The following table shows the result of references for the ‘Internal Audit’ concept from the EBSCO Business Database by decade. The period ranges from 1901 to 2010. The main objective of this exercise was to analyze by decade the number of times, the term or concept ‘Internal Audit’ is referred to using the abstract search of the EBSCO Database.
Table of references to the concept of ‘Internal Audit from 1901-2010.
The following graph is an illustration of how the term ‘Internal Audit’ has been used over the last eleven decades.
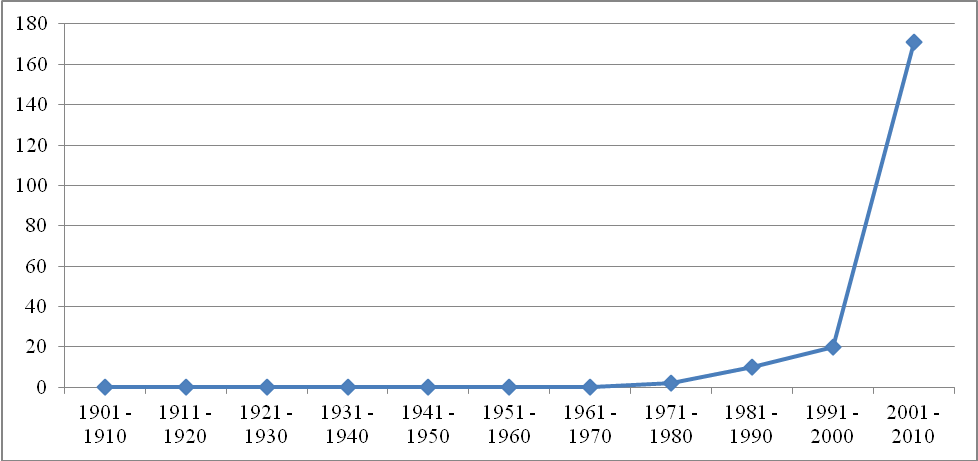
The graph clearly shows that the concept of ‘Internal Audit’ in the management of business enterprises was not of any importance up to the 1980s. There was no reference made of the concept of ‘Internal Audit’ for the first seven decades under consideration. This may have been occasioned by the fact that ownership and management of business enterprises had not been discretely segregated, and therefore there was no or little suspicion between owners and managers of business enterprises However, from the 1980s, the concept has been used repeatedly, thus, showing its increasing importance in the management of the business. With the continued upward trend, it is apparent that the concept of ‘Internal Audit’ is a must in any organization.
The term ‘Internal Audit’ refers to an independent, consulting activity and an objective assurance to improve operations within an organization. It assists an organization to realize its goals by developing bringing a dynamic, disciplined approach to evaluate and make better the results of the risk management, monitoring, and governance processes.
The internal audit process in an organization includes the responsibility to plan, organize and direct the performance of actions, which are designed to provide adequate security to meet the targets of
- achieving specific objectives,
- review of the economy, and efficient use of resources,
- protecting the company’s assets,
- reliability and integrity of the given information,
- comply with policies, programs, procedures, laws, and other regulations.
Besides, internal audit is a part of the model of corporate governance in the sense that contributes to the governance process of an organization by evaluating and improving:
- the process by which the aims and the values of the organization are established,
- the way of monitoring the achievement of the organization’s objectives,
- by ensuring the accountability of the firm and
- by protecting the organizations’ value.
The sharp rise in the use of the ‘Internal Audit’ concept between 2001- 2010 may be attributed to the Sarbanes-Oxley Law which was passed earlier in the decade. The law has set very stringent reporting rules that must be adhered to by all reporting organizations. These requirements may see the continued prominence of the concept in the coming decades.