Theoretical Background
The use of instrumental chemical methods allows for reliable and accurate analysis of samples, regardless of the application or purpose of such analysis. In the present work, Trimyristin, the main constituent of nutmeg, was extracted and analyzed. Trimyristin is a triglyceride of myristic acid and saturated fat without multiples in the structure (Figure 1).
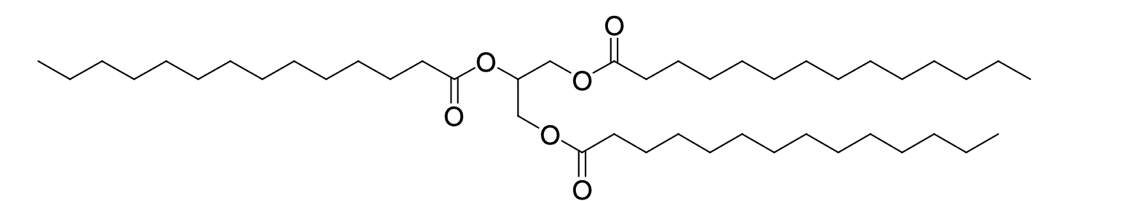
Ground nutmeg, widely used in the food industry as a spice additive and flavoring, is a rich source of Trimyristin. Studies have shown that Trimyristin also has clinical potential; in particular, it has proven antioxidant properties and may be helpful in the treatment of inflammation (Malau & Azzahra, 2021). Among other things, the main applications of nutmeg include cosmetic and perfume products and fragrance blends.
Uncomplicated instrumental extraction methods can be used to isolate Trimyristin from ground nutmeg. Since the substance to be analyzed is organic and found in a natural source, the use of solid-liquid extraction is a feasible strategy (Gilbert & Martin, 2016, p. 175). In this experiment, ground nutmeg is used as a solid phase, and dichloromethane is used as a liquid solvent.
In this case, Trimyristin is able to dissolve in the liquid medium, while the other impurities of the ground nutmeg remain as an insoluble precipitate. Recrystallization must be used to precipitate a pure sample. This process further purifies the resulting extract by transforming it from a solid precipitate to crystals (Gilbert & Martin, 2016, p. 169).
The thermometric analysis is used to determine the analytical purity of the resulting extract. Since the melting point is determined by the substance’s molecular structure and the presence of impurities, obtaining melting point data for the sample and comparing it to known data will allow the purity to be estimated. Thus, this laboratory work is aimed at obtaining Trimyristin from ground nutmeg and instrumentally evaluating the purity of the product in the output.
Procedure
This laboratory work was based on an experiment for the isolation and recrystallization of Trimyristin. In a 50-mL round-bottom flask with 2-3 boiling stones, 2.0 g of pre-crushed nutmeg was placed, and 10.0 mL of dichloromethane was added. A reflux apparatus was assembled, as shown in Figure 2.
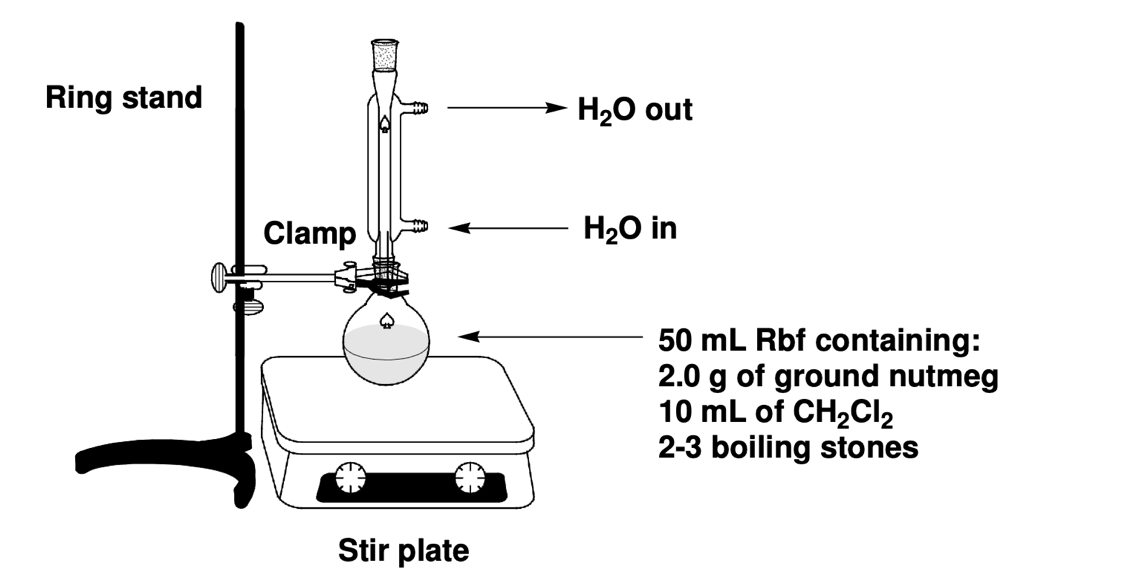
The mixture was gently heated for 30 minutes after condensation began and cooled to room temperature after this time. A Buchner funnel was used for vacuum filtration to sift out the solid residue of the mixture. The residue was washed with 5 mL of methane, then transferred to a 100 mL laboratory beaker for heating. Heating was performed on a hot stove in a fume hood at 130 °C until the dichloromethane completely evaporated. The oily residue after evaporation solidified as it cooled: the exact mass was measured.
Four mL of 95% ethanol was added to the resulting residue, and the mixture was heated on a hot stove until the precipitate was dissolved entirely. The solution was cooled to room temperature, resulting in the formation of crystals. Crystallization was enhanced by placing the solution in ice for 10 minutes, after which crystals were isolated by vacuum filtration.
The sample was washed with two portions of 1 mL of cold ethanol, after which it was dried for 5 minutes. The vial with the crystalline Trimyristin was sent for thermometric analysis to determine the melting point. The initial (50 °C) and final (60 °C) temperatures were set on the DigiMelt machine during the analysis based on the expected melting point for Trimyristin. After the analysis was completed, the crystals were put back into the test tube and sent for storage.
Results
Table 1 summarizes the results of the experiments performed. The mass of the solid residue was 0.478 g after the completion of the extraction. The mass decreased by 68.6% after recrystallization to 0.150 grams. In other words, 68.6% of the sample (m = 0.328 g) were impurities and solvents that were removed during the recrystallization step. The melting point range for Trimyristin was determined to be 51.5-53.7 °C.
Table 1: Results of the experiments
References
FS. (2019). Trimyristin, 95%, Thermo Scientific Chemicals. Web.
Gilbert, J. C., & Martin, S. F. (2016). Experimental organic chemistry: A miniscale and microscale approach. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning.
Malau, N. D., & Azzahra, S. F. (2021). Molecular docking studies of potential multifloroside and trimyristin as inhibitor for anti-malaria [PDF document]. Web.