Over the past few years, the business segment of food delivery apps has grown unprecedently. A prime example of such an application is Glovo, a business established in Barcelona in 2015 by Oscar Pierre and Sacha Michaud (“About us,” n.d.). Since then, the service has expanded from Spain to nearly twenty countries in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, operating in more than 800 cities (“About us,” n.d.). The LSE’s network includes such countries as Spain, Portugal, Croatia, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, Uganda, Morocco, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Kenya, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Poland, and Georgia (Figure 1).
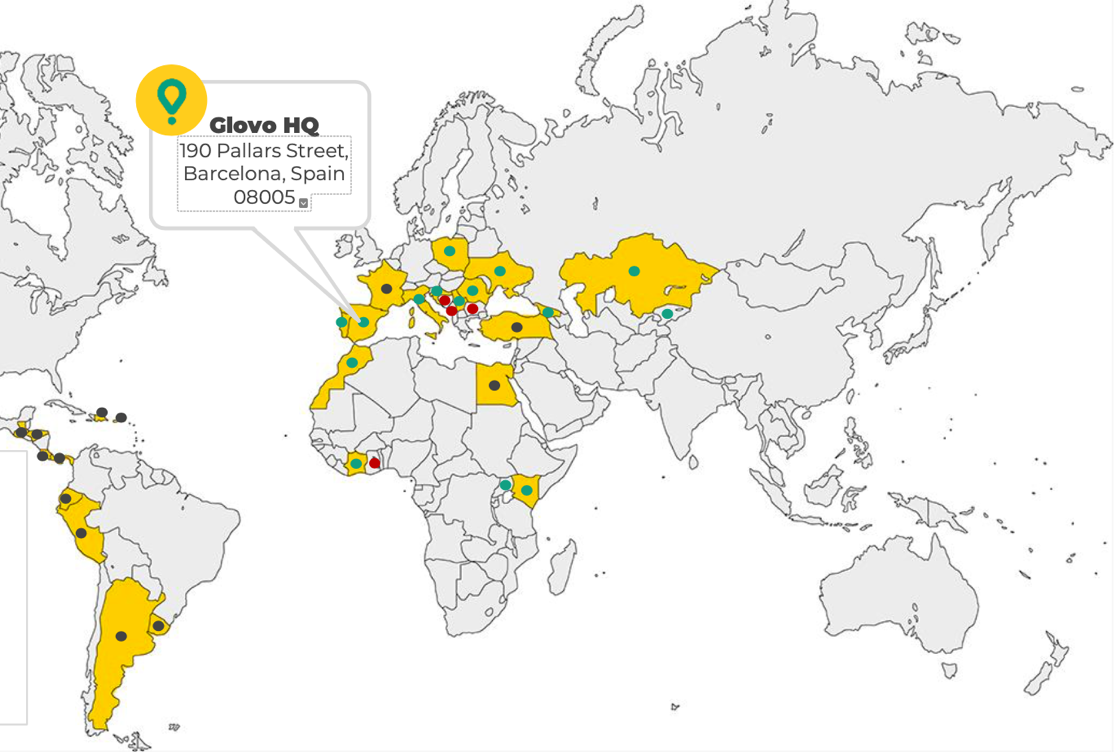
Fundamentally, Glovo is an online delivery service that cooperates with various local restaurants and shops to provide a one-place convenient delivery service to the customers of the area. As of now, Glovo cooperates with more than a hundred thousand shops and restaurants worldwide and has nearly ten million active customers to its name (“Social contribution report,” 2020). Operating mostly in the emerging markets, the online delivery services place major emphasis on the middle-income target market and customer share. Having recently gained much attention and relevance due to the outbreak of COVID-19, Glovo currently seeks new international markets to engage and expand its operational network.
International Markets
In terms of the present report, the notion of the international market will be perceived as a country or a group of countries a company seeks to enter. The two international markets chosen for Glovo include the United States and India. The rationale for choosing both includes the relevance and economic proximity of these two markets in the global context. While the US remains the world’s largest and diverse economy, India is rightfully considered one of the fastest-growing economies with an international growth potential (Joe et al., 2018). Hence, these two markets are of particular interest to Glovo.
International Market Selection: The Firm
The first step toward the successful IMS process is an assessment of the firm’s determinants for internationalization. According to Hollensen (2012), the degree of internationalization is a significant factor. Since Glovo currently operates in 29 countries, it has already adopted the internationalization strategy as a part of its marketing agenda. As far as the resources are concerned, the service operates a wide range of employees, contracts, and even cookrooms, yet most of its human resources are contractors who work on a temporary basis (Figure 2). The existing network of relationships for Glovo primarily concerns Europe, the Middle East, and South Africa, as these are the three centers of service concentration, so it would be more profitable for the company to extrapolate its services to the regions closer to the network.

United States
As far as the US environment is concerned, it has one of the most competitive food delivery markets globally. In 2020, the revenue of this market had reached nearly $26.5 billion (Curry, 2021). The market in the US is highly internationalized, as it both exports and imports a wide variety of goods from various markets. The primary competitors in the food industry are DoorDash, UberEats, Just Eat, and Grub Hub. The market itself is similar to the European segments, and no language barriers will be tracked, as Glovo has been initially created in Spanish and English versions.
India
Although the Indian environment is not as broad in terms of food delivery, this segment is also popular with this international market. In 2020, the revenue of the market constituted nearly $11 billion (“Online food delivery,” n.d.). Over the past years, the market has become highly internationalized as the majority of large enterprises expanded to India due to its economic potential and cost efficiency of the market entry (Joe et al., 2018). Since UberEats discontinued its operation in the market, the primary competitors are Zomato and Swiggy (Sharma, 2020). The market has been increasing steadily, yet Glovo is expected to become more acquainted with Asian culture prior to entry. The comparison of the markets may be observed in Table 1:
Table 1: International market comparison
In order to review the market selection process, the following model could be applied:
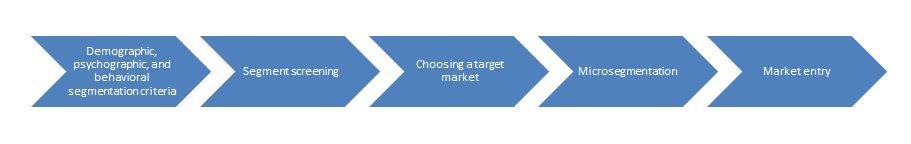
For example, when applying this model to the food delivery industry, it is necessary to emphasize the target customer image across the markets. For Glovo, these can include students, busy professionals, and remote freelance employees aged 18-35. Hence, both the Indian and US markets account for this audience. As far as microsegmentation is concerned, the two chosen markets are only discussed in the context of big cities with a big share of the young middle-class population and an extensive network of shops and restaurants in every neighborhood.
Entry Criteria
Market entry for an online food delivery service should pay much attention to the aspect of internationalization as a driving force of competition. Indeed, the modern examples of platform companies, including search engines like Google and services like Glovo and Uber Eats, are all characterized by their adaptability to any market in question (Simões, 2019). Glovo currently obtains an advantage of the ability to enter both international markets on equal terms. However, nowadays, while many companies strive for universality, others perceive internationalization as a foundation for an easier localization process. In this context, it is necessary to define the extent to which Glovo can find it easy to localize its product in both Indian and American markets.
In order to define the entry criteria for Glovo, it is necessary to dwell on the internal entry factors of the firm. Thus, Glovo is a large enterprise that has international experience in nearly thirty countries (Hollensen, 2012). As far as the product is concerned, Glovo prides itself in a high level of differentiation, as, unlike DoorDash or Swiggy, the company is able to present grocery, pharmacy, and on-demand courier delivery within the area. The product itself is not complex in its nature, as the procedure of performing operations remains the same across the international market, including hiring local contractors for commission and making deals with local shops and restaurants to expand the network.
It is of paramount importance to take into account the external factors that can affect the peculiarities of market entry. Considering the external factors outlined by Hollensen (2012), some of them, including market size and growth and high demand for the product, are equally beneficial in both Indian and American markets. The competition is high as well, as while there are many options in the US, the limited choice for food delivery apps in India contributes to market monopolization. Hence, the remaining concerns address the economic and social entry criteria. For example, while the economic environment of the US is more stable, the trade barriers for international business are high due to taxation rates. India, on the other hand, has an entirely opposite economic environment. The comparison of various significant criteria can be observed in Table 2:
Table 2. Market entry criteria assessment
Having closely considered the internal and external factors of the international market entry, it can be concluded that there are high rates of cultural distance and prevalence of contractual agreements with the workers and the restaurants. Thus, both international markets should opt for an intermediate entry mode. According to Hollensen (2012), this entry option is located between export and internationalization, as it accounts for partial control over the operations in the international market yet encourages the contractual relationship and agreements such as franchising and licensing. Since both Indian and American markets are far from the operating offices of the company, intermediate entry is cost-efficient and convenient for both parties.
Marketing Tactics
Although both international markets would be potentially beneficial for the company, the choice in favor of the Indian segment currently seems more viable and cost-efficient. The primary challenges in the area include cultural differences, the market prevailed by Zomato and Swiggy, and the lack of brand recognition in the Asian market in general. It is evident from the Uber Eats example that the global recognition of the brand does not account for its success in the Indian market, as both Zomato and Swiggy are unique to the area and culturally adapted delivery services. In order to combat them, Glovo needs both to optimize product recognition and product quality. Thus, the marketing tactics chosen include the tactics on product and communication.
Tactics on Product
Since the product of the company is delivery service, it is vital to adapt the service peculiarities to the demands of an average customer. For example, in many existing markets, Glovo obtains an advantage of a liquor license that allows the service to bring alcoholic beverages to customers. Both Swiggy and Zomato do not obtain such a function. However, rather than perceiving this as a product advantage, it is of paramount importance to realize that these delivery services refused this delivery option due to the governmental and cultural specifics of alcohol drinking. If a Spain-based company is rather used to delivering alcohol as a part of the meal, the Indian segment is more likely to appreciate public initiatives on healthy lifestyle and healthy alternatives to alcohol such as kombucha delivery.
The strategy on the product will help to define where the product should exist in the marketplace. A product innovation strategy, for its part, should concern application optimization, including the ability to track the delivery and online customer support via the application. Nowadays, India is expected to be one of the leading consumer markets in the world with increasing purchasing power. This tendency presents Glovo with an opportunity to expand their delivery network and the assortment of restaurants and shops to contract.
Tactics on Communication and Advertising
Indian consumer community is extremely influenced by the existing caste system. Although it is not as stereotypical as presented by media, the communication power still remains to be stronger within certain groups of the population. For this reason, while investing in the already successfully established social media communication strategy, Glovo should become aware of the classic advertising channels like word-of-mouth. Moreover, as far as food delivery is concerned, the majority of the Indian segment is used to shopping regularly in “kiranas” rather than big supermarkets. Hence, Glovo should communicate with small retail business entrepreneurs to enhance the chances of grocery delivery.
One of the primary reasons why Uber Eats was eventually acquired by Zomato was the company’s lack of culturally sensitive communication and advertising. The existing food delivery services in India are mostly chosen by customers not because of quality but due to recognition. For this reason, while saving money with the intermediate entry mode, Glovo should allocate more resources on targeting, especially considering the fact that they have already adopted multi-channel online advertising strategies on Meta-owned social networks.
Recommendations and Conclusion
Considering the aforementioned facts, it may be concluded that Glovo has a chance of entering the international markets both in Asia and North America. However, in order for the company to be more successful, it is of paramount importance to choose the markets with beneficial entry criteria and relevance among the target population. Although both market segments presented prospects for the company, the Indian market is more beneficial for Glovo in terms of easier entry criteria, less competition, and the growing tendencies in consumer behavior. The pandemic outbreak has elevated the interest in the service of online food delivery, so it is of paramount importance to make use of the current social context and expand globally.
The fundamental recommendation for Glovo is to embrace its unique feature of a personalized approach to delivery and reinforce it through the intermediate market entry. Specifically for the Indian market, it is recommended that Glovo embrace microsegmentation of the customer groups in order to present each with options. As far as marketing tactics are concerned, Glovo is expected to resort to product and communication tactics, as they are expected to benefit in the Asian marketing segment.
References
About us. (n.d.). Glovo. Web.
Curry, D. (2021). Food delivery app revenue and usage statistics. Web.
Hollensen, S. (2012). Essentials of global marketing (2nd ed.). Pearson.
Joe, W., Kumar, A., & Rajpal, S. (2018). Swimming against the tide: Economic growth and demographic dividend in India. Asian Population Studies, 14(2), 211-227. Web.
Online food delivery. (n.d.). Statista. Web.
Sharma. K. (2020). What went wrong with Uber Eats? Web.
Simões, V. C. (2019). The internationalisation of platform companies: Does the digital get rid of Geography? Información Comercial Española, ICE: Revista de Economía, (909), 37-48.
Social contribution report. (2020). Glovo. Web.