Introduction
With the incessant changes in today’s business landscape, companies are more than ever required to be customer-centric to ensure sustainability. Businesses should establish products or offer services that focus on creating value for the customers. Creating customer value involves a four-pronged strategy, including economic value, functional value, social value, and experiential value. Likewise, the marketing mix entails an emphasis on product, price, place, and promotion. This work focuses on economic value and product, two essential aspects for a business that also contribute immensely to marketing strategies and overall business success (Boha, 2020).
From a business perspective, economic value refers to offering products or services that match customers’ wants while also generating profits. Product is the intangible and tangible items that the business offers and may incorporate branding, packaging, design, and quality. The discussion details the relationship between product and economic value in the context of marketing, with appropriate examples to explain the connection.
Relationship Between Economic Value and Product
Economic value is the maximum amount a customer is willing to assign to a product based on experiences, expectations, and the options in the market. A well-designed product reinforces customer value while also remaining useful in distinguishing the firm’s offering from rivals. The connection between product and economic value is significant since the value a customer draws from the purchased item is proportional to its quality features and benefits. The expanded benefits a product provides, the bigger the economic value for customers, making them highly attracted to acquire the product (Chernev, 2022). Therefore, it is the prerogative of the business to offer products that carry the maximum perceived benefits while attaching prices that guarantee a profit.
The concept of value proposition can effectively explain the connection between a product and economic value. Value proposition communicates the unique benefits that a service or a product offers to the customers (Boha, 2020). It is an affirmation of intent, both in the market and inside the company. The proposition details the reason why the customer should purchase the company’s product or service. A well-designed value proposition can assist the business in distinguishing its product or service from those of competitors while still creating a perceived value that justifies the attached prices (Johnson & Weinstein, 2020). The ideal value proposition appeals to the customer’s robust decision-making drivers (Chernev, 2022).
Therefore, product and economic value are closely linked, and a business must emphasize creating an item that offers maximum benefits to prospective customers (Sri, 2019). A company needs to consider creating a value proposition to help communicate the unique benefits of the item, which will go a long way in shaping a customer’s purchasing behaviors.
Market-Related Examples
The relationship between product and economic value is significant for business success. We discuss market-related instances that exemplify this relationship. For example, Samsung’s S23 Ultra phone is a premium product with numerous unique features that could help offer economic value to customers.
The distinctive features include a high-quality camera equipped with a Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 Galaxy processor to enhance its performance (Galaxy S23 Ultra, n.d.). The phone has a 5000mAh battery that supports both wired and wireless charging. It also has an intuitive user interface, sleek design, and water resistance capability that make it outstanding. These features offer a considerable role to the customer and help justify the premium status that Samsung charges for this product.
It is apparent that Samsung’s value proposition is anchored in the notion that its S23 Ultra phone is innovative, user-friendly, and enhances customers’ experiences. Samsung’s economic value is directly linked to its products based on design and quality, positioning it as one of the leading technology companies.
Another example is Nike, a company that has developed its brand based on the unique value proposition for high-quality athletic wear. In the sports industry, Nike’s products are recognized for their durability, quality, and innovative designs that offer significant benefits to fitness enthusiasts and athletes (Running Shoes, n.d.). The company’s economic value is directly associated with product design and performance, making it one of the most highly sought-after athletic wear brands in the world.
In both examples, the economic value that a customer ascribes to a product is directly connected to the product, especially its quality, benefits, and features. Businesses that emphasize value propositions by offering products that offer maximum benefits to the customer at a reasonable price can attain a competitive edge and appeal to loyal customers. In addition, by comprehending the association between the product and economic value, a business can position itself as the leader in the segment and ensure long-term success.
Metrics
Table 1: Revenue and Net Income
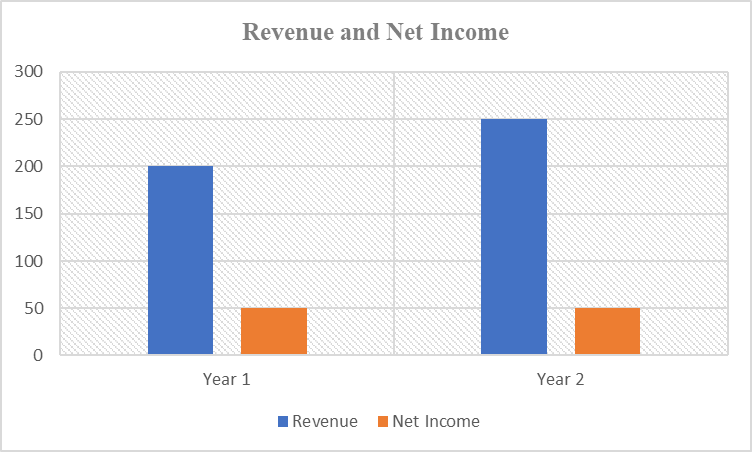
The graph and table above illustrate Samsung’s product and economic value metrics over a two-year duration. The company’s net income and revenue stayed comparatively stable. Specifically, revenue grew by $50 billion, which could be attributed to an increase in market share or other parameters such as effective marketing and brand positioning that make the product one of the best in the telecommunications sector. The net income remained high despite being similar in the two years under review.
Nike Example
Table 2: Units of Footwear and Average Price
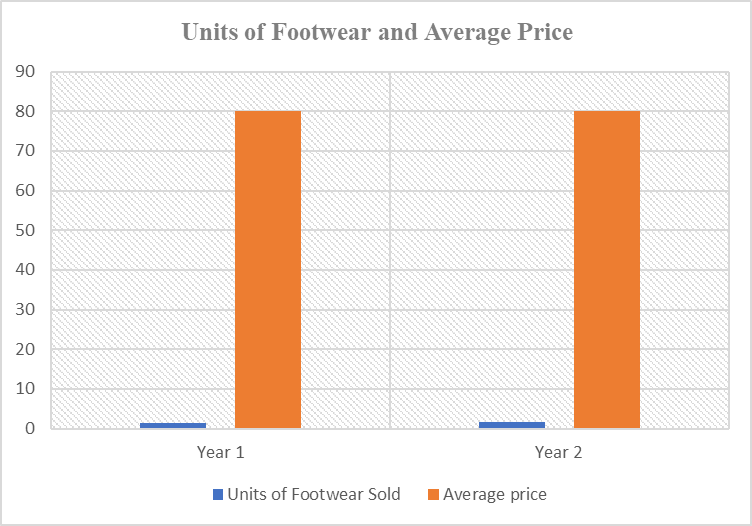
The graph and the table above show Nike’s product and economic value for two years. The units of footwear sold increased slightly in the year to about 100 million, showing impressive performance in the year under review. While the average price per item remained considerably similar over the two years, it is apparent that the company made considerable steps to sell more of its products.
The value proposition that its footwear creates makes the brand one of the best businesses in the sportswear industry. The consistency in units sold can be best explained by the design, benefits, and features that customers get from the product, making them willing to acquire the product and the economic value of the respective items. Nike and Samsung have different target markets and product offerings, but both have prioritized establishing products that create maximum benefits for customers with reasonable pricing.
Guidance for Marketers
Given the patterns that emerge from the graphs and tables in the above examples, marketers should concentrate on realizing a robust value proposition for the products since this informs the product quality and the willingness of a customer to purchase. This can be attained by focusing on value to customers while ensuring a competitive edge in the marketplace (Sri, 2019). Regarding Samsung, whereas the net income plateaued, revenue increased considerably, showing that more units of the products could have been sold. The customer might have perceived that the Samsung S23 Ultra is a product of higher value, informing the need for marketers to continue making high-quality products that create value for buyers.
Regarding Nike, the number of footwear units sold at the same price increased considerably over a two-year period, showing customers’ extreme liking of the products. Marketers should not only focus on creating value but also recognize the business aspect by offering products that can generate profits for the company. This can be attained by producing a product that emphasizes durability, quality, and continuous innovative designs to provide immense benefits to fitness fanatics and athletes (Johnson & Weinstein, 2020). Marketers can also study the metrics above to recognize emerging trends and adjust their marketing appropriately (Chernev, 2022). Focusing on products that offer much-needed value to customers can enable a company to establish a competitive advantage in the marketplace and lasting positive performance in its respective areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, product and economic value remain two essential elements of marketing strategies that are closely connected. Enterprises must establish products or offer services that emphasize creating value for customers. Apart from economic value, creating customer value should also involve functional, social, and experiential value. The concept of a value proposition effectively describes the linkage between product and economic value. Economic value is formed by selling products that match the customer’s needs while also making a profit.
References
Boha, J. (2020). Managing value propositions in service ecosystems. Springer.
Chernev, A. (2022). Customer science: Behavioral insights for creating breakthrough customer experiences. Cerebellum Press.
Galaxy S23 Ultra (n.d.) Samsung. Web.
Johnson, W., & Weinstein, A. (2020). Designing and delivering superior customer value: Concepts, cases, and applications. CRC Press
Running Shoes (n.d.). Nike. Web.
Sri, S. (2019). Economic value added for competitive advantage: A case of Indian enterprises. Cambridge Scholars Publishing.