Introduction
Physical activity is one of the critical components of people’s lives enabling individuals to remain healthy for a longer period. The heart rate of an exercising person is accelerating as muscles need more oxygen. Good health is associated with lower heart rate during exercise and longer endurance, which is referred to as cardiorespiratory endurance. This type of endurance is an important element of a person’s fitness, as it is a predictor of reduced risk of pulmonary and cardiovascular disease development (Lyons et al., 2020). Therefore, workouts aimed at improving this capacity are a part of the exercise for many.
Problem
Although physical activity is beneficial for all people, some individuals may have certain conditions that require specific attention to the intensity of their exercise. The more intensive exercise is, the higher the heart rate becomes. It has been acknowledged that rope jumping is a strenuous physical activity linked to a considerable increase in heart rate (Lyons et al., 2020). Some people may feel worse if they overload their cardiovascular system or can even have serious health issues (such as heart attack). Hence, it is necessary to choose the right load to improve one’s health without excessive exercise.
Materials and Hypothesis
In order to conduct the experiment and collect the data, the heart rate monitor watch Willful Smart Watch was utilized. The participants wore the watch before, during, and after a set of activities. Comfortable sports apparel and footwear were needed for the participants. It is hypothesized that the heart rate is higher after walking, with an increasing rate after running, and the highest rate after repetitive jumping. So, if the person chooses to perform repetitive jumping, then they experience the highest acceleration of the heart rate, while walking is a less intensive activity.
Procedure
In order to implement the experiment, three participants perform a set of exercises with measurements before and after the activity. Each activity will last 30 seconds, and the rest time between the exercise will be five minutes.
Data Table
Table 1: Heart Rate After Different Types of Exercise
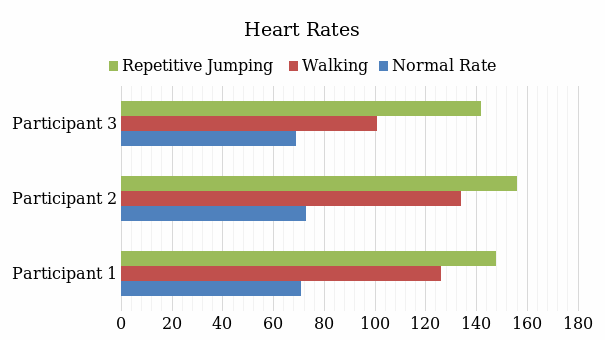
The findings suggest that the hypothesis is checked, and the heart rate increases with the intensification of exercise (see Table 1). Repetitive jumping is the most intensive activity leading to the highest increase (see Figure 1). All participants had approximately 50% acceleration of their heart rate (with normal rate and the one after repetitive jumping compared).
Analysis
The participants were young adult males aged between 20 and 23 years old (mean age was 21,7 years old). The dependent variable was the heart rate, while the independent variable was the three types of physical activity. The major factor affecting the results could be the physical condition of the participants. The controls of this experiment included the simultaneous performance of activities (the same time of a day) and the focus on the intensity of the participants’ exercise. The participants were non-smokers with no health conditions that could affect the results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is possible to state that the hypothesis is supported by the obtained findings. Repetitive jumping is the most intensive type of exercise associated with the highest heart rate compared to walking or rest. The experiment contributes to the understanding of the exact ways different types of physical activity influence heart rate. At that, the implementation of the laboratory experiment could be improved. It could be beneficial to use a more reliable heart rate monitor device such as a blood pressure monitor. It is also necessary to involve a larger sample to obtain more generalizable and valid data.
Reference
Lyons, T., Navalta, J. W., Stone, W. J., Arnett, S. W., Schafer, M. A., & Igaune, L. (2020). Evaluation of repetitive jumping intensity on the Digi-Jump machine. International Journal of Exercise Science, 13(2), 818-825.