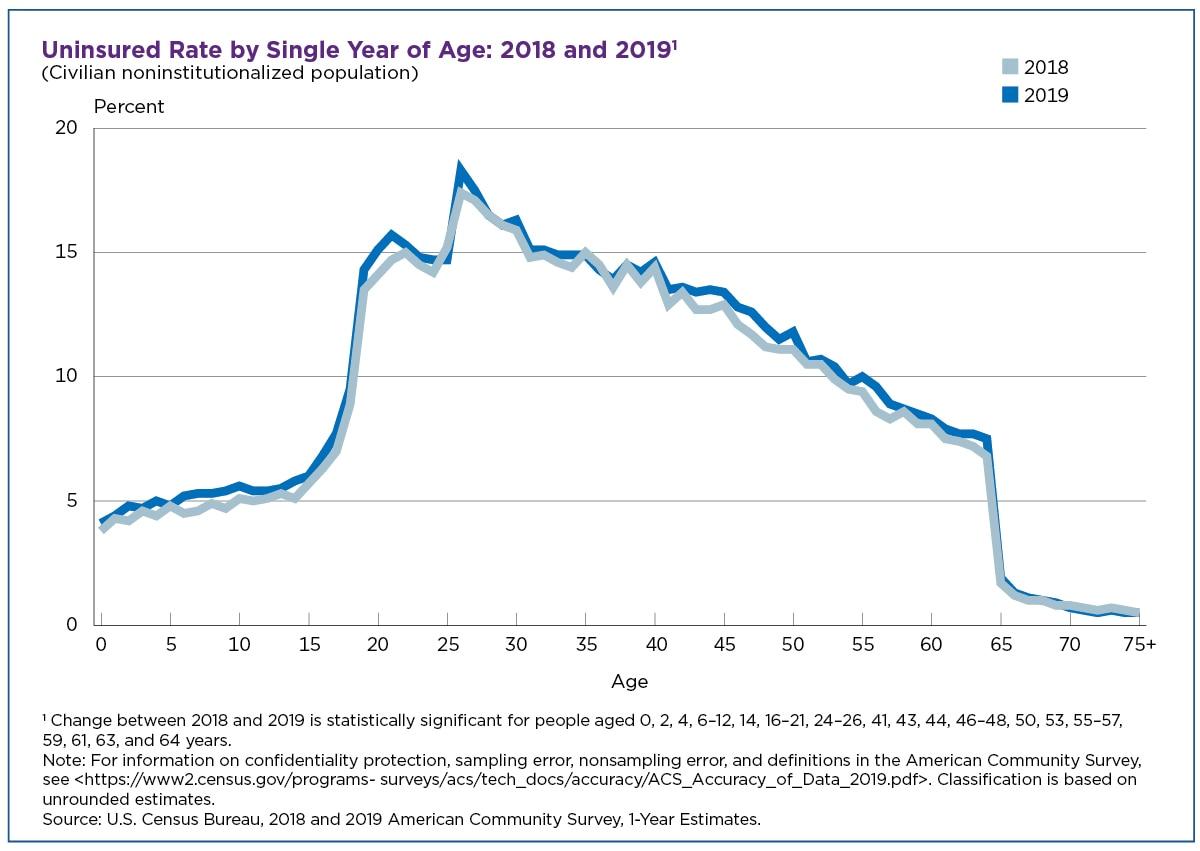
In the Affordable Care Act 2010 (ACA), age eligibility has led to contentious opinions regarding the legality, current law, and ethical concerns about age use. Conway (2020) supplements information on this age-restricted care, stating that adults aged 19-34 have the highest uninsured rate in the US, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) in 2019. The uninsured rate for the age group is about 15% compared to 5.7% for those under 19 years, 11% for older adults beyond 34 years, and 0.8% for the 65-year-old population (Conway, 2019).
The reason why this is being seen in US healthcare is the reality that younger people are healthier than older people. However, the problem hits hard when these people need medical attention for critical problems. As Figure 2 shows, young adults lose eligibility for public health at 19 years, which makes US healthcare uncertain (Conway, 2019). Basing eligibility on age should only be to create a working criterion instead of sidelining the majority of the population.
Cost of Pharmaceuticals
The rising cost of prescription drugs has challenged the US healthcare system. According to Kurani et al. (2022), the US spends more than $3.3 trillion on health care annually, where 10% of the amount goes to pharmaceuticals. That has led to many Americans demanding a reduction in the prices at which drugs are charged during clinical practices.
The US falls prey to the high cost of pharmaceuticals due to the global magnitude of expenditure on medical resources and research, leading to a 3-6% increase in prices yearly. The primary cause of the high cost of drugs in the country is a monopoly. “In the case of cancer, even when there are multiple drugs to treat a specific malignancy, there is still no real competition based on price because most cancers are incurable, and each drug must be used in sequence for a given patient” (Rajkumar, 2020, p. 4). The statement shows a lack of alternatives for many drugs, which makes the pricing expensive.
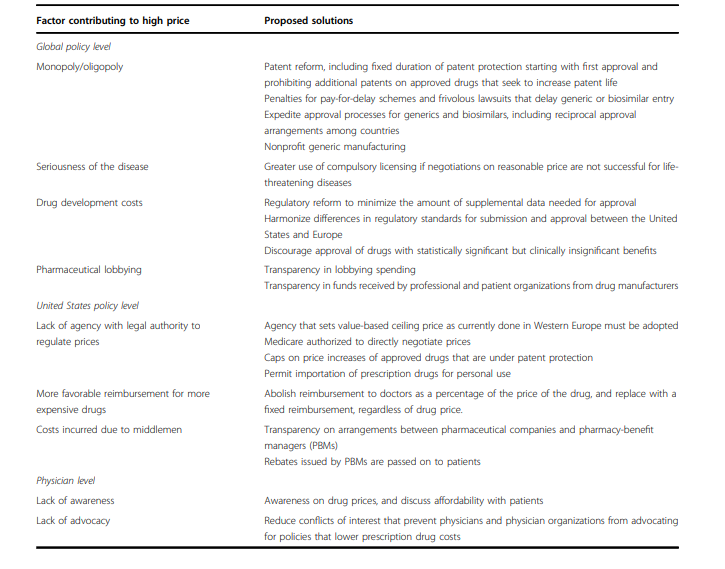
The high demand for the efficacy of the drugs makes the matter adverse since the cost rises with the demand. No competitive metrics are witnessed whereby drug supply control can ease the high costs (Rodwin, 2020; HHS, 2023). Additional reasons why the cost of pharmaceuticals is high in the US are the seriousness of the disease, the cost of development, and the few lobbying efforts of pharmaceutical firms. Other reasons can be seen in Figure 3 below, which opens readers’ minds to the extent of this problem.
Telehealth
Telehealth means using electronic information to support care facilities through modern technology with a long-distance clinical task between the care officer and patient. With the tech put in place to enhance healthcare, its scope, application, process, and capability issues have been rampant (Francis, 2022). The barrier in telehealth is a significant monetary constraint in delayed or no reimbursements after telemedicine has been practiced. According to Jin and Song (2022), more than 90 million people receive healthcare in managed systems, but no measure is used to control costs. Additionally, Medicare has been unable to reimburse significant amounts for the fee-for-service systems, making telehealth have underlying issues in healthcare (Higa et al., 2021).
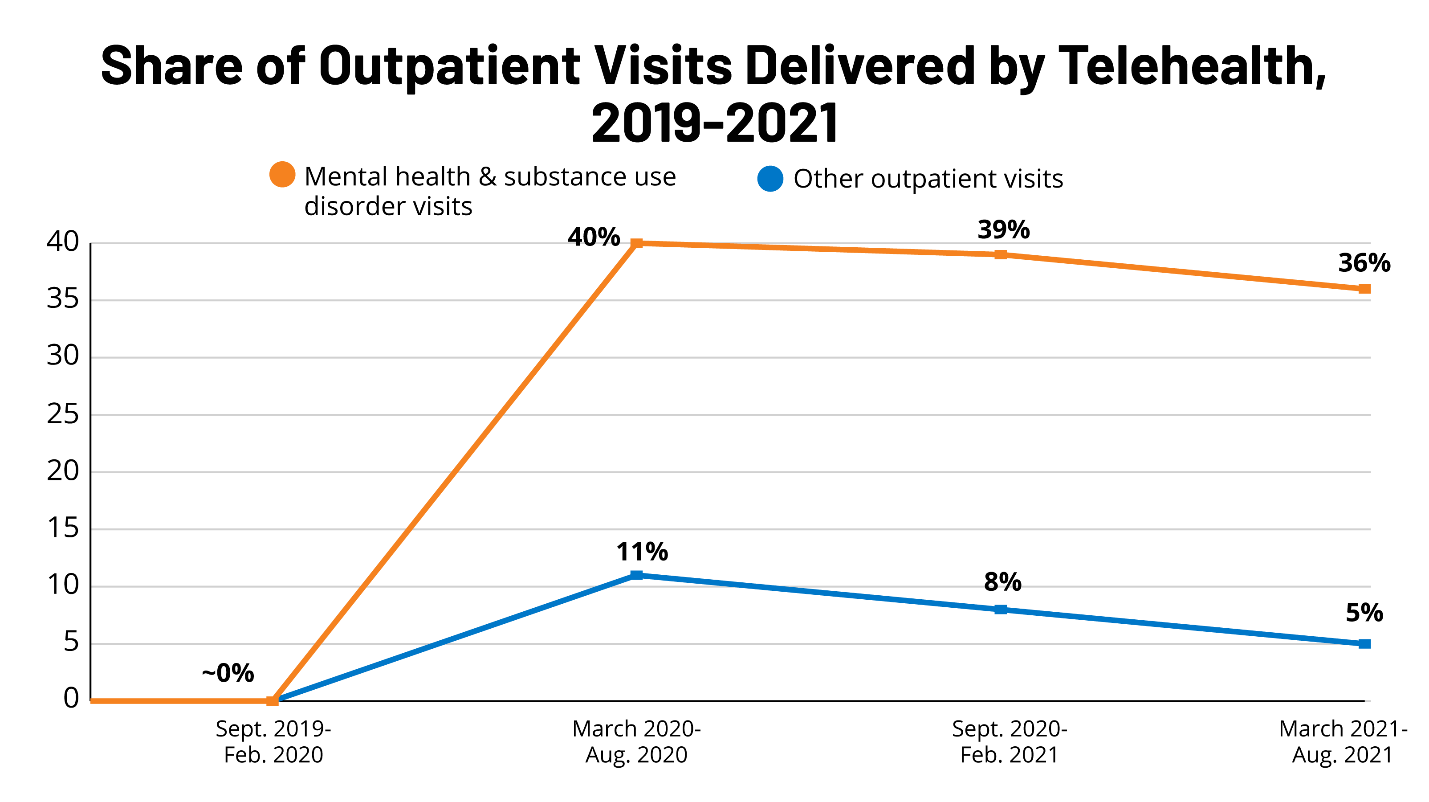
The other problem in telehealth is regulation, where licensing appears to be a key barrier, as various metrics must be met before accreditation for telehealth. For example, the Social Security Act limits the use of telehealth to particular providers in the US (Lo et al., 2022). Other significant challenges include the difficulty in adoption, as shown in Figure 4, changing technology, and cybercrime issues, which threaten patient data during the process.
Hospitals and Their Function
Many hospitals have primary devotion to specific ailments such as tuberculosis, psychiatric care, pediatrics, eye care, and cardiac care. Therefore, hospitals and their function mean that health services are limited to some diseases at the expense of others. According to Liu and Kelz (2018), specialized hospitals may have challenges in managing critical emergencies during an occasion that requires that since a particular physician or APN may not be present. In addition, the function of a given hospital may limit uninsured patients regarding their health condition, paralyzing the efficacy of providing health care in the US.
The existing gap in service provision is a threat to public health since it means people have to struggle to get to the general hospitals where they need a wide array of treatments. The other barrier in hospitals and their functions is overcharging due to the demand for a particular service. For example, hospitals specializing in cancerous diseases may exploit the patient’s condition and the facility’s establishment financially (WHO, 2023). These problems must be combated to ensure no widening gap in healthcare constraints in the US.
Public Health and Their Function
The country’s public health aims to protect the health of US citizens and the society where they live, work, and engage in long-term activities. “The conventional wisdom is that the American political system failed at public health—by prioritizing individual rights over collective safety, sowing doubt about the benefits of vaccines, masks, and another protective measure” (Varma, 2020 para. 1).
From that information, it shows the US public health functions have failed due to political reasons that have sparked a continuous challenge in meeting the health demands of people in the country. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have muddled the operational efficacy more so during the Coronavirus pandemic that hit the entire world (WHO, 2023). That means there is a need to have candid interventions on this matter.
In this case, the challenges include little preparedness for infectious disease emergencies, lack of prioritizing public health in terms of monetary allocation, and uncalled-for vices such as embezzlement and mishandling of public health funds. The decentralization of the public health system is a key concern since it relies on many state and local health agencies to operate (Varma, 2022). Many American citizens die from the pandemic at a high rate, which shows the incapability risk for US public health functions. The failure is highly witnessed due to a lack of advanced planning of healthcare uncertainties, which may bring adverse outcomes to Americans.
Eye and Dental Health in the US
Both eye and dental health have been problematic due to the burden of the disease, access, and affordability issues. There is a challenge of a high population in the US, which brings an increasing number of patients who require eye and dental services. The lack of access has led to inevitable exacerbations, a healthcare concern.
The other challenge is a shortage of dental health professionals, as many physicians and APNs have ventured into other areas. The annual cost for dental care in the US is about $136 billion, which is 3.7% of the total health care in the country (Giansanti, 2023). The skyrocketed cost of the subject may pose a risky situation when it comes to the well-being of Americans.
Obtaining care is a key challenge when it comes to eye care. That is due to a shortage of eye care human resources, little educational skills on personal measures to care for their eyes, and insufficient equipment and machinery to offer top-notch optician services in all US parts (Khanna et al., 2020). These problems must be combatted to reduce the underlying risk to the American public health system. More than 5 million adults are risking deterioration of eye health as they are unable to afford eyeglasses when needed, and the required resources are not catering to the full adoption of strategies to protect the group (Giansanti, 2023). Therefore, the information about this matter means there is a challenge that must be combatted as far as this population is concerned.
Discussion
From the literature review on the aspects above, it is easy to tell that the US healthcare system is full of challenges ranging from all realms in providing clinical care to its citizens. The major issue that is rampant in the subject is the citizens’ affordability issues due to insurance, the cost of pharmaceuticals, and high development costs in the US (Varma, 2022). It is true that access to healthcare in the US is not easy, minding that many people have financial problems and the disease prevalence rate is high. It is important to note that if an American cannot afford healthcare, there is a risk of poor living standards since a person will not stay with illness and manage to live normally.
Restricting the provision of insurance options based on age is demoralizing and threatens life expectancy for people facing medical issues in the country. The key goal of having older adults insured more than young ones is to protect people’s health at retirement age by avoiding mortalities (Francis, 2022). However, from what Americans observe, insufficient health insurance coverage for all populations, regardless of age, is making life difficult in society.
Recommendations
The country needs to adopt new strategies and ways to deal with the challenges in healthcare. This report’s first recommendation is for the US government to cut healthcare costs by controlling expenditures, promoting competition in the production of pharmaceutical drugs, and reducing prices through legal actions (Quinones, 2021). The second recommendation is that the country should design incentives that lower the utilization of low-value health services. For example, imposing spending targets and actualizing new payment reforms is called for in this matter.
The third recommendation is equal access to healthcare, where the US must adopt universal health coverage to ensure that all Americans and foreigners are insured without putting age, status, diseases, stratification, and other dimensions (Rock, 2022). For example, insurance can be made mandatory for all employed and non-employed, and a policy for comprehensive coverage can be developed for that matter.
The fourth recommendation is that the US should promote technological development in areas where critical care is required to meet the demand for these advanced practices in a clinical setting. On a similar note, reimbursement for telehealth should be executed through a legal framework that facilitates seamless transactions and ensures that all telemedicine costs are covered (Younger, 2018). The fifth recommendation is for the US Congress to offer reliable and stable funding to ensure all healthcare resources are assembled, and employees do not face challenges in delivering care services to patients.
An additional recommendation is that the US government must trigger more professional programs in the medical field and deploy a sufficient number of staff in respective hospitals to avoid the limitation based on a specialization factor witnessed. The country must have enough doctors and nurses in all healthcare sections, including eyecare and dental health areas (Nanniyur & Ramanujam, 2023).
Lastly, the public health system should be working collaboratively with general healthcare to avoid challenges such as lack of preparedness in emergency cases. For example, private and public hospitals should share data on certain trends concerning health care (CMS, 2022). The data will be useful in tackling any ineffective or dragging factor in health care.
Conclusion
The US healthcare system is challenged by affordability, access, insurance, public health constraints, specialization, health professions shortage, telehealth, and other predicaments. As a result, many citizens in the country have reported difficulty affording healthcare, leading to poor living standards. Additionally, there is a lack of enough staff in professional medical fields, which risks the public health commitment to Americans.
The literature review shows increased healthcare challenges, resulting in gaps leading to inequality, potential low productivity for Americans, and mortality rates. If the US had a firm legal and moral policy regarding the state of healthcare, many people would be eligible regardless of their social dimensions and capabilities. The government needs to adopt ways to counter these challenges. A raft of recommendations includes legal methods to implement low-cost healthcare, adoption of modern technological advancements in healthcare, and increasing professionals in the medical field through research and deploying enough working staff to deal with the issue, among other key concerns.
References
Ameringer, C. F. (2018). Us health policy and health care delivery: Doctors, reformers, and entrepreneurs. Cambridge University Press.
Beasley, D. (2023). U.S. new drug price exceeded the $200,000 median in 2022. Reuters. Web.
CMS. (2022). CMS framework for health equity. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Web.
Conway, D. (2021). Adults aged 26 had the highest uninsured rate, followed by 27-year-olds. Census. Web.
Francis, X. C. (2022). The Covid-19 healthcare coalition telehealth impact study. Telehealth and Medicine Today, 4(8), 37–45. Web.
Giansanti, D. (2023). Ten years of telehealth and digital healthcare: Where are we? Healthcare, 11(6), 875–894. Web.
HHS. (2023). HHS finalizes rules to strengthen Medicare, improve access to affordable prescription drug coverage, and hold private insurance companies accountable for delivering quality health care for America’s seniors and people with disabilities. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Web.
Higa, C., Krupinski, E. A., Birkmre-Peters, D., & Labasan, S. (2021). Challenges and opportunities to advancing telehealth: U.S. telehealth resource centers’ approach. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 3(7), 62–78. Web.
Jin, L., & Song, E. (2022). Design of a “B2B” telemedicine network: Pricing, staffing, and funding policy implications. Pennsylvania State University.
Khanna, R. C., Cicinelli, M. V., & Marmamula, S. (2020). Comprehensive eye care – issues, challenges, and the way forward. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology, 68(2), 316–324. Web.
Kurani, N., Kurani, N., Cotliar, D., & Twitter, C. C. (2022). How do prescription drug costs in the United States compare to other countries? Peterson-KFF Health System Tracker. Web.
Lazovich, D. A. (2018). Effect of parental permission and age restriction laws on us adolescent indoor tanning trends. American Journal of Public Health, 108(7), 851–853. Web.
Liu, J. B., & Kelz, R. R. (2018). Types of hospitals in the United States. JAMA, 320(10), 1074–1098. Web.
Lo, J., Rae, M., Amin, K., Cox, C., Panchal, N., & Miller, B. (2022). Telehealth has played an outsized role in meeting mental health needs during the Covid-19 pandemic. KFF. Web.
Nanniyur, S., & Ramanujam, R. (2023). Aravind eye care system: Delivering value-based eye care. Optical Reviews, 3(7), 47–56. Web.
Persad, G. (2019). What should we ask about age-based criteria in healthcare? Bill of Health. Web.
Quinones, S. (2021). The least of Us: True tales of america and hope in the time of Fentanyl and meth. Bloomsbury Publishing.
Rajkumar, V. (2020). The high cost of prescription drugs: Causes and solutions. Blood Cancer Journal, 10(6), 16–23. Web.
Rock, M. (2022). The U.S. dental insurance system prevents care for the whole person. Georgetown Medical Review, 4(7), 24–45. Web.
Rodwin, M. (2020). Average international market pricing for U.S. pharmaceuticals—lessons from Europe. Forefront Group, 2(5), 25–32. Web.
Varma, J. (2022). How public health failed America. The Atlantic. Web.
WHO. (2023). Considerations for implementing and adjusting public health and social measures in the context of covid-19. World Health Organization. Web.
Younger, D. S. (2018). Adolescent sports-related concussion: U.S. healthcare access, finance, and delivery. Annals of Behavioral Neuroscience, 1(1), 94–107. Web.