Background of the Study
Entrepreneurs constantly locate business opportunities and solicit resources to cover the gap, notwithstanding the uncertainties associated with the business. A successful entrepreneur forms a start-up business motivated by passion, resilience, and the desire to profit. Features of start-ups include but are not limited to having a perfect market match, having a solid corporate culture, and taking customer feedback seriously.
Start-ups are usually managed by passionate leaders who dream of competing with existing firms. Therefore, entrepreneurs working on new enterprises must conduct holistic market research to understand the uncertainties associated with the business and take the necessary steps to ensure the company’s sustainability. The corporate lens on justifiable revenue requires business owners to facilitate environmental, social, and economic sustainability to avoid business failure. Although starting a business is exciting, failing to understand the basics makes it fail before it flourishes.
Statement of the Problem
The goal of every entrepreneur is to start and manage a successful business venture. However, most entrepreneurial dreams are shuttered since many start-ups fail before they mature into profitable ventures. 90% of all start-ups are bound to fail, and innovation is key to enabling them to thrive (Aminova & Marchi, 2021, p. 41). Research by Alnassai (2023) inferred that entrepreneurship is among the most popular careers in the UAE, and many people are venturing.
Numerous elements contribute to the downfall of small businesses in the UAE. The common reasons that make start-ups fail in the region include higher competition, outdated business models, and the need for more information on the changes and emerging business patterns. Although the entrepreneurship ministry supports start-ups, the failure rate is still higher, and more investors are recording losses in their new investments (Yasin et al., 2021). Despite the UAE being ranked fourth on the global entrepreneurship index, start-up failures still need to be improved in the corporate domain (Alnassai, 2023). Understanding the reasons why most new businesses fail is the first step towards improving the new businesses’ success rate.
Different barriers threaten the success of start-ups in the UAE. Entrepreneurs must identify and solve them for their businesses to thrive. Some of the common barriers to the failure of start-ups include social capital barriers, unstable economic environment, and lack of resources (Alnassai, 2023). The failure rate differs in different regions, and most MNCs tend to invest in countries with a friendly economic environment for sustainability (Aram & Salipante Jr, 2003). The motivation of the study is to provide a solution to the challenges facing the upcoming business to make it possible for new entrants to thrive in the market. When the causes of failure are understood, solutions will be developed for business success.
Research Purpose and Objectives
The purpose of the study is to determine the reasons why start-ups fail in the UAE’s dynamic corporate domain. The research is defined using the research questions, which offer directions for the data collection, analysis, and outcome justification. The research questions motivate the collection of data on start-up failures and the recommendation of the best strategies to improve business success. The main research question guiding the study is as shown below:
- Why do start-ups fail?
The sub-research questions to guide the research into detail include:
- What percentage of SMEs fail within the first two years?
- What percentage of SMEs fail within the first five years?
- What are the most common reasons for SMEs’ failure?
- How can SMEs succeed, and what are the critical success factors?
Research Methodologies
Data Sources, Collection Methods, and Limitations
Surveys
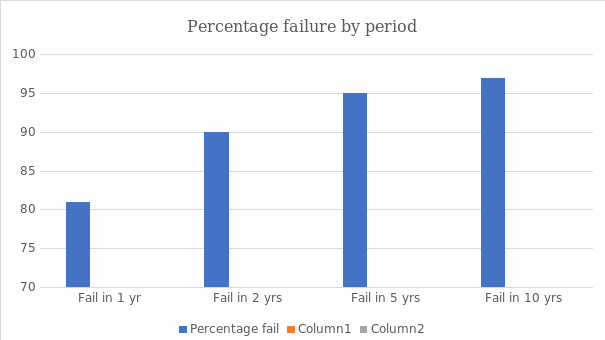
Previous surveys have shown significant trends in SMEs and start-up failure. A survey conducted by Polonsky and Waller (2015) showed that 91% of all start-ups fail in the first two years. The survey further indicated that 95% fail in the first five years of operation (Polonsky & Waller, 2015). The most common reasons for failure were financial mismanagement, failure to adapt to the dynamic market niche, and external factors such as infrastructure.
The survey further showed that the antidote to eliminate failure is to focus more on research and development, marketing, and financial management to increase success rates. A survey is flexible and dependable as it can be conducted at the researcher’s convenience (Eisenhardt, 1989). The critical limitation of surveys is the failure of the respondents to answer questions, which makes them uncomfortable. Consequently, the accuracy of the data collected will be jeopardized.
Interviews
The second data source includes interviews with people who started businesses and failed. Interviews conducted by Putra & Cho (2019) proved that more than 80% of start-ups fail in the first two years, while 89% fail after five years of operations. The causes cited by the respondents were changing government policies and competition from established businesses. According to the interviews, the critical success factors for SMEs and start-ups were franchising to established businesses and partnering with other entrepreneurs to improve revenue sources.
Interviews are advantageous because they are likely to offer more accurate information as the selected candidates have firsthand information on what led to the failure of their business (Eisenhardt & Graebner, 2007). The critical limitation of the data collection method is that it is time-consuming, costly, and takes longer to analyze the audio data (Eisenhardt, 1989). Researchers must set aside adequate time and resources to succeed in the data collection method.
Theoretical Framework
This study on why start-ups fail is informed by two theories, Drucker and the self-justification theory. The theories underscore the critical decision-making process when running start-ups and explain why one wrong decision may lead to organizational failure. The relationship between the business owner, the regulatory agencies, and the revenue collectors. The framework provided by the theories guides the investors on the best way to operate and acquire sustainability and success.
Self-Justification Theory
The self-justification theory explains how people tend to justify themselves regardless of the reality at their disposal. Leon Festinger is the psychologist who developed the theory to explain how cognitive dissonance is underscored by people’s needs to achieve internal consistency (Gelderman et al., 2019). The theory is quintessential for customer opportunism and defines how decisions are made in the long run.
For an investor to profit in the dynamic business landscape, moving with the trending issues is essential to remain relevant in the market. An example of cognitive dissonance may occur when the change occurring in the market is not acceptable to investors. Although the theorist did not know about financial management, he underscored that poor decision-making by the investor caused by the dissonance is likely to affect the start-ups negatively.
Drucker Theory
Peter Drunker coined an entrepreneurship theory explaining how investors respond to a change in the corporate domain. The corporate domain is ever-changing, and entrepreneurs must always view the change as an opportunity and invest for the business to remain relevant. The success of a business depends on the connectivity of different factors of the economy (Drucker, 2020). A successful entrepreneur must understand the connectivity and operate in line with them. However, many start-ups need to stand the test of time because when they are exposed to radical change and uncertainties, they are likely to fail (Putra & Cho, 2019).
The theorist underscored two critical points in business: marketing and innovation (Gelderman et al., 2019). If new start-ups do not analyze the business dynamics, the discourse will likely be negatively affected. Financial constraints sometimes limit SMEs from conducting market research and institutions’ research and development departments. Consequently, the business may miss important market and regulatory updates and become threatened. Start-ups and SMEs must, therefore, follow the suggestions of the theory to constantly research the changes in the market and make necessary adjustments in their operation to meet customer and compliance needs.
Concept Map
A concept map is important visual information representing how the research will be conducted to answer the research questions and present findings. The maps are essential as they show the relationship in knowledge and help the researcher follow the most accurate trajectory. The most important parts of a concept map include assembling, arranging, and assessing (Lee & Lings, 2008). The assembling procedure includes identifying the problem and the data required to answer the research questions.
The second step is arranging to ensure that data is organized and summarized for evaluation and discovery. The broad issue includes start-ups and SMEs and their role in the economy. Further, the reasons why they fail are determined and connected with the percentage of failure in the business environment.
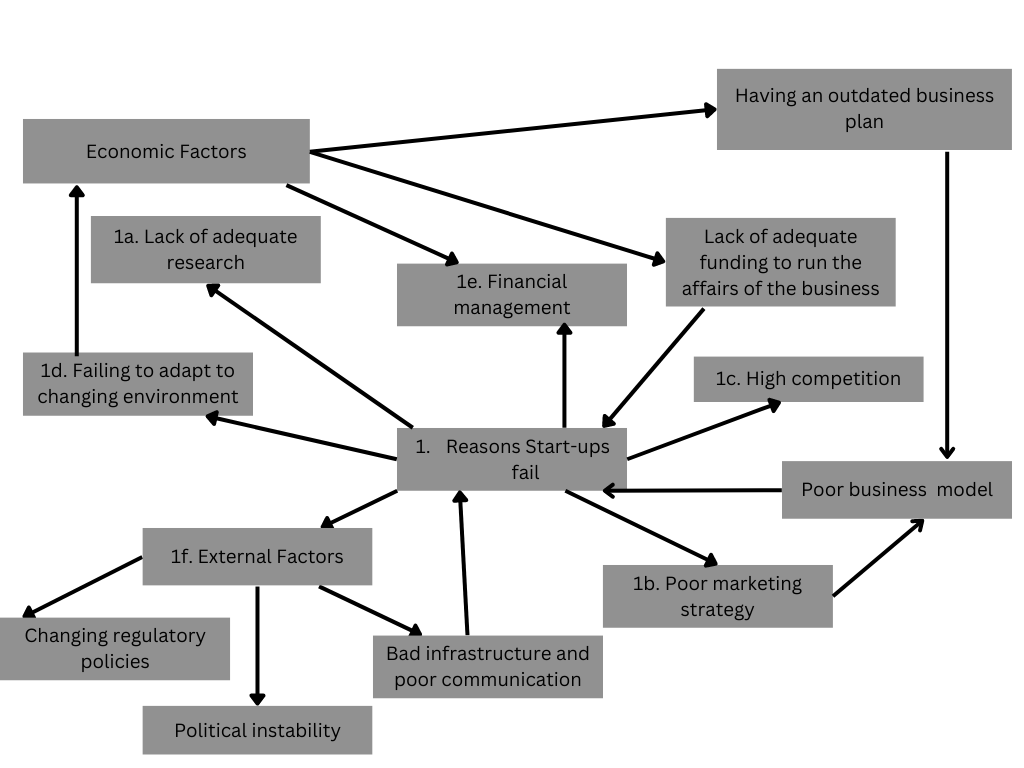
The research will establish the main reasons start-ups fail and focus on six key factors. The lack of adequate research and its role in small business success will be analyzed. Further, an analysis of the main strategies of the failed businesses will be analyzed to prove whether they were adequate for business success. Higher competition from existing firms and failure to adapt to the ever-changing environment will also be considered, as how they contribute to the failure of start-ups (Lallé, 2003).
Financial management is one of the economic factors that will be analyzed as a potential reason why start-ups fail before they attain five years. Another economic factor for analysis is the failure of the business to have adequate resources to meet the customers’ current needs. Businesses may sometimes be required to fund an entire project and be paid at the end of the project (Christensen & Raynor, 2003). Since small businesses and start-ups may not have the required financial resources, they may fail in the long run.
External and environmental factors play a significant role in the success of a business. SMEs and start-ups are affected by the manager’s decisions and external factors in the organization. When the regulatory policies change, such as increased taxes, the SMEs may not pay off the taxes as required. Further, infrastructure changes may affect the business and make it perform poorly. When a bridge gets damaged, a small shop may not afford fees to solicit other means of transport, leading to a failure (Lallé, 2003).
The external factors will be analyzed and connected to the factors leading to the failure of small businesses. Business plans, models, and standard operating procedures will be analyzed to determine their impact on the day-to-day running of the SMEs and how their failure affects the business. Once all the areas have been covered, the results will be analyzed and summarized as the key reasons for start-up businesses to be affected.
Limitations of the Study
The research aims at understanding the causes of failure in SMEs and start-ups. Previous knowledge in SME and start-up formation and management is critical in the research. Researchers without previous knowledge in the field are likely to be affected by informational bias, jeopardizing the study’s quality. Another relevant area for improvement in the study is the collection of accurate data due to the falsification of data. False information during the survey and interviews will likely jeopardize the research outcome (Lee & Lings, 2008).
The formulation of the research question is too broad and may require additional time to break it down to all the factors affecting SMEs and start-ups before the critical cause of failure is understood. The scope of discussion in the research will also be limited by experience in the business. Quality of research requires extensive knowledge of data collection and analysis. Lack of experience in the field of data collection may affect the research. Future considerations should focus more on the remedies to protect SMEs.
Conclusion
Start-ups and SMEs face numerous threats from established businesses and may not survive in the dynamic business landscape. As entrepreneurs venture into the business domain, they must understand that start-ups will likely fail in the first five years. Identifying the reasons behind failure may be a necessary first step to formulating policies and strategies to overcome the situation. Self-justification and Drunker theory provide quintessential frameworks for entrepreneurs and investors to understand the dynamic corporate landscape and make decisions that are aligned with their business needs. The concept map shows the guidelines on how the causes of SMEs and start-up failure will be analyzed and presented. Understanding the causes of the failure is the prerequisite for finding long-lasting solutions to make SMEs and start-ups successful.
References
Alnassai, J. M. I. A. (2023). A Study on the Barriers to Entrepreneurship in the UAE. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 16(3), 2-14. Web.
Aminova, M., & Marchi, E. (2021). The role of innovation on start-up failure vs. its success. International Journal of Business Ethics and Governance, 4(1), 41-72. Web.
Aram, J. D., & Salipante Jr, P. F. (2003). Bridging scholarship in management: Epistemological reflections. British Journal of Management, 14(3), 189-205. Web.
Christensen, C. M., & Raynor, M. E. (2003). Why hard-nosed executives should care about management theory. Harvard business review, 81(9), 66–75.
Drucker, P. F. (2020). Peter F. Drucker on the Network Economy. Harvard Business Press.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (1989). Theory building from case study research. Academy of management review, 14(4), 532-550. Web.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (2007). Theory building from cases: Opportunities and challenges. Academy of management journal, 50(1), 25-32. Web.
Facchini, F., Jaeck, L., & Bouhaddioui, C. (2021). Culture and entrepreneurship in the United Arab Emirates. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 12(1), 1245–1269. Web.
Gelderman, C. J., Mampaey, J., Semeijn, J., & Verhappen, M. (2019). Self-justification for opportunistic purchasing behavior in strategic supplier relationships. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 34(2), 451-462. Web.
Lallé, B. (2003). The management science researcher between theory and practice. Organization Studies, 24(7), 1097–1114. Web.
Lee, N., & Lings, I. (2008). Doing business research: a guide to theory and practice. Sage Publishers, London.
Polonsky, M. J., & Waller, D. S. (2015). Designing and managing a research project: A business student’s guide. Sage Publishers, London. Web.
Putra, E. D., & Cho, S. (2019). Characteristics of small business leadership from employees’ perspective: A qualitative study. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 78, 36-46. Web.
Yasin, N., Khansari, Z., & Tirmizi, K. (2021). Exploring the challenges for entrepreneurship business incubator hubs in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Globalisation and Small Business, 12(2), 190-212. Web.
Appendix 1: Percentage of SMEs Failing with Time
Table 1 – Percentage of SMEs Failing with Time.
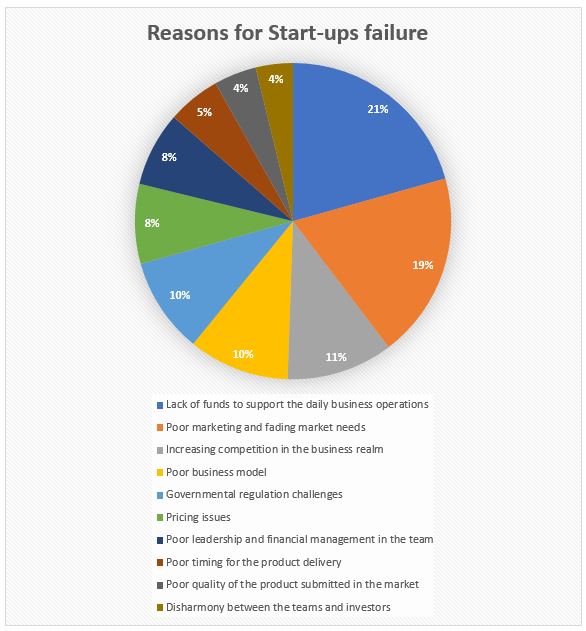
Appendix 2: Reasons Why Start-Ups Fail Worldwide
Table 2 – Reasons for SMEs’ failure.