Executive Summary
This research has been conducted as analytical analysis of Pret a Manger, the company that is going to prove the importance of changes that could contradict the visions of the company, and British Airways, the company that introduces a powerful example of how an organisation should implement changes and explain them to employees and customers. The challenges the chosen companies face demonstrate the importance of the identification of internal and external factors. The analysis shows that the size and the direction of a company may not matter in case the importance of change is underlined.
A brief overview of two different industries is offered in order to explain the positions of the companies and their opportunities in regards to the possibilities and goals of other companies in the same spheres.
The analysis of the models and the recommendations given helps to understand that both companies have enough powers and opportunities to promote changes and improve their work in a variety of ways.
In general, the models of management, the ideas of how to introduce and develop changes, and the necessity to make people informed about the intentions to change something in the already established system are properly explained in the project and help to create a transfer of learning of the two case studies devoted to Pret a Manger and British Airlines.
Chapter 1: Introduction and Project Background
Introduction
The business world changes quickly today. People have to deal with a number of new requirements and needs, make fast decisions, and clarify what kinds of innovations are appropriate and effective for them. Companies have to stay competitive and consider such issues as personal and public values, security, satisfaction, and sustainable development (Reiss 2012).
People want to choose correct strategies, define their integration, and succeed in organisational change management, project management, and leadership (Hornstein 2015). Leaders should think about their possibilities and the abilities of their company. According to Cameron and Green (2015), leaders have to deal with a number of paradoxes in their jobs including the necessity to build close relations with employees and keep the required suitable distance at the same time or the importance to stay diplomatic in all situations but also know how to express a personal point of view.
With increased dynamics and the development of international relations, many companies want to use their best services and make the choices that bring a lot of benefits. Still, the majority of organisational issues are complicated in their nature. Leaders have to be ready to understand what should be done and when and make the decisions that are beneficial for them, their employees, and their companies. The example of Pret a Manger shows how good and bad decisions could be made within one company and what steps should be taken to overcome the challenges.
Project Background
Since the development of fast food industry and the opportunities for customers, a number of companies in the restaurant business re-define its standards and try to invent new ideas to impress people and take leading positions in the market.
Customers do not want to spend their time and wait for some services in queues. They expect to have a good portion of services, enjoy the products offer, and feel comfortable when they communicate with the company’s representatives. Though a number of researchers admit that much depends on a team and the way of how people cooperate, it is also necessary to underline the role of a leader and their possibilities to organise people and explain what goals should be achieved (Gell 2014). The history of Pret a Manger, one of the famous chains of sandwich shops in London, tells a lot about the methods and tactics developed by its leaders.
Pret a Manger was founded by Julian Metcalfe and Sinclair Beecham in 1986. The main reason for why they wanted to create a new organisation was the inability to find a place where “proper sandwiches” could be found (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012). They tried to focus on the quality of food and choose all ingredients properly. It should not be another fast-food shop. It should be the company that appreciated its chance to provide people with high-quality services. Pret a Manger created new standards for fast food organisations in several years.
Project Problems
In this project, several problems Pret a Manger should find the solutions for can be identified. Each of them has its ground and explanation. These problems are based on internal and external issues.
Organisational Behaviour Problem
Pret a Manger struggled to open a new line of shops that was called “twin shops”. Therefore, a number of effective and clear steps are required to prove that this new concept could not contradict the main idea of Pret a Manger that was to prepare food at shops where it was sold.
Quality Management Problem
The idea to open new twin shops could put the quality of food and services under a question and make people think about the difference between Pret a Manger and other fast food shops.
Human Resource Management Problem
Pret a Manger worried that the idea of twin shops could influence the connection between employees and their further abilities to communicate with customers and offer the services in the same way.
Innovation Problem
The presence of “twin shops” made the company think about the necessity of trucks or other transportation means.
Business Model Problem
The company realised that the growth of shops promoted some alterations to be made to its business model. Still, it was difficult for the company to understand what modifications were appropriate.
Project Questions
Organisational Behaviour Management Question
What are the factors and behavioural changes that make Pret a Manger being confident that they can open a new line of shops?
Quality Management Question
How could “twin shops” change the work of Pret Manger stores?
Human Resource Management Question
How could the removal of the manufacturing element influence the work of the company and change the attitudes of employees to their duties and responsibilities?
Innovation Question
How much money should be spent on the development of transportation issues?
Business Model Question
Could a new business model or some improvements to the model change the concepts of a company and violate the element that made the company as it was?
Project Aim
The aim of the project is to describe, evaluate, analyse, and compare organisational changes in two different companies and understand what recommendations could be given to the companies and their leaders, in particular, to solve the challenges, promote the development, and improve the quality of services customers expect to get.
Project Objectives
To present a list of recommendations and make sure that the situations in the companies could be changed for better, several objectives should be established in regards to the questions and problems raised above.
Organisational Behaviour Management Objective
To clarify the behavioural factors and requirements that should be taken into consideration when companies want to promote changes and involve a number of people in these improvements.
Quality Management Objective
To determine the extent to which it is possible to change the work of the company and the system under which a number of employees have been working for a long period of time.
Human Resource Management Objective
To evaluate how organisational changes, both improvements and challenges, could influence the work of people and their employees’ satisfaction with their working conditions.
Innovation Objective
To understand what kind of improvements could be offered by the company in regards to the abilities and resources available.
Business Model Objective
To investigate the ways of how changes could be implemented and explained to employees and customers.
Significant of the Project
This case proves that the success of the company depends on the qualities and abilities of their leaders (Smith et al. 2014). On the one hand, changes promote the development of a company (Vukotich 2011) and make people work hard to achieve the best results and benefits. On the other hand, the examples show that not all decisions and changes are always appropriate for companies.
Therefore, change management in public organisations is an integral part of a working process that could gain forms of planned improvements and emergent approaches (Voet 2013). Competent managers and leaders have to be confident in the importance of change and identify enough reasons for making new steps and developing new strategies that could touch the work of all employees, the choices of all customers, and the needs of the whole company (Hayes 2014).
Project Structure
The project is divided into several sections with each of them has its purpose and impact on the understanding of the topic.
Chapter 1: the introduction to the case and the explanation of the project’s aim, research questions, objectives, problems, and the significance of the work are given.
Chapter 2: the description of the case study where the questions of organisational change and leadership are discussed.
Chapter 3: the statement of the main problem in the case study, the plan of analysis, and the identification of the theoretical frameworks are offered.
Chapter 4: the analysis and evaluation of findings and techniques used by the company are introduced.
Chapter 5: a list of recommendations and limitations in regards to the company are offered.
Chapter 6: the analysis of British Airways as the company that showed how to succeed in change management is offered on the basis of the already done work and findings


History of the Company
Pret a Manger was founded by Metcalfe and Beecham in 1986. The main reason for why they wanted to create a company was the inability to find a place with “proper sandwiches” (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012). They tried to focus on the quality of food. It should not be another fast-food shop. They wanted to introduce a shop where certain respect and attention to customers were paid. Metcalfe and Beecham borrowed £17,000 from a bank to buy the name of the company, open their first shop, and hire motivated and friendly staff.
Certain financial difficulties occurred at the end of the 1990s and at the beginning of the 2000s because of the politics of its new CEO, Andrew Rolfe. He wanted to expand the company domestically and internationally to enter the market of the USA and Japan. Pret a Manger was not able to compete with other famous international organisations at the global level and lost its uniqueness as a friendly and food of high-quality shop. Pret a Manger had to make some changes, and the solution to fire the current CEO and invite Clive Schlee to perform the functions of the company’s CEO was made.
Competitive Advantages
Four competitive advantages including the attention to the quality of food, recognition of customers, location of shops, and successful employee management were identified (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012).
Food Quality
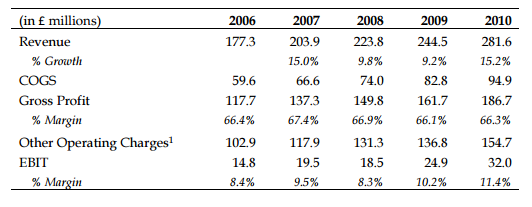
Pret a Manger identified its production and introduced it to its customers. At first, sandwiches were the only product available to customers. With time, the chain was enlarged, and customers could also order coffee, salads, soups, and pastries (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012). The vision of the company was the idea that health could not be sacrificed.
In every shop, there was a kitchen, and the company was able to maximise the freshness of food offered to people. In comparison to other fast-food shops where kitchens were centralised, Pret a Manger was not able to minimise its food preparation costs. Still, it was not the goal of the company. Schlee convinced its stakeholders that a person could have a unique attitude to selling the food that was prepared independently. The results were impressive and reflected on the income statements of the company.
Customers
The cooperation with customers and the quality of services Pret a Manger offered to people is one of the key features of the company. For example, the regulars of the shop could count on free coffee or pastries. Every customer should be provided with the required service in no more than 60 seconds because people visit the shop not to wait but eat.
Several Pret Manger shops have more than five managers. The possibility of communication between customers and its CEO is possible. Such an attitude to customers attracted many people because they wanted to be a part of a team that offer its services. Nowadays, customers are free to leave their responses, share their opinions, and introduce their suggestions about changes they want to see in the company.
Shops
Shop locations and appearances play an important role in the company as well. Natural lights attract the attention of people. Each shop is located not far from each other. At the same time, shops do not cannibalise each other and co-exist peacefully (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012).
Employees
Employees should not be trained to be hired. Potential employees are welcome to demonstrate their personal approaches to work with customers. They have to be friendly and sensitive to customers’ needs. There is no place for a bad mood or rude behaviour. All promotions and approvals for employees are introduced in the form of a game.
The leaders of the company believe that if employees like what they do and can use their potential and abilities to their full extent, the results of such work could be impressive indeed. Bonuses are the priorities for employees. Pret a Manger’s employees should be ready to make hundreds of decisions per day and earn bonuses. Besides, the establishment of organisational culture is an important part of Pret a Manger. Socialisation and parties are supported by all members of the Pret a Manger team on the basis of the achievements demonstrated in a certain period.
Assumptions
From the case study offered by Frei, Goldberg and Sice, the following assumptions could be given:
- Pret a Manger does not want to stop;
- Pret a Manger is a good example of how change management should be organised;
- No biases to stakeholders, leaders, and managers are observed.
Chapter 3: Problem Statement and Plan of Analysis
Problem Statement and Plan of Analysis
The evaluation of the data offered in the case study helps to identify the main challenges a company could face in case some changes and improvements could be offered and introduce the main benefits and strengths of the company like Pret a Manger. The authors of the case study focused on the circumstances under which Pret a Manger made its decisions and support changes and the problems that should be solved using the potential of the company and the resources available. With the intention to prove the worth and importance of twin shops, there are a number of problems and challenges that have to be identified.
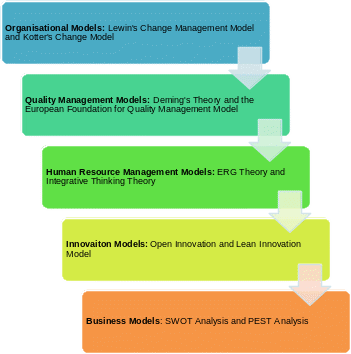
The organisational and behavioural issues of the company could be discussed within the frames of several organisational models such as Lewin’s change management model and Kotter’s change model, quality management models including Deming’s theory and EFQM model, and HR management models such as ERG theory and integrative thinking theory. Finally, business issues that have been raised in Pret a Manger could be solved with the help of the innovation models like open innovation and lean innovation and general business models including SWOT and PEST analyses.
Every theory and every model are based on the necessity to find a solution to the problems stated in the first chapter. There are five main issues for consideration in this case study. Each group of problems introduces the necessity to think about the alternatives or the methods on how to improve the situation: organisational behaviour problems, quality management problems, HR management problems, innovation problems, and business model importance.
Organisational Behaviour Problems
Lewin’s Change Management Model
Pret a Manger is a customer-centred company with an intention to address all people, who visit shops, with sincerity and passion. Its leaders understand that not all companies, fast-food shops, and even restaurants have the same goals. Therefore, the company struggles to introduce the services that could impress customers and prove that its employees have a number of ideas to be developed. It means that some changes should occur in the company.
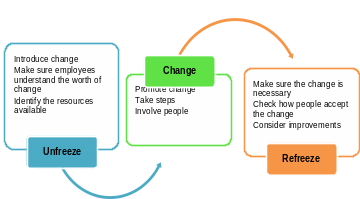
Lewin’s theory is one of the tactical models that could be offered to the company. This model consists of three stages in the frames of which change is compared with an ice block for people to unfreeze, change, and refreeze (Paton & McCalman 2008). The usage of this model is beneficial for Pret a Manger because it is one of the simplest ways to introduce, make, and understand change (Cameron & Green 2015).
Kotter’s Change Model
Kotter’s eight phases of change is another tactical model that could be used by Pret a Manger to succeed in implementing the idea of “twin shops” (Assen, Berg & Pietersma 2009). The peculiar feature of this model is the possibility to take small steps, make sure all of them are successful, and stop the process in case some stage cannot be completed.
It could be applied to the companies of different sizes and cultures (Kotter & Cohen 2013) and help leaders to avoid mistakes and continue developing an organisational culture (Rothwell et al. 2009). The following steps and decisions should be taken and made to understand if Pret a Manger is ready for “twin shops” and the challenges the change could lead to.

Quality Management Problems
Deming’s Theory
Deming’s theory is one of the models that could be used by the company to improve its management and quality control over all steps taken and the decisions made. There are four main points that should be considered and understood by leaders and managers. They include system appreciation (when employees and leaders have to understand the ways of how the whole system works), variation knowledge (when people should realise their opportunities), knowledge theory (when people comprehend what they should know), and psychology knowledge (when people use a certain portion of knowledge to understand human nature and its peculiarities) (Pyzdek & Keller 2012).
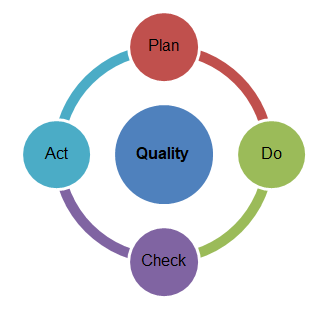
If all these points are considered by people, they get all chances to demonstrate high-quality work and results (Aguayo 2010). In addition to the system of profound knowledge developed by Deming, there is also a clear guide on how to implement improvements and take the steps that bring some benefits to the company. The following example shows how to use Deming’s cycle in business and make an improvement complete, planned, and measured:
European Foundation for Quality Management Model
European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) model is one of the recognised brands worldwide (Stimpfle 2011).
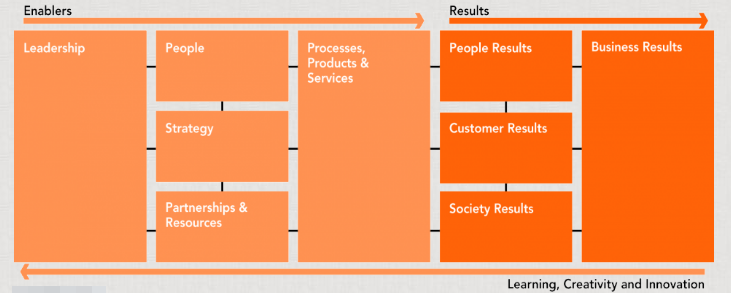
It helps to achieve good results in quality management by identifying a number of criteria according to which people should work, make decisions, strive for changes, and consider its own visions, missions, and values. There are nine criteria that are divided into two main groups, “enablers” and “results” (Chapman 2014). The main benefit of this model is that it could be applied to any organisation by using as many concepts as possible and identifying the required portion of knowledge (EFQM: model criteria 2012).
Human Resource Management Problems
ERG Theory
The concept of motivation is crucial for any company’s work. It is not for employees to get orders and do everything possible to meet the established goals. It is necessary to stay motivated, consider personal and professional needs, and take the steps with desire and readiness (Koontz & Weihrich 2006).
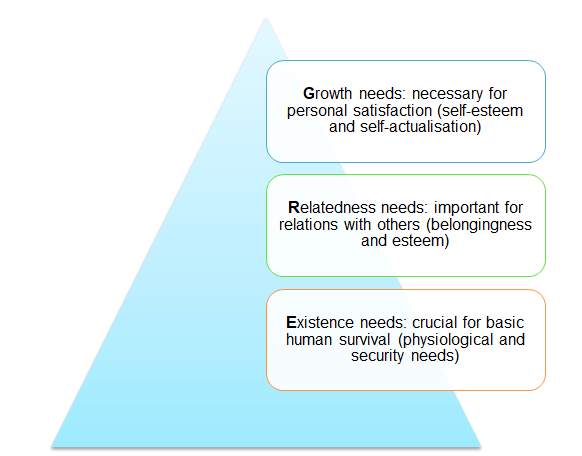
Alderfer, the developer of ERG theory, supports the idea that all people have needs, and these needs could be of different types. Still, despite its variety, all of them are arranged in a certain hierarchy that cannot be neglected (Aswathappa 2005). In comparison to Maslow’s theory with five stages identified (Griffin & Moorhead 2011), Alderfer introduces three categories the consideration of which is important in the work of any organisation.
According to this model, several types of needs could motivate people at the same time. Alderfer admits that the identification of the components cannot be neglected because people should understand if their needs and the consideration of these needs could lead to satisfaction, frustration, progression, or regression (Nelson & Quick 2014).
Integrative Thinking Theory
In the company, people have to understand their opportunities and duties. It is not enough to accept the changes as something integral and required. It is important to comprehend why leaders want changes to be applied.
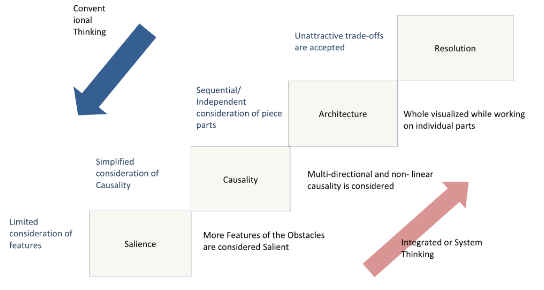
Integrated thinking is the theory developed by Martin and introduced as the process with the help of which it was possible to avoid tensions and find the solutions, not by means of choosing one best option but generating creative resolutions and combine the ideas (Uppal & Rahman 2013). There are four main steps that should be taken to clarify if the work of people is presented at a high level and if there is a need for some improvements.
Innovation Problems
Open Innovation Model
Innovation is the process that includes search and selection of the best ideas, exploration and synthesis of steps, and thinking as the convergence of outcomes that could be expected (Rogers 2010).
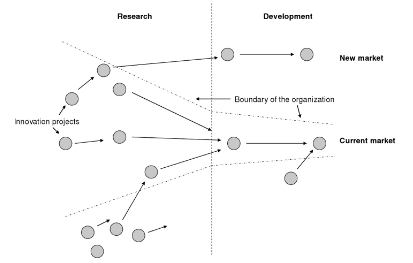
Chesbrough offered the Open Innovation model as an opportunity to understand what kind of general knowledge should be mobilised and generated into a new dynamic that promoted innovation processes (Benezech 2012).
Lean Innovation Model
Innovation is a concept that cannot be ignored by the company. People, who offer the services, should be ready for innovations and help other stakeholders explain the worth and need for improvements. Therefore, it is important to follow a certain order of the steps.
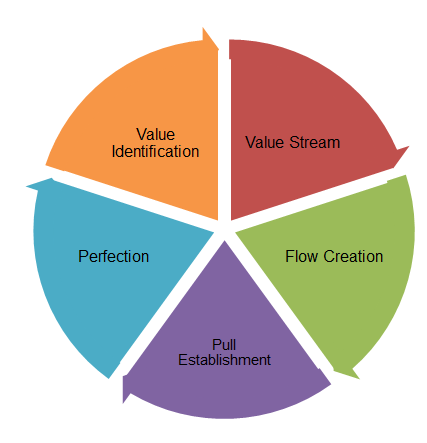
Lean innovation is the model with the help of which companies achieve the required results in a fast way by means of efficient learning available to its employees and leaders (Agan 2014). Sehested and Sonnenberg (2010) admit that it is important to focus on the innovation process and learn as much as possible in order to implement a system for the required process improvements. There are five main stages that should be taken into consideration: the specification of value, the identification of value stream, the evaluation of interruptions in value flow, the necessity to pull value, and the promotion of perfection again (Al-Hakim et al. 2016).
Business Model Problems
SWOT Analysis
The necessity to introduce a new approach in selling food requires the evaluation of various internal and external factors. The company should be ready to clarify what changes are appropriate, what decisions are effective, and what outcomes could be expected.
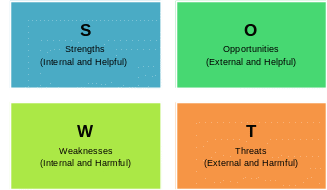
The SWOT analysis is one of the frequently used marketing tools with the help of which values of the companies could be estimated (Ferrell & Hartline 2010). This analysis makes a researcher look at the strengths and weaknesses of a company and identify opportunities and threats of a company (Speth 2015).
PEST Analysis
The consideration of the factors that can influence the work of the whole company is important in the sphere of business. Pret a Manger is the company that focuses on different spheres of business and succeed in the majority of them due to the results the analytics show.
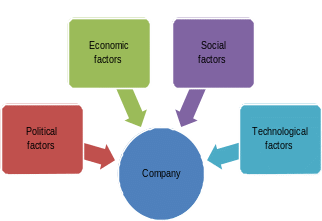
The PEST analysis is the evaluation of political, economic, sociological, and technological factors that could influence the company’s performance and identify its possible development and improvements (Chapman 2011). All these external macro factors affect companies in a number of ways (Blery, Katseli & Tsara 2010), and a researcher has to understand what factors are important for future analysis of a chosen organisation.
Research Details
It is important to understand that any kind of business research should not be organised in a kind of vacuum (Bryman 2008). Wilson (2014) business research is not only a process of enquiry and investigation but the synthesis and collection of knowledge about business-related issues and the peculiarities of decision-making processes.
Therefore, the choice of research methodology should be properly made regarding the philosophical, theoretical, and systematic aspects of the analysis. The success of business research depends on how a researcher could identify the characteristics of a topic, describe ideas, conduct and explain the worth of the literature review, clarify the possible sources of information, create a plan, and introduce several research questions to be answered (Hair et al. 2015).
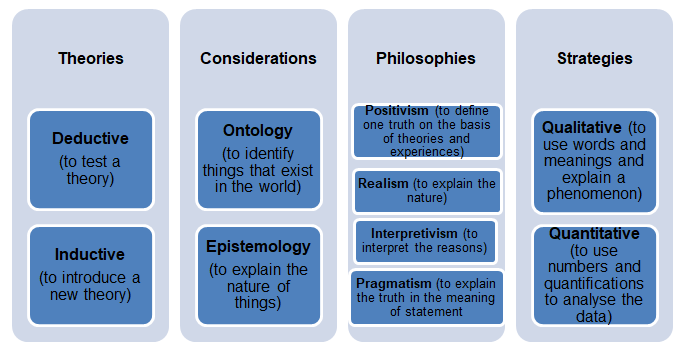
The context of research and its methods may include the following factors: research theories that could be divided onto deductive and inductive, research considerations that could be epistemological and ontological, research philosophies that include positivism, realism, interpretivism, and pragmatism, and research strategies that could be qualitative and quantitative (Creswell 2013).
Ethical Issues
The main problem of the company described in the case study is the inability to understand the importance of change and prove its urgency to the stakeholders. People lack information about twin shops and their effectiveness. The result of such poor distribution of information is the inability of customers to understand how the shops depict the peculiar feature of the line developed by Pret a Manger.
Therefore, ethical considerations should touch upon the necessity to make sure that all participants of change management operations and other stakeholders of the study are provided with clear explanations and definitions to start working on the project. Polonsky and Waller (2014) underline such issues as the necessity to provide participants with anonymity, expose the situations that could provoke mental stress, use special techniques, avoid the cases when participants are involved in research without being aware of the fact and when information is sold. Besides, it is inappropriate to use such methods as deception and coercion and offence participants (Polonsky & Waller 2014).
Research Limitations
Limitations of the research are the outcomes and conditions that could influence the successful performance of the study. Conclusions should be based on the work done and the limitations identified. Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill (2009) offer to use such issues as the size of the sample, the nature of research, or some restrictions based on geographical or cultural diversities and introduce them as the main limitations in business research. Change management is the field that could be limited by a number of aspects, and a researcher has to understand the essence of all limitations.
Chapter Four: Analysis and Findings
Chapter Summary
The main goal of this chapter is to introduce real-life applications of the models and techniques identified in the third chapter of the project. Pret a Manger is the company that should be analysed and investigated. The models should help to understand the case study within the frames of which Pret a Manger is introduced. It is not enough to describe the case study and underline the company’s weak and strong aspects. In this chapter, it is expected to identify the problems and analyse them with the help of models offered. Such practices and experiences can help to make future recommendations, explain the alternatives, and understand if Pret a Manger is able to cope with its main challenge that is based on the necessity to prove the urgency of “twin shops” in the company.
Application of Techniques to Organisational Problems
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Lewin’s Change Management Model
There are three main stages Pret a Manger should be ready to take. The necessity to introduce “twin shops” concept is urgent for the company. Still, it is important to understand that each change has its price and impact on the company. Lewin’s model is one of the earliest models of change planning and management (Cummings and Worley 2014). It seems like Pret a Manger follows the stages identified in the model but, at the same time, neglects some crucial aspects and promotes the appearance of certain constraints.
Unfreezing. Pret a Manger introduces the change and informs about the necessity to implement new “twin shops” in the already existing system. The company also succeeds in identifying the resources that could be used in this change. However, the case study shows that not all Pret employees were enamoured with the offered idea. In other words, not all employees were provided with the required portion of information (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012).
Change. The required number of people were involved in the promotion of a new idea. Pret a Manger identified certain benefits and limitations that were connected with “twin shops”. It means that some steps were taken, people were ready for a change. However, the promotion of change was weak that caused the development of the question if the company was ready for the offered change.
Refreezing. Pret a Manger was not sure it had enough reasons to prove the importance of the change. The evaluation of customers’ attitude showed that the majority of regular customer put the vision of the company under a question and could not accept the fact that the main feature of the company that is the possibility to prepare food at shops had to be neglected.
Findings
- There is a necessity to take a break, distribute information, and make sure that all stakeholders understand the worth of the steps taken.
- Much attention should be paid to the customer’s sector.
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Kotter’s Change Model
Sense of urgency. Pret a Manger wanted to expand its stores and invite many customers.
Guiding coalition. The case study does not identify how many people were involved in the process of change. However, it was mentioned that employees of “twin shops” got additional responsibilities.
Vision and strategy. Pret a Manger underlined its vision connected with the necessity to serve customers fast and offer high-quality food.
Communication of vision and strategy. A new idea changed the vision of the company and frustrated many customers.
Empowerment. Employees realised that their functions and responsibilities had to be changed considerably by the necessity to transfer food at different shops.
Short-term wins. Pret a Manger got more stores where its food could be sold.
Consolidation of gains. Employees suffered from the elimination of connection.
New cultural approach. “Twin shops” had to promote new opportunities for employees and abilities for customers to reach Pret a Manger shops in a short period.
Constraints. Not all customers were informed about the nature of “twin shops”. People wanted to be sure that they could buy food prepared at shops.
Findings
- Explanations matter in Pret a Manger.
- Changes and improvements can be harmful and beneficial for both, customers and employees.
Application of Techniques to Quality Management Problems
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Deming’s Theory
The process of business improvement should follow four main phases that help to understand the current state of affairs, clarify the opportunities, identify the resources and implement changes (Watson 2008).
Plan. An operation manager admitted that new “twin shops” were planned to be opened in great locations that were not large enough to have kitchens within them (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012).
Do. What Pret a Manger did was the introduction of two separate shops where food prepared at one shop was transported to another shop.
Check. The evaluation of customers’ opinions proved that not all people were satisfied with the idea to buy food not prepared at those shops.
Act. No changes were made to solve customers’ discontents. Still, new “twin shops” were opened.
The main constraint was connected with poor evaluation of the opinions and the introduction of new alternatives for customers.
Findings
- Alternatives cannot be ignored in the company because people should understand that they have options and the rights to choose.
- Leaders have to follow a plan according to which evaluation and analysis help to understand the pros and cons of the achievements made.
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using European Foundation for Quality Management Model
Leadership. Pret a Manger’s leaders played an important role in the company. As soon as Schlee was hired as its CEO, the company achieved a lot as the customer-centred organisation.
Strategy. The company determined its future directions and underlined the necessity to expand the number of stores. Still, the inability to find the shops that were large enough to have kitchens in there made the company develop a new strategy to attract customers.
People. The importance of people could not be neglected because shops are open to provide more people with an opportunity to buy high-quality food in a short period.
Partnerships & Resources. The performance of the organisation could be improved by the development of the relations with the companies that offer safe and fast transportation services.
Process/Products/Services. New stores were new opportunities to provide the same services at different places. Pret a Manger shops introduce the standards according to which services are offered to people.
Results. Customers could find more stores at different places. Employees could develop their skills and try themselves in new roles. Society gets benefits from the Pret’s sustainability strategy and the intentions to help homeless people get back into society (Braw 2013). Its overall impact on business is impressive indeed because the company tried to underline the importance of quality and the necessity to extend the services at the same time.
The main limitation is the inability to prove that “twin shops” do not deviate from the values of the company but just add a new standard.
Findings
- Pret a Manger should not focus on people only but consider external and internal resources.
- Twin shops have to include new services to prove their importance.
Application of Techniques to Human Resource Management Problems
Analysis of Pret a Manger using ERG theory
There are three types of needs to be considered as the possibility to improve the services and working conditions developed by Pret.
Existence needs. The company met many safety and physiological needs including food, water, security of health, employment, and property. Pret a Manger did not want to neglect all these rules and consider those needs.
Related needs. Employees at all Pret stores demonstrated how to respect each other and how to respect customers. They developed friendly relations and regarded their team as their family.
Growth needs. The idea to belong to Pret team was the idea to belong to a group of people that lacked prejudice, promoted creativity and morality, and understood the worth of self-esteem.
The only constraint that could be observed was poor confidence that had to be used in the promotion of new strategies.
Findings
- Exchange of information should be organised at a high level.
- People should not be afraid to ask questions and offer their suggestions.
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Integrative Thinking Theory
Salience. The company needed more stores to promote its services and ideas and offer jobs to many people.
Causality. The development of “twin shops” could involve more people from different spheres and prove that the quality of food did not suffer.
Architecture. The company had to introduce new stores and prove that the same products and opportunities for customers could be promoted.
Resolution. The results of the change did not influence the quality of work. However, new opportunities changed the opinions of customers about the quality of food offered at Pret.
Constraint. Pret stores got a chance to be extended. However, Pret employees did not use their chances to explain to their customers that the quality of food and services was not changed but was spread.
Findings
- The company should be ready to talk to its customers and explain the necessity of all steps.
- Employees have to understand their responsibilities in regards to their customers.
Application of Techniques to Innovation Problems
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Open Innovation Model
In the sphere of business, open innovation is a profitable way to innovate because it helps to reduce costs, save time, and increase revenues (Chesbrough 2011). There are several decisions Pret a Manger should make to succeed in innovation.
Market intelligence. The company had to investigate the current positions of its competitors and underline its strengths. Not many companies pay attention to the ways of how customers are served. Pret stores introduced a new approach to customer-company relations and proved that improvements are possible in the same city with the same stores.
Acquisitions. New “twin shops” required certain acquisitions and the necessity to think about personal transportation methods. It was not appropriate for the company to depend on someone’s services. Therefore, Pret a Manger needed to increase its innovative capabilities in case “twin shops” ideas was approved and developed in different cities across the globe.
Findings
- Investigations have to be organised to explain the role of twin shops in the industry developed by Pret a Manger.
- Explanations and the exchange of the facts have to be properly developed in the company.
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using Lean Innovation Model
There are five stages the company should be ready to take:
Value identification: the necessity to open more Pret shops and introduce prepared-at-shops food in the same way it was offered later to Pret customers.
Value stream: the search for suppliers and the change of employees’ roles and duties should be considered as the main part of Pret’s value stream.
Flow creation: the company did not pay attention to the necessity to exchange the information with its customers about the impact of “twin shops” on food offered.
Pull establishment: the pull of customers has been towards food that was prepared at shops and bought there. Pret’s response to that change included the possibility to hire new people, provide new customers with the same high-quality services, and get high revenues in a short period.
Perfection: In this sense, the perfection is the creation of new shops which should not contradict the core value of the company but offer customers the same high-quality services and food.
Findings
- Suppliers have to be involved in the changes of the company.
- New people should be found to introduce the changes in the most effective ways.
Application of Techniques to Business Model Problems
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is the identification of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that show how Pret a Manger uses its sources and achieve the goals.
Figure 4-5: SWOT Analysis. Source (Author’s design).
Findings
- Evaluation of different sectors in the industry is required.
- Analysis of the company and its positions should be developed during the change implementation process.
Analysis of Pret a Manger Using PEST Analysis
Certain macro factors should be considered to understand if Pret a Manger is ready for change and has enough resources to rely on. The evaluation of these factors helps to identify further steps and possible improvements.
Political factors: trading agreement policies are properly identified by the company. The countries where Pret shops could be found support the healthy-eating image, and Pret a Manger should take the steps to prove its image and its worthiness. Business and labour freedoms play an important role in the company.
Economic factors: due to the fact that Pret shops are located in big cities, its economic situation depends on the general economic situations of the countries. Many people became money consciousness but still focused on having high-quality services and respect.
Social factors: the company focused on cultural, age, and gender differences and made sure that every customer and employee was treated fair.
Technological factors: Pret a Manger had to consider such technologies as the Internet, online purchase, and online communication. People were eager to use their opportunities with Pret.
Findings
- Different factors can influence the way of how changes can be accepted by the stakeholders of the company.
- Pret a Manger’s people have to learn their opportunities.
Chapter Five: Proposed Solutions to the Problems
Solution for Organisational Behaviour Problem
The company with all its attention to the needs of customers and the enthusiasm of its employees cannot demonstrate success in all its beginnings and changes. Instead of being afraid of competitors, Pret a Manger should fear itself and innovations offered (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012). When any company starts expanding its operations, opening new stores, and offering new employment opportunities for people, it is expected to gain as many benefits as possible and promote growth and value.
- Brand recognition plays an important role in the company.
- Pret a Manger is an international company that introduces its food and beverages of the same high quality. The company should have the guarantees that all changes are favourable for the company and for all customers.
Recommendations
- It is recommended to explain the development of new stores without kitchens and describe how food could be transported from the nearest shops with kitchens. Lewin’s change management theory could be used to implement the change and make sure it works effectively.
- The question of loyalty and quality was raised. Pret a Manger has to provide its regular customers with the guarantees that the quality of services and food cannot be changed. New customers should appreciate a chance to visit Pret a Manger at a different place of their cities. It is recommended to implement Kotter’s strategy with the help of which the company can predict the mistakes and avoid them.
Action Plan
- To create online forums and advertisements within the frames of which it is possible to inform customers and employees about the essence of “twin shops”, the worth of new stores in the same cities, and the benefits people could get with this idea.
- The case study shows that not many people really understand the process of “twin shops” implementation. What people see is the emergence of new Pret shops without kitchens. Therefore, the attention to the exchange of information and the necessity to make sure that all stakeholders including regular and potential customers and employees are aware of the coming change and its benefits and possible shortages;
Solution for Quality Management Problem
The success of change management depends on the correctness of the model chosen by the company, and the theory leaders have to rely on when they implement changes. Management is the process that should not focus on changes only. Managers and leaders have to understand that the success of their business depends on how they could create, develop, and optimise their working process and divide the roles to be performed (Gerth 2013). The example of Pret a Manger shows that it is possible for the company to consider the opinions of its customers and even provide people with guarantees that all their messages are read and analysed, and the best ones could be realised with time.
- The company should work according to a certain system and never neglect the steps that have been established beforehand.
- Employees have to share their opinions and try to understand what customers want to get from the company.
Recommendations
- The company could use the Deming’s system with the help of which the nature of customers and their expectations could be identified.
- The identification of people, resources, and processes is possible with EFQM strategy.
Action Plan
- To involve customers into new shops by making them as direct participants of the game or a quest. For example, it is offered to potential customers to take a quest and find a new “twin shop” considering the location of the shop they are located at the moment. As soon as customers are intrigued to find a shop, they have one more mission to complete.
- Customers have to compare the quality of food offered in two types of shops and be provided with guarantees that if the quality differs, all food could be free for them during the next month. However, such idea could be a challenge for the company that is not confident in the quality of its production. Pret a Manger gives a 100% guarantee that all food and beverages are of a high-quality. Customers will not be frustrated. They will enjoy the game offered to them by the employees of Pret a Manger and discover new locations of their favourite shops.
Solution for Human Resource Management Problem
The division of responsibilities depends on what goals and outcomes the company expects to achieve (Larson & Larson 2012). The main problem is the inability to understand if the expansion of store lines by Pret a Manger was really effective. Solutions are:
- To prove that “twin shops” changes are appropriate and necessary to the company, and
- To introduce new strategies on how to expand the company’s business and stay loyal to the customers’ expectations and opinions.
Recommendations
- ERG model can help to identify the needs of the company and connect them with the needs and expectations of customers.
- Integrated thinking theory could be recommended as an opportunity to understand what is necessary for the company and what can be done to help customers accept the change properly.
Action Plan
- It is expected to hire several new people, who could demonstrate their respect to Pret customers and employees and introduce some new strategies of how to inform people, make them interested in the twin concept, and help them to learn the nature of “twin shops” and understand that the quality of food does not suffer from the innovations and changes offered.
- Before rejecting a new idea, it is necessary to make sure that all approaches and explanations have been tried, and no effective results have been achieved.
Solution for Innovation Problem
Pret a Manger is the company that wants to use all its opportunities and not to stay still. In 2005, first twin shops were opened by Pret a Manger as change the company could benefit from. The peculiar feature of such shops was a close location to the already existed shops but the absence of their own kitchens. On the one hand, such idea provided more people with an ability to buy tasty food offered by Pret a Manger.
On the other hand, the appearance of such shops contradicted the vision of the company according to which food should be sold by people who prepared it. The absence of kitchen was not inherent to Pret a Manger shops. The question about the worth of such twin shops was raised for a number of times. The following solutions are possible:
- To explain that the absence of the kitchen does not influence the quality;
- To provide customers with a chance to compare the qualities of services in different shops.
Recommendations
- Open innovation should help to integrate general knowledge with the required innovations.
- Lean innovation strategy is helpful in terms of value identification and flow creation.
Action Plan
- To attract the attention of people to visit new “twin shops” and offer a captivating system of sales and benefits. For example, it is possible to provide customers with an opportunity to visit a twin shop and enjoy a discount offered from the original shop. Such involvement should provide customers with a desire to avoid unpredictable spending and buy the food they used to buy at Pret shops.
- A new pricing policy should not differ considerably from the prices set at old stores because the company could face the losses that could be hardly prevented or solved.
Solution for Business Model Problem
One of the possible ways to analyse the activities of the company and provide the required list of recommendation is to use a RACI matrix. Jacka and Keller (2009) identify this type of matrix as a possible method to visualise the roles and duties of all stakeholders of a process.
As a rule, it is expected to list the actions on the left side of the matrix and identify the positions that have to understand their roles across the top of the matrix. Each role has its own title: “responsible” (R – ultimate responsibility for one person for each step), “accountable” (A – actual doers of the activities), “consult” (C – support and analysis of the work done), or “inform” (I – awareness of the changes but no approvals are required) (Jacka & Keller 2009).
Recommendations
- SWOT and PEST analyses are recommended to understand what kind of work should be done and what changes are expected in the company.
- The use of the matrix can help to create a system with the help of which the work of the company can be organised.
Action Plan
The following matrix is created in order to clarify what kind of people could be involved in the new strategy development, what their contributions could be, and how much time could be required to observe some changes and effects of innovations.
Figure 5-4: RACI Matrix. Source (Author’s design).
Regarding the choices of departments and positions of people, it is necessary to underline that CEO has to take responsibility for each activity taken and the decision made. However, this person should not be a direct doer of all actions. In many cases, it is enough to gain control over the decisions made. In some situations, it is necessary to provide people with the required pieces of advice, information, and goals that have to be achieved. Besides, it is also recommended to evaluate the current values, visions, and missions of the company and compare if its employees violate some norms and standards, and their actions contradict the expectations of people.
Limitations
In the case under consideration, there are three main limitations that have to be explained. The identification of the limitations is the activity that helps to understand what could weaken the already existence system and what could prevent achieving good results in change management.
The first limitation is connected with human resource issues and the inabilities to find a group of people, who could take direct responsibility for the changes that occur because of the “twin shop” concept. Pret a Manger does not have enough resources to introduce the change and explain how crucial the improvements could be for the company.
Pret employees have to understand why they need to attract people’s attention instead of focusing on producing good food and selling it to shop visitors. As there are no training programs and practices for employees (Frei, Goldberg & Sice 2012), the company should hire people, who know what to do and how to introduce the information in the most effective ways.
Another limitation touches upon the availability of sources and the necessity to use new resources to complete the function and open effective “twin shops”. Pret employees have to think about the delivery details and make sure that customers understand how safe and secure each transportation operation with Pret a Manger is.
Finally, there is a need to understand that the work of Pret a Manger depends on the quality of a human life consideration. Therefore, the last limitation is the direct dependence of the company on customers and their needs. First, customers and their incomes predetermine the possible level of revenues in the company. Second, customers’ mood and behaviour predetermine the nature of relations at shops. If a customer visits the shop in a bad mood, it is hard for a manager to provide such customer with a required portion of the support, understanding, and help. Therefore, the connection between the company and its customer is one of the unique features in the world of the fast food business and the main limitation of the company in regards to its success.
Concise Generalised Action Plan for Pret a Manger

Prelude to Chapter Six
The following chapter will introduce a new case where the changes in British Airways Company will be discussed. The point is that British Airways is one of the companies that has already introduced itself as a powerful organisation with a number of opportunities. It is a serious competitor in its market. At the end of the case scenario, it is expected to make the conclusions that demonstrate how changes should be organised and what steps have to be taken by a company, its leaders, and its employees. Change management is the challenge for many organisations, and British Airways may be used as a good example to be followed.
The main issues that should be discussed in the sixth chapter include business growth, innovation strategies, mindset change, customer experience, and market repositioning.
Chapter Six: Application of the Findings: British Airways
British Airways History and Background

British Airways is one of the well-known airline companies in the whole world and one of the largest organisations in the airline industry of the United Kingdom (Jarvis 2014). The achievements of British Airways turned into the achievements of the whole civil aviation industry. The company had enough powers to dictate new rules, establish new standards, and demonstrate its impact on an ordinary passenger. During the last several ages, the company underwent a number of changes.
For example, it was privatised in 1987 (British Airways n.d.). The decision to privatise the company was made after it was clear that a number of challenges connected with management and finances could not be solved in a short period of time. It was necessary to analyse the reasons for industrial strives and help people to comprehend their roles in the company.
Therefore, the story of privatisation of this airline company is the story of success that turned an unprofitable state-owned organisation into one of the thriving international business examples with its turnover being increased more than 1.5 times and operating profits increased from £162 million to £600 million (Cole 2003). In 2006, it became one of the four largest international carriers that served about 30,000 million passengers annually (Belliotti 2008). Alex Cruz performs the functions of the company’s CEO and chairman.
Company Strategy and Objectives
Being one of the largest international airline companies and a global leader among premium carriers, British Airways established a multi-channel distribution strategy in 2015 (Bylykbashi 2015; NDC Case Study 2015). There are five main strategic objectives of the company:
- To provide customers with premium services and meet the needs of customers;
- To extend its services in global cities;
- To deliver outstanding services (British Airways 2009);
- To become a leading airline company in London because London is the home city of the company, and it remains to be an emotional and financial heart of the chosen sphere of business (British Airways 2010), and
- To improve the margins of the company in regards to the needs and expectations of regular and potential customers.
Values and Missions
More than 35,000 people work at British Airways and create a true luxury image for the company day by day. There are many instruments the employees and their leaders use to succeed in management, and corporate communication is one of the best and effective tools chosen by British Airways team. According to Tench and Yeomans (2009), corporate communication helps to promote harmony and understanding. British Airways pays its attention to such issues as corporate culture, behaviour, and self-development.
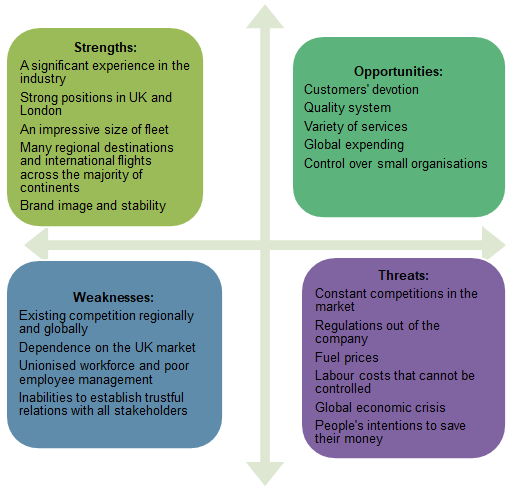
SWOT of British Airways
Company Problems
There are two main problems that should be discussed within the frames of the company under analysis.
Human Resource Management Problem
Employee diversity and organisational behaviour are the two main components of human resource management that have to be improved in British Airways.
Strategic Management Problem
A variety of strategies and goals of the company makes its leaders and employees make fast decisions and take the steps that support the balance between what customers expect and what employees can do to meet those expectations.
Business Competitiveness Problem
British Airways has a number of services as well as a number of competitors. Nowadays, people have a variety of choices when they decide to fly with comfort. British Airways has to be ready to compete and understand its abilities.
Research Questions
Each problem has its own question to be answered.
Human Resource Management Question
How can British Airways organise the work of its employees with different goals, abilities, and needs?
Strategic Management Question
What steps should the company take to promote the balance between customers’ needs and employees’ opportunities?
Business Competitiveness Question
What can the company do to stay competitive in the airline industry in regards to the services and opportunities offered by other local and international companies?
Research Objectives
Human Resource Management Objective
It is necessary to explain the improvements that could be offered to the company in order to understand the needs of employees and make them be eager to work in teams and compete between the departments to introduce the best services.
Strategic Management Objective
It is important to promote the changes with the help of which British Airways could organise its work in regards to the goals and missions established.
Business Competitiveness Objective
The company should clarify what can steps can be taken to stay competitive and what decisions have to be avoided.
Analysis of British Airways
Human Resource Management Problem
There are many ways on how to improve the work of people in their workplace. A number of models were introduced by different theorists, and the ideas developed by Henry Mintzberg could be used in regards to the situation in British Airways. According to the model developed by Mintzberg, there are three types of work people could be involved in: informational, interpersonal, and decisional (Birkinshaw & Mark 2015).
Informational work makes people think about how to introduce and exchange information to all people in a company. Interpersonal work promotes the cooperation between people and discusses the opportunities that could be used. Finally, decisional work presupposes the necessity to make decisions that are clear and though. It is important to understand the types of work that should be done and to identify the roles people should be ready to perform.
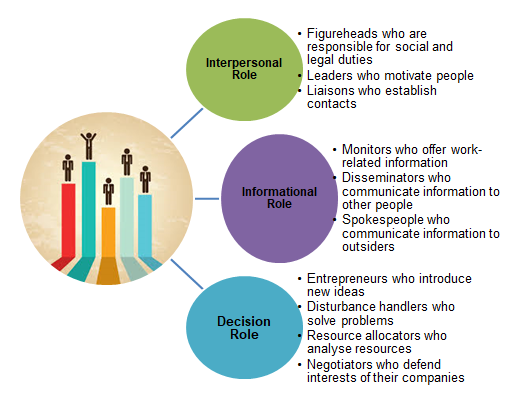
This model could be implemented to British Airways as a possibility to clarify the roles of every employee and the duties people should perform. Mintzberg’s classification of duties is not complicated. As soon as the company distributes the roles in a proper way, employees realise that there are certain spheres where they have to work. With the help of this classification, people could be divided into several groups and compete in order to demonstrate which team could introduce the best achievements. It is not enough to explain to British Airways employees what they should do.
It is important to motivate them and show that their achievements are crucial not for the company only but for themselves as individuals, who have to be developed, educated, and trained. There is no place for hierarchies and discriminations. There are just several departments and categories that could create the standards and make people follow them. Andersen (2009) underlines the fact that nearly everyone likes various types of competitions and games. Therefore, competitions among employees turn out to be a chance to make them work better, understand and achieve the goals set and use their best abilities that could not be discovered earlier.
Strategic Management Problem
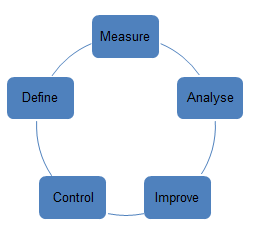
Lean Six Sigma is one of the possible approaches to be used to improve the quality of the services offered by a company, reduce possible variations, and eliminate the volume of waste that could prevent a good work of an organisation (Furterer 2016). The peculiar feature of this model is the possibility to use qualitative and quantitative elements of the analysis with the help of which a working process could be improved.
There are five main stages a company should pass through in order to understand if it could promote the improvements and choose the strategy that is appropriate for employees and customers.
1 – it is necessary to define problems and objectives in a company;
2 – it is expected to understand what should be improved in a company and why;
3 – it is obligatory to analyse the situation and clarify what factors should be taken into consideration to start a working process;
4 – it is important to implement the improvements that could be helpful for the company, and
5 – it is required to make sure that all improvements are sustainable and bring certain results.
British Airways has already demonstrated the methods that could be used to take the leading positions in the market. It was privatised and improved. Still, there are a number of problems and shortages that could not make this company the best representative in the industry. Some people continue complaining that British Airways cannot organise its baggage services and solve the problems of delays that happen from time to time. It means that a new strategy should be offered to make sure that all organisational details are considered.
Define: the main problem is the presence of customers’ discontents about the quality of services offered. Still, it is wrong to define it as a significant problem till the number of complaints achieves a certain limit. It is necessary to understand that unpredictable events could happen in the company, and customers could suffer without any intentions of the company to break their promise and reject its values. For example, there was a situation when hundreds of passengers faced flight cancellations because of French air traffic control employees (Press Association 2016). It was not a direct company’s fault. Still, British Airways should do something to please its customers and make them forget about that accident.
Measure: the reason for why the company should take some steps is the necessity to avoid similar situations and make sure that every customer is satisfied with the services offered.
Analyse: it is possible to focus on the opinions of customers and their feedbacks. Assessment tools and direct communication with customers should help to improve the relations between the employees of the company and improve the attitudes of customers about the company. Besides, such changes could influence the reputation of the company and open new opportunities with time.
Improve: the main worth of the idea is to change the opinions of people and make people see the advantages of the services offered by British Airways. Effective strategies and employee attention to the customers are the critical elements in all companies not only in the airline industry but in a majority of spheres. People want to be sure that they get the best services from the best people.
Control: one of the possible ways to check the effectiveness of the chosen strategy is to make the leader of British Airways talk to the passengers and ask about the quality of services offered. There is no need to gather information from other people or ask to perform some work instead. The leader should know what other people think of their company.
Business Competitiveness Problem
The airline industry is competitive indeed (Morrison & Winston 2010). A number of companies try to introduce their services and prove that their offers are the best options for people. The example of British Airways shows that a single concept as airline privatisation could change the current state of affairs and change the leaders in the industry (Belobaba, Odoni & Barnhart 2015).
The problem of the company could be solved with the help of Five Forces Analysis model developed by Porter. It consists of five main issues that are threats of new entrants, threats of substitutes, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and industry rivalry (Hill & Jones 2009).
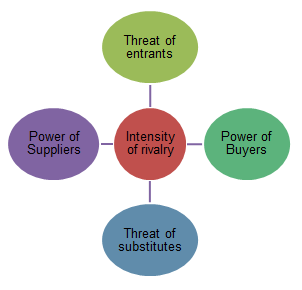
Threats of Entrants: This factor is usually low still very important for all new organisations. Airplane brands and services of the company vary, and entrants can hardly introduce the services of the same quality. British Airways has nothing to worry about.
Threats of Substitutes: This point is significant because air travel remains to be popular but can be easily substituted by cars, trains, or buses, and the companies like British Airlines present impressive opportunities for people.
Power of Buyers: This type of buyers remains to be moderate because many already developed airline companies are ready to introduce new ideas and impress people, and people do not have enough alternatives to rely on in case they want to travel.
Power of Suppliers: This power is great indeed because the company depends on fuel suppliers and trade unions that define the quality of the work that could be offered.
Intensity of Rivalry: British Airways is a part of a very competitive industry. It has a number of credible sources, intentions to meet the needs of people, and create good working places. Still, competitors are able to take the same steps and impress people the same or even better ways. Therefore, competitions cannot be neglected by the company.
Proposed Solutions for British Airways
There are two main problems British Airways has to deal with. Therefore, there are two types of solutions that should be given to the company. Each solution is based on the evaluation of the already done work and the possibilities of the company to make some changes without significant losses and challenges.
Human Resource Management Solutions
The necessity to manage humans in their work cannot be neglected. This element remains to be an important part of the work and the way of how the whole company should work and introduce its services.
As soon as British Airways notices that some problems, shortages, or challenges occur in the human resource department, there is a need to make some changes and help people to cope with their problems. In the current situation, British Airways have some uncertainties because of the necessity to organise the work of employees with different goals, abilities, and needs. The question of employee diversity is burning for the company, and the possible solutions could include the following:
- Divide people into groups in regards to their roles so that people could share their experience, plans, and expectations from the company. People, who pursue the same goals but take different positions could exchange much helpful information and improve the abilities of each other by turning someone’s weaknesses in someone’s strengths.
- Make people think that British Airways is a huge arena for employees’ competitions. There is no place for weak people, who do not try to change something in their lives. The company and the process that occur in there are the main elements of a kind of “gladiators’ fight” with the only goal to survive and not to lose a face.
- Promote the importance of such concepts as dignity, respect, and self-development regarding the roles people should perform in the company.
Strategic Management Solutions
It is not always easy for a company to recover from losses or challenges it faces. However, the challenges of British Airways are not catastrophic. At the moment, the company has to find out the balance between customers’ needs and employees’ opportunities. There are a number of ways out, and the following solutions could be taken into consideration when the company has to improve its strategies and managerial details:
- Provide customers with information that the company is able to identify its problems and recognise the mistakes it has already made. There is no need for the company to say “sorry”, but it is crucial to make people believe that British Airways does give empty promises or neglect customers’ trust.
- Consider the existing values and missions and make changes to underline what the company could offer to its passengers in regards to the opportunities and resources available. The company should take some new marketing activities to prove the correctness of the activities chosen.
- Improve the company’s quality and services and gain control over the external changes that could not be understood by customers or predicted by the company. It is necessary to hire people who are able to make fast decisions and stay enthusiastic.
Business Competitiveness Solutions
The main suggestions that could be offered to British Airways include the importance of differentiation, cost leadership, and the evaluation of the values that are crucial for the company.
Recommendations
RACI Matrix for British Airways is developed to clarify the steps that the company could make.
Applications
Any sphere of business cannot avoid certain change and improvements from time to time (Finch 2011). The world is constantly changing, and people have to understand that the already applied methods and ideas cannot stay the same for a long period of time. New opportunities and the development of new knowledge and expectations make people change their needs and think about the actual services and products they could get.
The situation of British Airways shows that the company could be one of the best representatives in its field and have the largest resources but could be vulnerable at the same time. Change management is the activity that helps to analyse the current state of affairs and understand if some changes are necessary. Besides, change management involves a number of people with their own need, experiences, and knowledge.
Taking into consideration the material and opportunities investigated in British Airways, the following areas of learning should be identified and introduced as the main concerns for the company, its leader, and its employees:
Sustainability: Any company that has to survive change should remember about sustainability and its impact on people.
Motivation: Success of the company depends on the level of motivation offered to employees by its leader.
Reorganisation: The company should not be afraid to make changes and introduce new values only in case there are enough grounds to prove the urgency.
Change management: Regardless the situations and needs of the company, there should always be a plan according to which all team members identify their roles and take steps.
Innovations: The current improvements and innovations should not confuse companies but open new opportunities.
In general, British Airways, as well as Pret a Manger, demonstrated good examples on how to organise people, consider the needs of customers, and stay competitive. There is no need to make the decisions that cannot be explained. Even fast acts and decisions have to be weighed and properly introduced to all stakeholders. Only if the exchange of information is properly organised, changes and innovations are not dangerous but beneficial for companies.
Transfer of Learning
This section aims at discussing the findings from the analysis of two huge companies, Pret a Manger and British Airways, and their changes and transferring the learning as an opportunity to combine the experience of Pret a Manger and British Airways. The knowledge that was obtained during the analysis could be transferred between the airline and fast food industries. In order to identify, comprehend, and use the benefits of transfer of learning, it is suggested to create a framework and combine the findings on Pret a Manger with the findings offered to the situation of British Airways.
Analysis, findings, and management concepts that could be transferred to British Airways
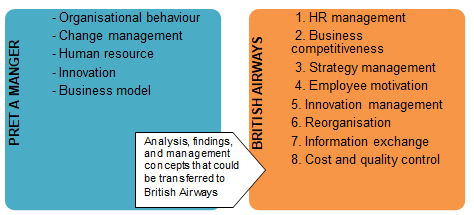
This figure shows that the implementation of findings offered to Pret a Manger is possible to the situation British Airways is at the moment. Both companies regardless the differences of their industries and the nature of services have to understand that changes cannot be avoided in their business.
It is not enough to get ready for something new; it is also necessary to comprehend how innovations and changes could be accepted by employees, customers, and society. Below, there is a list of responses that could be taken from the case study of Pret a Manger and implemented in the case of British Airways, the company that knows a lot about success, changes, and requirements that should be met.
Transfer of innovation management in companies
Both companies cannot ignore the importance of changes in their industries. The majority of changes can be explained with the help of innovations that become available in a short period of time. Pret a Manger is well-known for its values and attention to customers. Latest innovations cannot support the idea that companies have to communicate with customers directly but use the opportunities and substitute face-to-face communication with online forums and technologies.
British Airways have good chances to get benefits with online services and innovative ideas because the travelling industry presupposes the possibility to make fast reservations and book tickets. Pret a Manger has to understand that innovations should be properly used not at the expense of traditions and values that were developed during the ages. Innovation management should be thorough and properly explained.
Transfer of Pret a Manger HR services
Pret a Manger was created on the basis of certain values and requirements. Employees have to understand that customers of the shops do not visit their shop just in order to wait but to be served in a short period of time. The team of Pret a Manger respects the choices of their customers and thinks about every client as a part of a family to share the best products with.
British Airways has a bigger team in comparison to the team of Pret a Manger with not all employees working directly with customers. Therefore, HR management of Pret a Manger should serve as a good example for British Airways with an opportunity to promote training for employees and their high-quality cooperation with customers.
Transfer of the abilities to compete using successful business models
The fast food industry has a high level of new entrants’ threat. Still, Pret a Manger tries to use its best business models and impress customers with high-quality services and respect. British Airways could use Pret a Manger’s cooperation with customers’ example and impress its own customers with the intentions to discuss personal affairs and the reasons for why the services of British Airways are chosen.
Transfer of strategic management
Pret a Manger is one of the first organisations that offered the idea of twin shops as a new kind of services offered to customers. British Airways could introduce a twin company with the help of which customers should not wait in queues and spend much time getting their answers.
Transfer of motivation and reorganization
Employees of both companies under analysis have to understand that their personal attitudes to work define the quality of services offered to customers. Therefore, they have to stay motivated and organized all the time. Pret a Manger’s employees try to participate in different activities, hire new people and make the suggestions that could improve the work of the company. British Airways should take a few lessons offered by Pret a Manger and use employees’ motivation as one of the main goals to be achieved.
Transfer of information exchange
Any kind of change and innovation have to be properly explained to people who are interested in the development of the company. For example, Pret a Manger’s policies include direct communication with customers and provision of information. British Airways relies on online forums and chats to share news and explain the standards. Information exchange should be improved in both companies. To success, the both companies should observe the examples of each other.
Transfer of cost and quality control
Pret a Manger and British Airways are the companies that could be called the leaders in their own industries. Still, Pret a Manger relies on its low-cost strategy, and British Airways uses its quality strategy. The companies should try to exchange their companies to attract the attention of customers.
List of References
Agan, T 2014, ‘The secrete to lean: innovation is making learning a priority’, Harvard Business Review.
Aguayo, R 2010, The metaknowledge advantage: the key to success in the new economy, Simon and Schuster, New York.
Al-Hakim, L, Wu, X, Koronios, A & Shou, Y 2016, Handbook of research on driving competitive advantage through sustainable, lean, and disruptive innovation, Business Science Reference, Hershey.
Andersen, NA 2009, Power at play: the relationships between play, work and governance, Springer, New York.
Assen, M, Berg, G & Pietersma, P 2009, Key management models: the 60+ models every manager needs to know, Pearson Education, Harlow.
Aswathappa, K 2005, Human resource and personnel management, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, London.
Basu,R 2009, Implementing six sigma and lean, Routledge, New York.
Belliotti, R 2008, Common use facilities and equipment at airports, Transportation Research Board, Washington.
Belobaba, P, Odoni, A & Barnhart, C 2015, The global airline industry, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester.
Benezech, D 2012, The open innovation model: some issues regarding its internal consistency, Journal of Innovation Economics & Management, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 145-165.
Bensoussan, BE & Fleisher, CS 2008, Analysis without paralysis: 10 tools to make better strategic decisions, FT Press, Upper Saddle River.
Birkinshaw, J & Mark, K 2015, Key MBA models: the 60+ models every management and business student needs to know, Pearson, London.
Blaikie, N 2009, Designing social research, Polity, Cambridge.
Blery, EK, Katseli, E & Tsara, N 2010, ‘Marketing for a non-profit organisation’, International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, vol. 7, no.1, pp. 57-68.
Braw, E 2013, ‘Interview: Pret’s CEO on integrating sustainability and helping the homeless’, The Guardian.
British Airways 2009, The way we run our business. Web.
British Airways 2010, Our strategy and objectives. Web.
British Airways n.d., History and heritage. Web.
Bryman, A 2008, Social research methods, Oxford University Press, New York.
Bryman, A & Bell, E 2015, Business research methods, Oxford University Press, New York.
Bylykbashi, K 2015, ‘BA’s restructure puts marketing at the forefront of its business strategy’, Marketing Week. Web.
Cameron, E & Green, M 2015, Making sense of change management: a complete guide to the methods, tools and techniques of organisational change, Kogan Page Publishers, London.
Chapman, RJ 2011, Simple tools and techniques for enterprise risk management, John Wiley & Sons, Danvers.
Chapman, RJ 2014, The rules of project risk management: implementation guidelines for major projects, Gower Publishing, Surrey.
Chesbrough, H 2011, ‘Everything you need to know about open innovation’, Forbes.
Cole, GA 2003, Strategic management, Cengage Learning EMEA, London.
Creswell, JW 2013, Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks.
Cummings, TG & Worley, CG 2014, Organisation development and change, Cengage Learning, Mason.
EFQM: model criteria 2012.
Ferrell, OC & Hartline, M 2010, Marketing strategy, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Finch, E 2011, Facilities change management, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester.
Frei, RX, Goldberg, R & Sice, S 2012, ‘Pret a manger’, Harvard Business School.
Furterer, SL 2016, Lean six sigma in service: applications and case studies, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Gell,A 2014, The book of leadership: how to get yourself, your team and your organisation further than you ever thought possible, Hachette, London.
Gerth, C 2013, Business process models: change management, Springer, Paderborn.
Goertz, G & Mahoney, J 2012, A tale of two cultures: qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences, Princeton University Press,Woodstock.
Griffin, RW & Moorhead, G 2011, Organisational behaviour, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Hair, JF, Celsi, MW, Money, AH, Samouel, P & Page, MJ 2015, Essentials of business research methods, M.E. Sharpe, London.
Hayes, J 2014, The theory and practice of change management, Palgrave Macmillan, London.
Helms, MM & Nixon, J 2010, ‘Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now?: a review of academic research from the last decade’, Journal of Strategy and Management, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 215-251.
Hill, G & Jones, G 2009, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach, Cengage Learning, Mason.
Hornstein, HA 2015, ‘The integration of project management and organisational change management is now a necessity’, International Journal of Project Management, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 291-298.
Jacka, JM & Keller, PJ 2009, Business process mapping workbook: improving customer satisfaction, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Jarvis, P 2014, British airways, Amberley Publishing Limited, Gloucestershire.
Jong, JPJ, Vanhaverbeke, W, Kalvet, T & Chesbrough, H 2008, Policies for open innovation: theory, framework and cases, VISION Era-Net, Helsinki.
Koontz, H & Weihrich, H 2006, Essentials of management, Tata McGraw-Hill Education, London.
Kotter, JP & Cohen, D 2013, The heart of change: real-life stories of how people change their organisations, Harvard Business Press, New York.
Larson, E & Larson, R 2012, The influencing formula, Watermark Learning, Minneapolis.
Morrison, S & Winston, C 2010, The evolution of the airline industry, The Brookings Institution, Washington.
NDC case study: British Airways prepares for the future 2015.
Nelson, DL & Quick, JC 2014, ORGB: organisational behaviour, Cengage, Stamford.
Paton, RA & McCalman, J 2008, Change management: a guide to effective implementation, SAGE Publication, Thousand Oaks.
Polonsky, MJ & Waller, DS 2014, Designing and managing a research project: a business student’s guide, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks.
Press Association 2016, ‘BA and easyJet hit by delays after French air traffic control strike’, The Guardian.
Pyzdek, T & Keller, P 2012, The handbook for quality management: a complete guide to operational excellence, McGraw Hill Professional, London.
Reiss, M 2012, Change management, Books on Demand, Nordestedt.
Rogers, EM 2010, Diffusion of innovations, Simon and Schuster, New York.
Rothwell, WJ, Stavros, JM, Sullivan, RL & Sullivan, A 2009, Practicing organisation development: a guide for leading change, John Wiley & Sons, Danvers.
Sabri, EH, Gupta, AP & Beitler, MA 2006, Purchase order management best practices: process, technology, and change management, J. Ross Publishing, Fort Lauderdale.
Saunders, M, Lewis, P & Thornhill, A 2009, Research methods for business students, Pearson Education, New York.
Sehested, C & Sonnenberg, H 2010, Lean innovation: a fast path from knowledge to value, Springer Science & Business Media, London.
Smith, R, King, D, Sidhu, R & Skelsey, D 2014, The effective change manager’s handbook: essential guidance to the change management body of knowledge, Kogan Page Publishers, London.
Solomon, MR 2014, PMP exam cram: project management professional, Pearson IT Certification, New York.
Stimpfle, A 2011, The enabler criterion ‘leadership’ of the EFQM model: six companies of the financial services sector in comparison, GRIN Verlag, New York.
Tench, R & Yeomans, L 2009, Exploring public relations, Pearson Education, Harlow.
Uppal, J & Rahman, T 2013, Business transformation made straight-forward, QR Systems, Woodbridge.
Voet, J 2013, ‘The effectiveness and specificity of change management in a public organisation: transformational leadership and bureaucratic organisational structure’, European Management Journal, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 33-382.
Vukotich, G 2011, 10 steps to successful change management, American Society for Training and Development, Alexandria.
Watson, GH 2008, Strategic benchmarking reloaded with six sigma: improving your company’s performance using global best practice, John Wiley & Sons, Denver.