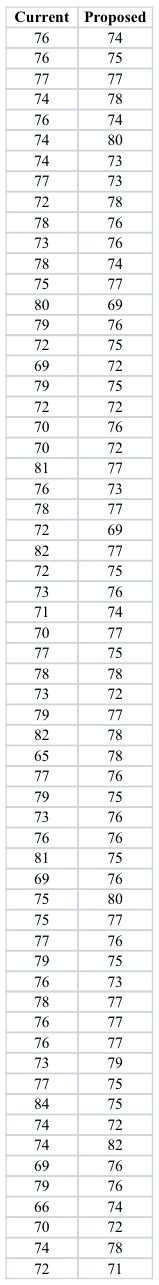
Descriptive Statistics Summary of Training Time Data
The F-Test Two-Sample for Variances is used as a statistical tool to test the variance of two samples. Like other comparative F-tests, this method aims to compare two variances and find statistically significant differences (LT, 2023). This paper used two samples, Current and Proposed, each containing 61 data records, for the analysis (Appendix). The samples contained time values for the Current and Proposed educational method, and the answer to the research question was to determine if the distribution of one of the samples was more dispersed than the other or if there was no difference between them.
Standard Deviation and Variance Analysis
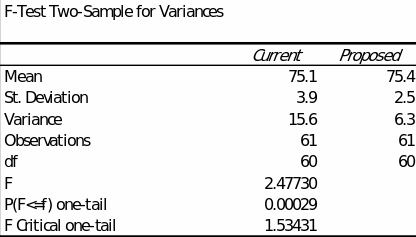
The analysis was performed using built-in functions in MS Excel, shown in Figure 1. To begin, it is helpful to discuss the findings of the descriptive statistics for each of the samples. As can be seen, the average training time for the current training system is 75.1 (SD = 15.6), and for the proposed one, it is 75.4 (SD = 2.5). The variance of the first sample (V = 15.6) is more than twice as high as that of the second sample (V = 6.3). However, the significance of such differences must be confirmed at the inferential level, mainly using the outcomes of the F-Test Two-Sample for Variances.
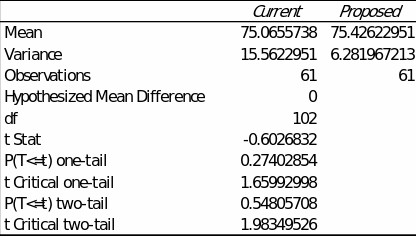
Based on the results, there are statistically significant differences in variance between the two samples (F(60) = 2.48, p <.001). Given the results of descriptive statistics, the instructional time in the proposed educational strategy sample has a lower variance (spread) than the current process sample. In addition, the conclusion of the additionally conducted t-test for unequal variance shows that the mean values of instructional time between the two samples are not different (t(102) = -0.60, p =.55), as shown in Figure 2.
Discussion of Findings and Recommendations
The results indicate that the learning time between the two pedagogical strategies will be similar, but there is less variance in the proposed solution. The proposed solution eliminates the unequal learning environment and creates a more uniform time for all students. The proposed solution should be adopted as it positively affects the standardization of study time. Additionally, it would be interesting to analyze gender differences in the solution’s effectiveness to assess whether all genders benefit sufficiently. The results are expected since the proposed strategy was precisely to improve educational outcomes for students.
Reference
LT. (2023). Test of two variances. LibreTexts Statistics. Web.
Appendix