Introduction
Implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals is increasingly becoming relevant in modern society as uniformity in offering medical services is important. Medical practitioners are expected to embrace the evidence-based practice in their places of work to ensure that their colleagues can easily understand what they have done on a patient because of the common standard of practice.
However, Godshall (2016) says that several factors have become barriers to the implementation of evidence-based practice. They hinder the ability of the practitioners to embrace the new standard of practice in some ways. This becomes a major problem as doctors and nurses find it difficult to harmonize their practices as per the new standards. The purpose of this study is to determine the extent to which educational programs on the research methodology and practices reduce the barriers to implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals.
In this study, the independent variables are the educational programs that are believed to influence the dependent variable, which is the implementation of evidence-based practices in the hospitals. The project will study the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. The researcher formulated a research question that will help in guiding the process of data collection. The question will also form the basis of the research objective. The following is the research question that was formulated for the study:
To what extent do the educational programs on the research methodology and practices reduce the barriers to implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals?
The following are the definitions of terms used in the study:
Educational programs: a plan designed by relevant national educational institution meant to define the leaning progress on various subjects at different levels of formal education (Persily, 2014).
Research methodology: a systematic analysis that one uses in a given study to arrive at a given conclusion (Godshall, 2016).
Barriers: obstacles that make it difficult to achieve a specific goal or to undertake a given activity (Harvey and Kitson, 2015).
Evidence-based practice: a conscientious use of current best evidence to make decisions when handling patients (Ross, 2012).
Theoretical Framework
In this study, the researcher will use a theoretical framework that will define how the independent variables relate to the dependent variables. Of interest will be to explain, through the theoretical concepts, how educational programs on research methodology and practices can reduce barriers to implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals. The guiding concept will be the implementation of evidence-based practices in hospitals. The following framework will be used to help in answering the research questions.
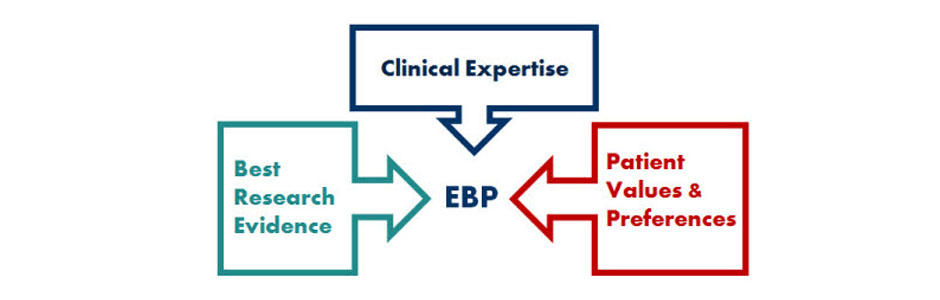
As shown in the figure above, the proposed theoretical framework proposes three factors that must be considered when using this concept. The first factor is clinical expertise. The officer must understand that his or her professional skills are paramount in offering care to the patient. New best practices should only be used to sharpen the skills and experience of the practitioner.
The second factor is the best research evidence. This concept emphasizes the need for doctors to ensure that they embrace the best research practices in everything that they do. Instead of holding on to the old methods, the practitioners are encouraged to embrace new methods based on recent studies. The third factor is the patient’s values and preferences. The practitioners are required to factor in the needs and expectations of their patients. Their values should be respected and preferences are given priority as much as possible. The patients should be made to feel that they are respected and valued.
Review of the Literature
According to a report by Harvey and Kitson (2015), medical practitioners are under great pressure to ensure that they offer the best care to their patients in their areas of practice. As technology keeps on changing, new methods of offering care to patients are emerging through scientific research. New best practices are emerging not only for the nurses but also for the doctors and other clinical officers. Each time a new best practice is introduced into this field, it is expected that the practitioners will change their practice and methods of offering care to their patients.
However, Godshall (2016) says that several barriers have limited the ability of the practitioners to implement evidence-based practices in their operations. One of the major impediments to the implementation of evidence-based practice is the inability to share information among the practitioners. For a doctor in a given hospital to implement a new method of offering services to patients, he or she must get information about the new method. However, sometimes healthcare institutions restrict the new information that they get from their internal research. Such a restrictive practice makes it difficult for new methods to be practiced at other institutions.
Eliminating these barriers is critical in ensuring that services offered in various healthcare institutions are improved. In a study by Ross (2012), it was determined that educational programs on research methodology and practices can help in eliminating some of the fundamental barriers to the implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals. According to Dossey and Keegan (2013), educational programs on research methodology makes it easy for practitioners to understand a common pattern through which evidence-based practice can be implemented. Whenever a new concept of offering patient care emerges, the practitioners will have a convenient way of testing it before introducing it to the entire population of the patients they serve. They will have knowledge and skills to determine whether a new method proposed is capable of delivering high value to the patients or not.
Using the theoretical model proposed above, a practitioner will emphasize three factors. The first factor will be the best research evidence that has been introducing on how to care for the patients under one’s care. The second factor is one’s clinical expertise. A nurse must use his or her professional expertise to question the new best practice and its ability to offer care to patients.
Persily (2014) says that before a nurse can embrace a new method, he or she must question the new concepts and determine whether or not they go against the knowledge and experience they have gained in their practice. In case they go against their professional knowledge, then they should not implement it until they get to understand why there are contradictions. As such, the new methods should not be implemented blindly without factoring in the knowledge and skills of the practitioner. Lastly, a nurse must ensure that the new method is in line with the interest and preferences of the patient. Some patients may prefer a given approach to caring for them because of some reason.
Methodology
Study Type
This research will embrace both qualitative and quantitative methods. Quantitative methods will enable the researcher to determine the magnitude of the dependent and dependent variables. On the other hand, qualitative methods will help in explaining why specific relationships exist between the variables and why a given approach should be considered when addressing the problem.
Study Design
The researcher will use observational research design. The rationale for using this research design is that it allows the researcher to conduct surveys and case studies to understand a given concept. In this study, it will be critical to understanding the views of the sampled participants about the research problem. This non-experimental research design is easy and simple to use and can cover a relatively larger population than experimental research design.
Sampling and Sample Size
It was important to come up with a manageable sample of the entire population of nurses to take part in this study. Given that any experienced nurse is capable of answering the research, the researcher opted to use simple random sampling as the most appropriate method of selecting participants in this study. A sample of 50 nurses working in local hospitals will be included in the study. A questionnaire will be used to collect data from them.
Method of Protecting Human Subjects
It will be important to ensure that human subjects are protected. The researcher will ensure that the names of all the sampled participants are not revealed. The sampled participants will be assigned codes that will be used instead of their names. They will be requested to sign consent forms to confirm that they have willingly accepted the researcher’s request for them to be part of the study.
Data Analysis
The most appropriate data analysis approach for this research will be the use of mathematical methods based on the chosen research design. Data collected from the participants will be coded and analyzed using mathematical tools. The researcher will use the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) to analyze the coded data statistically. The output of the analysis will be presented in graphs and charts to make the results clear. Given that the chosen design will also involve qualitative analysis, the findings will also be displayed by directly quoting the respondents.
Applicability to Nursing
This research applies to the field of nursing. It focuses on a problem that is significant to nursing, which is addressing the barriers to the implementation of evidence-based practice in hospitals. It would also contribute to nursing knowledge by enabling the nurses to know how to overcome these barriers. This proposal can be replicated by another researcher because it outlines all the methods that should be followed. The study will affect nurses in various areas, including ambulatory care nurses, burn care nurses, cardiac care nurses, camp nurses, case management nurses, clinical nurses, and certified nurse midwives among others.
References
Dossey, B. M., & Keegan, L. (2013). Holistic nursing: A handbook for practice. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Godshall, M. (2016). Fast facts for evidence-based practice in nursing: Implementing EBP in a nutshell. New York, NY: Springer Publishing Company.
Harvey, G., Kitson, A. (2015). Implementing evidence-based practice in healthcare: A facilitation guide. New York, NY: Routledge.
Persily, C. A. (2014). Team leadership and partnering in nursing and health care. New York, NY: Springer Pub. Co.
Ross, T. (2012). Survival guide for health research methods. Milton Keynes, UK: Open University Press.