Why is this important?
At present, the global community is concerned about the well-being and health of people, which is the basis for the harmonious development of society. Food insecurity is one of the most pressing public health issues relevant for both developed and developing countries. This problem is defined as a “household-level economic and social condition of limited or uncertain access to adequate food” (as cited in Seligman & Berkowitz, 2019, p. 320). In other words, food insecurity describes a situation where a household cannot afford to buy an adequate amount of food. In recent years, the medical community has been paying more and more attention to the problem of world hunger, trying to find ways to provide proper nutrition for affected people.
The growing concern of the global community with the problem of world hunger is due to the sharp increase in the level of food insecurity after the pandemic. United Nations reports that in 2020 the number of people affected by this problem has increased by almost 10% (Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, 2021). In particular, according to estimates, from 720 to 811 million people in the world 2020 face food insecurity (Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, 2021). Although most undernourished people live in less developed regions, including Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean, even in developed countries like the US, the number of food-insecure citizens reaches over 11% (Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, 2021; Miller & Thomas, 2020, p. 1). Thus, the problem is global in nature, and its scale is growing every year, which requires the development of appropriate public policy measures.
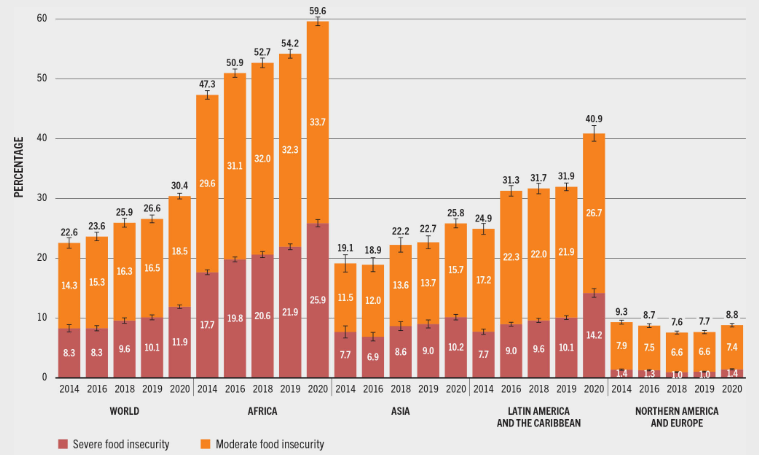
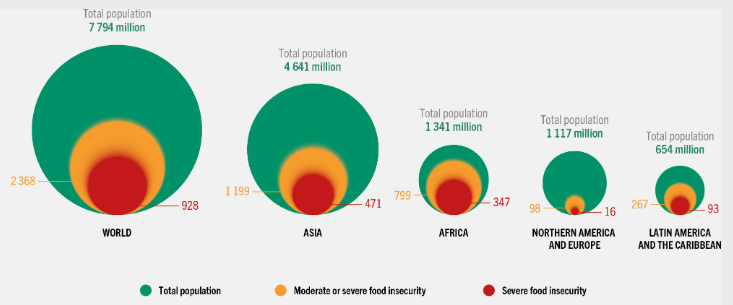
Food insecurity has a number of negative health and well-being implications, making it a primary public health concern. In addition to being associated with metabolic disorders, food insecurity can lead to chronic diseases, including “diabetes mellitus type 2, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and congestive heart failure, dyslipidemia, and chronic kidney disease” (Seligman & Berkowitz, 2019, p. 321). This problem has a particularly significant negative impact on children, contributing to the development of developmental disorders that result in health problems during their lifespan (Hartline-Grafton & Hassink, 2021). It is also important that the general deterioration in the population’s health, the development of chronic diseases, and the decline in well-being among children lead to increased health care costs. Food insecurity from a global perspective, leads to a slowdown in economic development, which is relevant for both developed and developing countries.
Recommendations
In order to form a recommendation within the framework of public policy, it is necessary to determine the causes of the existing problem. The researchers note that the main source of food insecurity is financial instability and economic distress, which have been exacerbated by the pandemic as a result of job losses and a general reduction in economic growth trends (Hartline-Grafton & Hassink, 2021; Seligman & Berkowitz, 2019). In developing countries, these factors are also supported by the low availability of quality food, especially in remote areas (Hartline-Grafton & Hassink, 2021). Thus, public policy should focus on expanding financial opportunities and economic support for the affected population. The public policy provides the following recommendations for addressing food insecurity problems in the world:
- Expansion of financial support programs for affected groups in developed countries through increased benefits under the programs of supplemental nutrition assistance;
- Introduction of similar programs in developing regions through the financial support of international organizations;
- Simplification of the procedures for applying for participation in financial support programs for people affected by the problem;
- Improving the availability of quality food in geographically remote areas prone to food insecurity.
Thus, the basis for this public policy is the introduction and expansion of support for supplemental nutrition assistance programs. For the affected population, achieving a greater level of economic stability is most important, which is possible through the provision of monthly food benefits. In the long term, this policy may result in an overall increase in food security, an increase in the economic well-being of the affected population, and a restoration of economic development. The key aspect of the policy involves international collaboration on the dissemination of economic support programs. To achieve significant results, the cooperation of international and local public organizations is necessary. In particular, funding for the program within the policy is provided by local resources for each country or region. At the same time, international organizations will provide an advisory function to develop appropriate plans and strategies for the implementation of programs on the example of already existing achievements.
References
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2021). The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2021. FAO. Web.
Hartline-Grafton, H., & Hassink, S. G. (2021). Food insecurity and health: Practices and policies to address food insecurity among children. Academic Pediatrics, 21(2), 205-210.
Miller, D. P., & Thomas, M. C. (2020). Policies to reduce food insecurity: An ethical imperative. Physiology & Behavior, 222, 1-5. Web.
Seligman, H. K., & Berkowitz, S. A. (2019). Aligning programs and policies to support food security and public health goals in the United States. Annual Review of Public Health, 40, 319-337. Web.