Strategy Formulation and Business Strategy
Business strategy in a consolidated form is the “direction and scope of an organization in the long-term which enables it to achieve competitive advantage through configuring its resources within a challenging environment in order to meet the needs of the market and expectations of the stakeholders.” (Dess 2010, pp.67). Business strategies can be found at different levels of the organization namely at the corporate level, the business level and the operational level.
This paper will focus on the various aspects of business strategy such as its formulation, planning, evaluation, and implementation. These concepts will be discussed by analyzing the strategy adopted by Goodmark Industrial Ltd., hereafter referred to as Goodmark.
Strategic formulation of a business can be a multifaceted assignment. “Strategy is the business word for game plan. All businesses have strategies, either planned or unplanned.” (Briefcasebooks, n.d.). Following is a model in which a simple business is carried out.
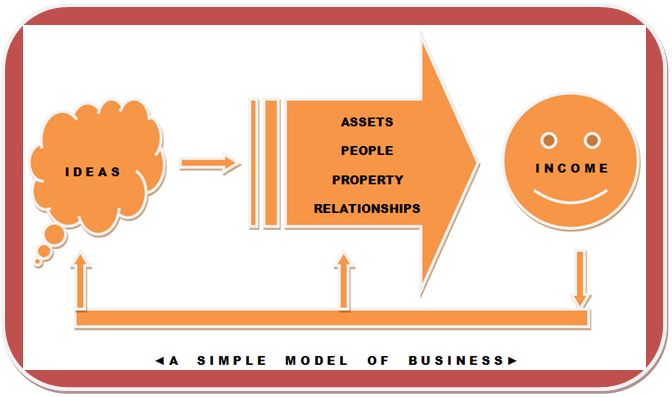
Mission Statement
Mission statement is a short write-up in straightforward and to the point terms about a company’s operations and the reason of its existence. Mission statement is a sort of marketing tool because it describes the nature of business to the employees, customers, suppliers, and media. “A Mission Statement defines the organization’s purpose and primary objectives. Its prime function is internal – to define the key measure or measures of the organization’s success – and its prime audience is the leadership and the stockholders.” (Mindtools, n.d.).
Goodmark’s mission statement is as follows.
People have not but I have; people have but I have the fine works. (Goodmark-new, n.d.).
If the mission statement of Goodmark is carefully examined, it is packed with motivation. The motivation is meant for both, the management as well as the employees. It shows that the company is doing some extraordinary work that is unmatchable. It is also interpretable that the company does precision work. By merely reading the mission statement of Goodmark a person can know the precision factor of the company.
Vision Statement
A vision statement is a written description of what the firm strives for and what it intends to achieve in the long-term (Bryson, 2004, p.89). The vision statement defines the future accomplishments of the company and also what the business wants to achieve. “A Vision Statement defines what your business will do and why it will exist tomorrow and it has defined goals to be accomplished by a set date. A Vision Statement takes into account the current status of the organization, and serves to point the direction of where the organization wishes to go.” (Mayhew, 2009).
Goodmark’s vision is as follows:
Corresponding to the continuously developing social demand, we have to harbour our own grateful hearts to work and behave like human beings attentively. Using good faith, the spirit of ‘strive for perfection’, we can repay the society, wholeheartedly serve the customers, and create our perfect tomorrow together (Goodmark-new, n.d.).
Goodmark’s vision statement clearly indicates that its future goal is to “create a perfect tomorrow together.” It also motivated the employees because according to the vision statement, the company is committed to the society as well and seeks the participation of the employees in order to achieve the visionary goal.
Core competencies
Core competencies are the qualities and abilities that are of utmost important and crucial for a business accomplishing competitive advantage. “The starting point for analysing core competencies is recognizing that competition between businesses is as much a race for competence mastery as it is for market position and market power.” (Tutor2u, n.d.).
Goodmark’s core competencies are:
- Products of high quality.
- Precision that is difficult to imitate.
- Good sales network in different countries.
- Competitive prices.
Significance Of Stakeholder Analysis
Goodmark’s stakeholders include its employees, shareholders, customers, suppliers, competitors and government departments (regulators). It is important to gain stakeholder buy-in to a selected strategy due to the following reasons. Winning the support of employees will enhance efficiency in the implementation of the strategy (Petrescue, 2010, pp. 476-482). Employees are likely to be more efficient in implementing a strategy that they support. Shareholders are likely to finance the strategy if they support it. Customers will maintain their loyalty to the firm if they are convinced that the strategy used to produce goods and services will create more value for them. Finally, the government as a regulator will only allow the firm to operate if it supports its strategies (Boyes et al, 2007, p 101).
Environmental and Internal Audit
There are two kinds of audits that are usually done namely, the external audit and the internal audit. The external audit is done on variables that the organization cannot control. The internal audit is done on the variables that can be controlled by the organization. As far as environmental audit is concerned, it is again external as well as internal. According to the Confederation of British Industry, Environment audit is explained as, “the systematic examination of the interaction between any business operation and its surrounding. This includes all emissions to air, land and water legal constraints; the effects on the neighbouring community, landscape and ecology; and the public’s perception of the operating company in the local area.” (CBI, 1990). Strategic audits are normally conducted to enable the management to establish a match between internal operations of the firm and the business environment it operates in (Porter, 1996, pp. 61-78).
External Audit
The external environmental audit can be better understood with the help of the PESTEL analysis. PESTEL means the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors that can affect a business. Following is a representation of a typical PESTEL analysis.
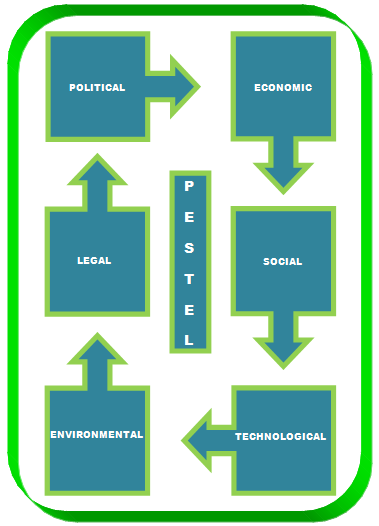
Political: China is a Communist country. As such, the rules are very stringent. The Communist Party of China (CPC) has a strong hold over the country population and as such, the government is stable. This stability enhances the chances of businesses to flourish.
Economic: Guangdong province has topped the overall GDP rankings in China, among the provincial level divisions and third among all the provinces. “They are Guangdong, with 3.9 trillion Yuan GDP ranking first.” (English, 2010). It is almost 12.5% of the total GDP of China. Considering these factors, there is a lot of scope for development in China, Guangdong in particular. Goodmark has benefitted from “the preferential policy of China’s opening up & reform.” (Goodmark-new, n.d.).
Social: “Guangdong’s total population hit 110 million for the first time in its history. The figure includes 79 million registered permanent residents and 31 million migrants who have lived in Guangdong for more than six months.” (Chinadaily, 2005). Owing to the population, the local market has enormous potential for business.
Technological: Chinese technology is known worldwide. China is a huge and fast developing country and as such, the modern technological inventions are being used in all spheres of life. Goodmark can make good use of such technologies in order to upgrade or expand its business.
Environmental: The main product of Goodmark is plastic moulding. Plastic is a source of pollution; air and water. “Industrial practices in plastic manufacture can lead to polluting effluents and the use of toxic intermediates, the exposure to which can be hazardous.” (Advameg, 2012). Goodmark takes necessary precautions to prevent the pollution from spreading.
Legal: The laws regarding business are very stringent in China. Moreover, since Goodmark is exporting its products to countries like USA, Japan, etc., it has to be very cautious, alert and have complete and up to date information about the prevailing import laws in such countries.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT is a method of analysis to assess the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of an organization. Following is the SWOT analysis of Goodmark.
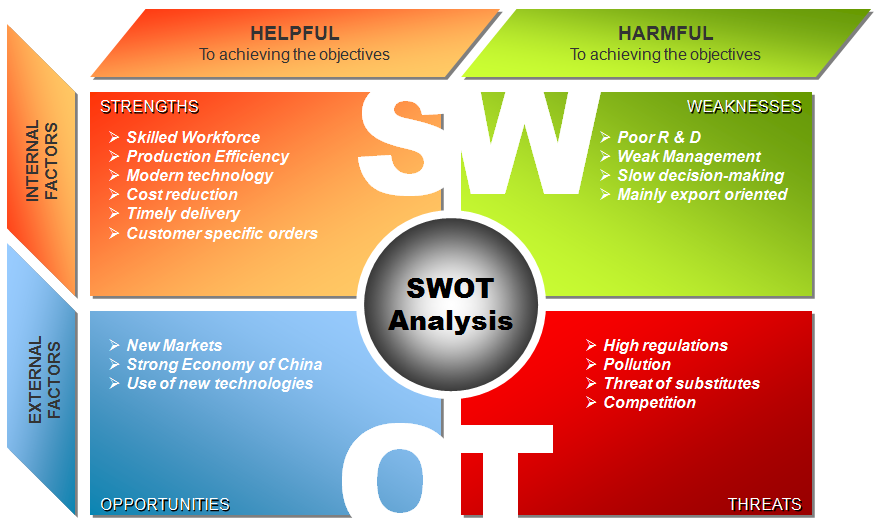
Strengths:
Goodmark’s strengths can be described as follows. First, it has been able to achieve manufacturing efficiency through the use of modern technology and precision equipment. This translates into cost reduction and on time delivery (Hollensen, 2010, p. 56). Second, Goodmark has a highly skilled workforce especially in its engineering and design department. Consequently, it is able to produce goods that satisfy the specific needs of the customers. Third, it has a superior reputation in the industry (Goodmark, 2011). Goodmark has a quality assurance policy and has since received several quality certifications in the industry. Finally, it has a huge market share. Currently it serves both domestic and international customers in Japan and Thailand.
Weaknesses:
The weaknesses of the firm are as follows. Goodmark’s market base (80%) is mainly composed of foreign owned firms and the export market (Goodmark, 2011). This means that it is losing money by failing to serve the Chinese owned companies. It has complex hierarchical management system. This leads to inefficiency by slowing the process of making decisions.
Opportunities:
The opportunities available to Goodmark include the following. The economic growth means that the company can easily find new markets for its products. As it joins new markets, its profits are likely to increase (Porter, 2000, pp. 1-8). The strong economic growth in China, Japan, Thailand and Malaysia (Goodmark’s main markets) translates into a high demand for the company’s products. Due to the integration of Asian economies, the emerging technologies in countries such as Japan are readily available to Goodmark. Thus it can adopt the new technologies and increase its production.
Threats:
The threats facing Goodmark include the following. There is high regulation in the industry since manufacturing plastic products involves a significant pollution to the environment. Thus, Goodmark has to spend more of its resources in complying with environmental regulations (Boyes and Melvin, 2007, p 101). The threat of substitute products is also very high. For example, the plastic chairs made by the company are facing intense competition from those made of wood. Finally, the threat of new entrants is high. Consequently, Goodmark is likely to lose part of its market share as more firms join the industry.
Strategies Adopted by Goodmark
According to Porter’s generic strategies, Goodmark is following a differentiation strategy focusing on producing goods and services with unique attributes. Consequently, the goods are valued by buyers and considered to be superior or different from those produced by competitors. The differentiation strategy has been adopted by Goodmark due to the following reasons. First, it is able to benefit from reliable scientific research. The firm not only benefits from its own research and development initiatives but also access the findings of research works conducted in other countries such as Japan. By utilizing the advanced production technology resulting from research and development, the firm has been able to produce high quality products.
Second, Goodmark has highly skilled and talented professionals who are able to design and produce high quality products. Third, the firm’s customer-oriented culture has enabled it to develop a strong sales team which is capable of convincing customers about the high quality of the products. Finally, Goodmark has “a corporate reputation for quality and innovation” (Goodmark, 2011). In order to maintain its image, the firm has to continue focusing on producing goods that are superior in the industry through both product and process innovation. (Please note that Porter’s generic strategies are further discussed later in this paper).
Strategic Planning
Currently, Goodmark is using the strategic fit approach to formulate and implement its strategy. The first thing that comes to mind is the business idea. Then the management thinks about the purpose and the advantages of the business that they are planning to start. Then the customers are identified. The approach involves aligning customers’ needs with the strengths of the company (Skrt et al, 2004, pp. 107-122). Consequently, Goodmark’s management usually conducts research on customers’ needs alongside the company’s internal strengths. This enables the firm to develop products that meet the needs of the customers. The greater task challenging the management of Goodmark is how to reach the customers or the market. Once the market is identified, the management figures out the trends and factors that might have an impact on the business. The process ends with the implementation of all these aforementioned steps.
The weakness of the strategic fit approach can be eliminated by adopting a strategic foresight approach. It involves envisioning what customers will need in future and how such needs can be satisfied. Its main strength is that it helps the firm to identify new markets and new products (Sadler et al, 2008, p. 147). The main problem with the strategic foresight approach is that the firm might not be able to correctly predict customers’ future needs. However, Goodmark can address this problem through research on customers’ needs and industry dynamics. In any sort of business, a good rapport or relation with the customers is a must. The management should always welcome any complaints or suggestions from the customers.
The same should be carefully examined. This is the public participation. In fact addressing to the complaints and accepting the suggestions is a sort of development to the business. There are many ideas which the management might not have but the same can be had from the public. Another option to improve the profitability might be to reduce the variable expenses or costs. In order to have a substantive growth, Goodmark has to decide the profit it wants to make within the next financial year, and of course the sales required for such profits. The company should allot targets to its sales professionals and increase the staff if need be. The profits made will be more than the salaries paid to the increased staff.
Strategic Plan
Following are the illustrations of a typical business plan that should be followed in any sort of business, whether big or small and a business development relationship.
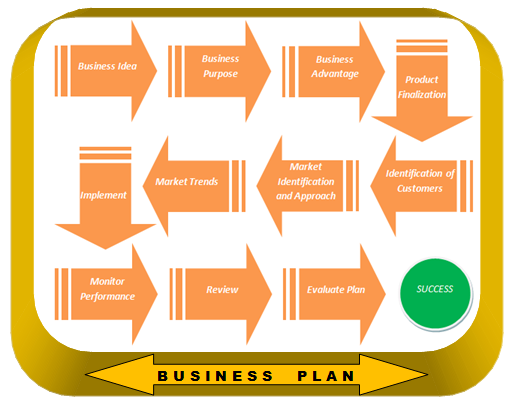
With regard to Goodmark Industrial Limited, the business plan is based on the aforementioned basic plan. As per the company’s mission statement, the main idea and purpose behind the business is to create unique products so that it can have a competitive edge over its competitors. The advantage that Goodmark has is the expertise in moulding of fine and precisely designed products. Once the mould is ready, it is compared by experts with the original product. Deviations, if any, are corrected prior to going for actual production. A final check is done after the corrections have been made. Goodmark has its own set customers who are satisfied and confident about having perfect products in future as well. In order to increase its customer database, the company is always on the lookout for new customers. Such customers either come directly to the company, due to mouth publicity from the existing customers, or the marketing team approaches them with the company profile and references of satisfied customers.
The company is very alert as far as the market trend is concerned. There are new companies that enter the market with similar products. The company wants to be aware of such companies, their products and prices being offered. Even though such companies keep on coming and vanishing, but there are some companies that can pose a threat to Goodmark and as such, the company always adheres to its policy of uniqueness. Goodmarks research and development department is always on the move in improving the quality of its products. Presently, the main task for the R&D department of Goodmark is to develop some substitute for plastic. Plastic is the main raw material of the company. Since plastic is a major source of environmental pollution, the company, in adhering to the international environmental specifications, wants to develop some substitute for plastic so that it can contribute to the environmental protection. Once the substitute is developed, it will be a major break-through in the world of moulding and Goodmark can benefit from the patent rights.
The market performance of the company is frequently monitored and any steps that are considered necessary are taken to improve the performance.
Alternative & Future Strategy
In order to formulate future marketing strategies Goodmark should follow the Ansoff Growth Matrix strategy. It is based on the principle that the growth of a business depends on the kind of product (new or existing) that it markets and the kind of market (new or existing) in which it markets its products. Following is a diagrammatic description of Ansoff Growth Matrix:
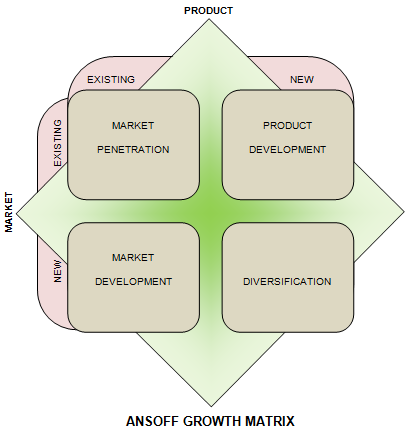
As is evident from the above diagram, there are four strategies that are adopted in Ansoff Growth Matrix:
- Market Development: Under this strategy, the business lays stress on marketing existing products in fresh markets.
- Market Penetration: Under this strategy, the business lays stress on marketing existing products in existing markets.
- Product Development: Under this strategy, the business lays stress on marketing fresh products in existing markets.
- Diversification: Under this strategy, fresh products are marketed in fresh markets.
In order to sustain its market share, Goodmark follows market penetration, market development and product development. The company has stringent marketing strategies such as reasonable pricing, advertising, promotion, etc. Goodmark’s prices are such that other companies cannot compete. The motive of Goodmark’s R&D is to device new products that are better than the existing ones. Goodmark is also trying to invent some substitute for plastic that will be eco-friendly and economical.
Goodmark is aware of the high risk involved in such circumstances and as such, is very particular about having knowledge of its competitors’ products. Goodmark also considers the other external factors like political, economical, social, technological, and legal factors that may affect its business in new markets. Goodmark doesn’t encourage the diversification strategy since it involves a lot of risk. In earlier strategies, either both the market and the product are known or one of them is known. But in diversification, both are new and as such it will be a gamble to introduce new products in new markets. The company doesn’t know what kind of market it will be and the customers don’t know what kind of a product it will be.
Apart from the aforementioned strategy, the company management has to lay stress on the most important aspect i.e., the development of a new product (substitute) because:
- Quality wise the products are at par with the best. But the price has to be reduced if Goodmark wants to retain its existing customers and garner new ones.
- Due to the incessant competition, Goodmark has to focus on the quality and pricing of its products.
- For reducing price, Goodmark should either reduce the overhead costs or find some cheap raw material. The quality of the raw material should not be compromised while looking for a cheaper source of raw material.
- A substitute for plastic can also be invented. This will serve a dual purpose of being eco-friendly as well as saving on the cost of raw material.
Realization of Strategy Implementation
Before the implementation of any strategy, a company should analyse the strategy to be followed. The analysis can be done by various proven methods like the PESTEL analysis, the SWOT analysis, the Five Forces analysis, Market Segmentation, Directional Policy Matrix, Competitor analysis, or Critical Success Factor analysis.
The management should then understand the stakeholders’ expectations, identify the strategic options and evaluate and select the appropriate strategic options.
Once the strategy is analysed and selected, the implementation part comes. This is the most important and vital part of the process.
The following simple illustration shows the three main factors of strategic management mechanism.
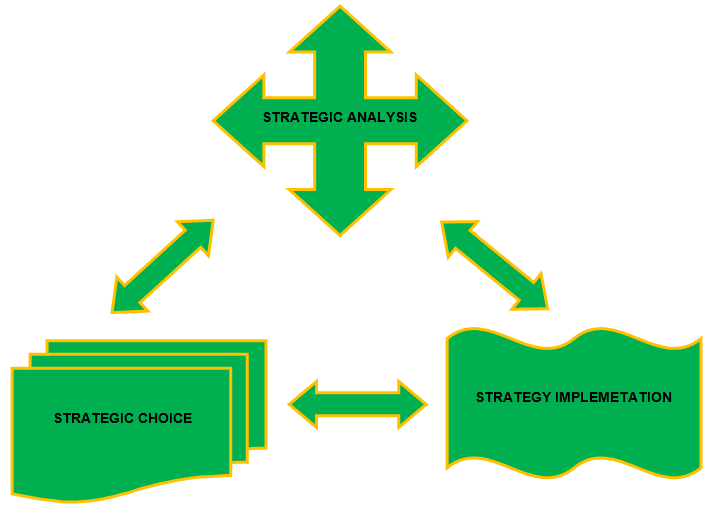
There are certain basic requirements for the realization of the strategic implementation. Following are the main elements:
- Execution of the strategy is another important element of strategic implementation. The strategy should be executed in such a manner that all the employees have a part to play in the execution. Resources required for the execution should be put in place prior to the execution. People should be given responsibilities and should be deemed answerable for any lapse in the execution.
- An efficient leader: In order to keep the efforts of the masses concentrated in one direction i.e. achieving the goal, an efficient leader is a must. Without a leader, the efforts of the employees will be scattered and the motive will not be achieved. An efficient leader will have the motivation injected in the employees and they will work as a team and teamed efforts seldom fail.
- Even if both the aforementioned points are adhered to, a third element, ‘Performance Management’, will be required to complete the circle of achieving the aims. Having Performance Management means to have a control on the performance of departments and individuals. Proper communication is a must in performance management. The concerned department or individual should be properly conveyed the expectations. Targets should be given to departments or individuals. Proper monitoring should be done whether the departments or individuals are performing up to the desired level or not.
The best way to judge the realization of the strategic implementation is to monitor the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). The management should keep an eye on whether the Key Performance Indicators are being met or whether the employees are working towards meeting the requirements of the Key Performance Indicators. But prior to this, it should be ensured that the employees are well aware of the company’s mission and vision statements.
Comparison of goals and objectives of two companies
Following are Goodmark’s roles and responsibilities:
Roles
- To expand the company’s operations in the region.
- To reduce environmental pollution by trying to develop substitute for plastic.
- To introduce new and better products in the market.
- To increase the company’s profitability.
Responsibilities
- To increase the company’s market share by 25% in the next four years.
- To reduce the green house gas emission by 30% in the next three years.
- To increase the company’s product portfolio by 15% in the next two years.
- To increase the company’s profitability by 20% in the next three years.
Following are the roles and responsibilities of M. C. Tietz Plastics, Inc.:
Roles
- To manufacture products according to the specifications.
- To adhere to the requirements of ISO 9001:2000.
- To achieve customer satisfaction.
- To reduce contamination and hence contribute in safeguarding the environment.
- To work towards the growth of the company.
Responsibilities
- To keep the prices competitive.
- To deliver custom moulded thermostat plastic parts to customers.
- To maintain proactive customer focus and communication.
- To maintain good working relationship with customers (Source: M.C. Tietz, 2005).
Analysing the roles and responsibilities of these two companies, it is clear that both the companies are committed to the preservation of the environment. Since plastic is a hazardous product and is not bio-degradable, both the companies take proper precautions so as not to contaminate the environment. Customer satisfaction is of utmost importance to both the companies. By making environment friendly products, the companies will be indirectly helping the people in having a cleaner atmosphere. In all the actions that these companies do, the main goal is the overall progress.
Resource Requirements
In order to implement the new strategy, Goodmark will have to employ various new resources for a successful implementation.
Marketing:
- The company should have a separate department for the complaints and suggestions from the customers.
- In order to sustain the competition in existing markets, Goodmark needs some people to be assigned the task of gathering information on competitors
- In new markets, the company needs to distribute (up to a certain extent) free samples of its existing products so that people have the confidence in Goodmark products.
- If the company wants to launch new products, then also some samples have to be distributed in order to have the customers’ feedback.
Human Resources:
- Proper training of employees should be arranged frequently. This will help the employees to keep up with the pace of new technological devices and software.
- The company will have to employ more staff to carry out all these works.
- For new markets, it is advisable to employ old and experienced staff personnel to carry out the marketing.
Operations:
- The company frequently reviews its policies and makes amendments if necessary.
- The management of Goodmark is always on the look-out for reducing the cost of its products.
- The prices are evaluated at regular intervals.
- Relations with old customers are revived.
- The employees are kept involved and their feedbacks are sincerely studied and implied if necessary.
- The company explores new markets and products in order to expand its business.
Finance:
- The finances are managed well by the company.
- Effective stock holding policies should also be formulated to avoid shortage of materials during the implementation process.
Research & Development:
- A separate budget will have to be allocated for this purpose. The R&D staff will have to be paid salary even though they won’t be participating in the revenue generation for the company. Also, money shall be required for materials required for developing the new product (substitute).
- In order to find a substitute for plastic, the company will need more people in the R&D department. These people will be engaged in the research for new product (substitute) and at the same time, after the product has been developed, will have to engage in the testing the viability of the new product. Such people will not be able to concentrate on any other work. Hence the management should be ready for this.
- The management of Goodmark should be patient as the development of a new product will take time. As per assumptions, it will require at least one year for the new product development.
Besides, the management should be in a position to equip the employees with the skills needed during the implementation stage (Linnenluecke et al, 2010, pp. 357-366). For example, regular staff training can help in improving employees’ skills. Third, materials are needed in order to implement a new strategy (Lichtenthaler, 2011, pp. 317-330).
Use of Targets and Timescales to Measure the Effectiveness of Strategy
Strategic plans are based on objectives which act as benchmarks for assessing the effectiveness of the strategy (Huang, 2011, pp. 641-653). The main objective of Goodmark is adhering to the international environmental standards. These standards require the company to minimise the use of plastic since it is a hazardous product. Goodmark can set a time period of one year to develop a substitute for plastic. This much period will be sufficient for the scientists employed by Goodmark to come up with a substitute. Goodmark can set a target of increasing its market share by 15%.
Thus the strategy will be the parameter used to measure the effectiveness of the strategy (Gimbert et al, 2010, pp. 477-497). Best practice in strategic planning requires all objectives and targets to be achieved within a specific time. For example, Goodmark’s target of increasing its market share by 15% can be achieved within 3 years. Thus the timeline (3 years) will be the parameter used to measure the effectiveness of the strategy. In conclusion, a strategy is effective if the targets associated with it are achieved within the set timeline.
Moreover, the prices are set keeping in mind the time factor and also the target to be achieved. If both the factors are not achieved, it means the company was not able to successfully complete the strategy. Prices are formulated by the formula of – more quantity less price. So if the set target is not achieved, it means lesser quantities have been sold for lesser value. This may, sometimes, amount to losses. So achieving the targets in the given time frame is very crucial to any organization.
References
Advameg 2012, Pollution Issues – Plastic. Web.
Boyes, W & Melvin, M 2007, Microeconomics, Cengage Learning, New York.
Briefcasebooks n.d., What is Business Strategy?. Web.
Bryson, J 2004, Strategic Planning for Public and Non-profit Organization, John Willey, New York.
CBI 1990, Narrowing the Gap: Environmental Auditing Guidelines for Businesses, CBI, London.
Chinadaily 2005, Guangdong Becomes Most Populous Province. Web.
Dess, G 2010, Strategic Management, McGraw-Hill, New York.
English 2010, GDP of 31 Provinces in China Released. Web.
Gimbert, X, Bisbe, J & Mendoza, X 2010, The Role of Performance Management Systems in Strategy Formulation, Long Range Planning, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 477-497.
Goodmark 2011, About Goodmark. Web.
Goodmark-new n.d., Enterprise Synopsis. Web.
Hollensen, S 2010, Marketing Management, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Huang, C 2011, Corporate Governance, Corporate Social Responsibility and Corporate Performance, Journal of Management and Organization, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 641-653.
Lichtenthaler, U 2011, Outbound Open Innovation and its Effects on Firm Performance, R&D Management Journal, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 317-330.
Linnenluecke, M & Griffiths, A 2010, Corporate Sustainability and Organizational Culture, Journal of World Business, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 357-366.
Mayhew, B 2009, Mission Statement & Vision Statement Definition and Purpose. Web.
M.C.Tietz, 2005. M.C. Tietz Plastics, Inc. Web.
Mindtools n.d., Mission Statements and Vision Statements. Web.
Petrescue 2010, The Strategic Planning within the Producing Road Vehicles, Annals of University of Craiova: Economic Series, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 476-482.
Porter, M 1996, What is Strategy? Harvard Business Review, vol. 1, no. 1, pp.61-78.
Sadler, P & Craig, J 2008, Strategic Management, Kogan Page, New York.
Skrt, B & Antorcic, B 2004, Strategic Planning and Small Firm Growth, Managing Global Transition, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 107-122.
Tutor2u n.d., Core competences. Web.