Real-World Example of an Exponential Function
Exponential functions are all around us: they are not confined to the pages of a textbook but are the basis for many processes and operations that take place in real life. Since I am in business administration in health care, and my field is directly related to financial operations, I was interested in the role of exponentials in finance.
One of the fundamental functions applicable to health care, among others, is the compound interest function. In general, it can be represented as A = P(1+r/k)kn, where P is the initial investment, r is the compounding rate, k is the number of compounding periods in the reporting period, and n is the number of years (Fernando, 2023). If the data is known, it helps to determine, for example, the future value (A) of the investment.
In finance, this function is helpful because when our medical organization takes a loan from a bank, I can do the calculations and determine the most favorable terms (Graham, 2023). This involves finding the best interest rate or total loan amount over n number of years. It is essential to keep in mind that the growth in the compound interest function is exponential, which means that the amount of credit or savings in a bank deposit will grow nonlinearly, as shown in Figure 1.
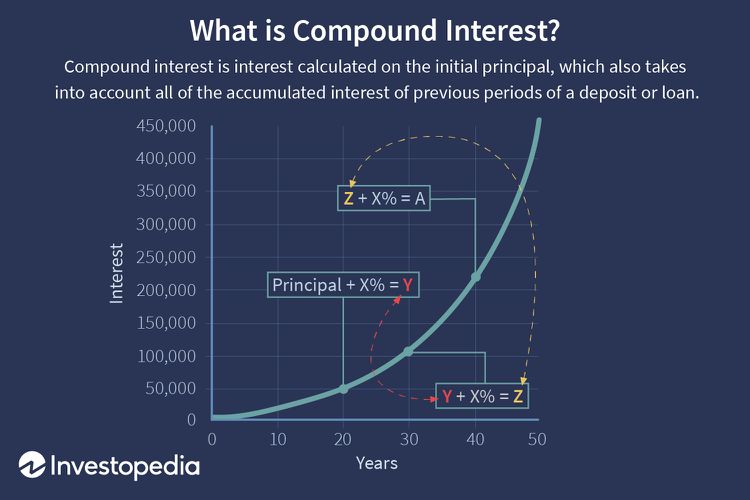
Meaning of the x and y Variables and Behavior of the Function
The above graph shows the total amount of interest as a function of time: the more years that have passed since the loan was taken, the more interest has accumulated. The amount of interest accumulated is used as Y, and the years elapsed since inception are used as X. It is noteworthy that the outcome of this function can be both favorable and unfavorable.
If we are talking about business loans, this means that the company will have to pay additional funds (Y) on top of the amount taken initially. If, on the other hand, our company decides to create a bank deposit to which interest on the balance is added at specific intervals, then as the years go by (X), the deposit will grow more and more (Y). As we can see, the graph is experiencing exponential growth, which means that the more years that have passed, the sharper the graph becomes. In other words, as X grows, the amount of accumulated interest first increases almost linearly and then abruptly goes into a stage of nearly vertical growth.
References
Fernando, J. (2023). The power of compound interest: Calculations and examples. Investopedia. Web
Graham, K. (2023). What is compound interest and how is it calculated? ROCKET Mortgage. Web.