This analysis of internal and external factors influencing IKEA will inspire a great paper. Check it out if you need to write a PESTLE analysis of environmental factors affecting IKEA.
Introduction
IKEA is a worldwide recognized home furnishing seller. It has quickly developed since it was started in 1943 by Ingvar Kampard. At present, it is the world’s leading furniture retailer, renowned for its Scandinavian mode. The mainstream of IKEA’s products is flat-pack, all set to be accumulated by the consumer.
IKEA offers over 9,500 products, including home and office furnishings, equipment, lighting, and accessories. This extensive range is obtainable in all IKEA outlets, and consumers can order a good deal of the collection online through IKEA’s website. At this point, there are 18 outlets in the UK, with the first one launched in Warrington in 1987. In July 2009, IKEA introduced its products in Ireland and opened an outlet in Dublin (Times, 2010).
Over the last 60 years, IKEA has grown from a simple entrepreneur into a cluster of companies with 76,000 associates. At the same time, an exceptional corporate culture with its own set of principles has been developed. The achievements of IKEA have been built upon zeal and eagerness, a steady aspiration to renew and progress, cost-consciousness, and readiness to provide a hand and take accountability (IKEA, 2003).
IKEA is a one-stop store for all the requirements at residence, offering various household and office products. These products have been carefully selected for the customers to make their homes more attractive and comfortable. Consumers can access all kinds of merchandise under one roof, making the shopping experience excellent.
A wide variety of products and designs one can select from attracts millions of customers to IKEA stores across the globe every year. The key goal of IKEA is to assist customers in implementing their own ideas for beautifying their surroundings by offering them an extensive range of well-premeditated furniture and ornaments for their homes and offices at a very reasonable price.
Sweden is where the foundations of IKEA come from, while its product designs are derived from different parts of the world, making it one of the most diversified and progressive companies. At IKEA, customers can explore different products and make their buying decisions with the assistance of the IKEA staff.
Characteristics of IKEA
Both for the company’s customers and co-workers, IKEA is a combination of unique characteristics. Simplicity is an essential factor at IKEA. It is evident in everything from how the management operates to how employers and employees relate to one another and the customers. Managers and associates work together, utilize the same car parks and eat side by side in the same cafeterias (IKEA, 2003).
The company’s personnel are an immensely important resource for IKEA, and they are constantly working together to improve things and enhance quality. By daring to be unique, believe differently, and inquire about how things are done, IKEA copes with difficulties and excels in its field (IKEA, 2003).
IKEA is also famous for offering the same product variety in all countries. The company’s products range from 8,000 to 10,000 depending on the outlet’s dimension. The company’s international strategy consists of adjusting to the specific peculiarities of the country in which an outlet operates. The store locations, design, and display are adjusted according to market requirements and consumer behavior. For instance, in China, the store layouts imitate the design of many Chinese apartments, and because many Chinese apartments have balconies, the outlets even contain a balcony sector (Miller, 2010).
IKEA exhibits its massive range of more than 10,000 items in cheap out-of-town outlets. Most of its products, especially furniture, are sold as knocked-down kits for customers to take the products to their homes and amass themselves. The company wins considerably due to the dimension of each store and the large production runs made possible by selling the same variety of furniture all around the globe.
It enables the company to compete with business rivals on quality, undercutting them by up to 30% in price (Artisan, 2004). With its mouth-watering crèche and Scandinavian coffee, an IKEA store is believed to be an absolute shopping destination for value-aware, car-borne customers. In the Harvard Business Review, Richard Norman and Rafael Ramirez pointed out that IKEA had obliged both consumers and suppliers to imagine worth in a new way “In which customers are also suppliers (of time, labour, information, and transportation), suppliers are also customers (of IKEA’S business and technical services), and IKEA itself is not so much a retailer as the central star in a constellation of services” (Artisan, 2004).
Out of the numerous exceptional characteristics of an IKEA store, possibly the most attractive characteristic to the buyers is the appropriate names given to every stock-keeping unit (SKU). Diaconis, a marketing manager of IKEA, said, “Instead of simply calling a product 123456, we name a bookcase ‘Billy’ or a fabric ‘Anna’, Sofa names are usually cities or rivers in Scandinavia, fabrics are steaks’ names, and the wall units are boys’ names. The reason is that IKEA wants to project the feeling that the products are a part of the family” (Artisan, 2004).
Operations of IKEA
IKEA is highly concerned with the company’s internal operations. It has always ascertained a target price before creating a product. This method was in contrast to the customarily followed practice of initially developing the product and then pricing it according to other furniture producers’ actual cost and markup. The designers of IKEA had to acquire and calculate all the costs, like raw material, manufacturing, and distribution, until the item reached the retail store within a specific target price (ICMR, 2010). Supply Chain Management plays a vital role in the decision-making process at IKEA. It is the most critical responsibility because IKEA has 202 retail outlets worldwide, covering at least a million consumers daily throughout the year (ICMR, 2010).
The company carries 3.5m stock units and provides 10,000 different types of products. Almost 10% of them are new yearly (All Business, 2005). Supply chain planning is sometimes complex for the company because the outlets are spread across thirty-two countries. As a rule, an IKEA retail store opening is a public event, and customers must travel hundreds of kilometers to shop there. Furthermore, the company has 1600 suppliers in numerous regions, divided more or less evenly between Europe and Asia. IKEA has 27 central distribution centers in 16 countries (All Business, 2005).
Internal Factors Analysis
The factors an organization can control are internal factors, and those an organization cannot control are external ones (Times, 2010).
The internal analysis aims to identify strategically essential strengths and weaknesses on which a firm should ultimately base its strategy. Ideally, this goal can be achieved, firstly, by identifying critical internal factors such as distribution channels, cash flows, locations, technology, and organizational structure and, secondly, by evaluating these factors. The internal factors analysis is neither linear nor simple. The steps tend to overlap, and the managers in different positions and levels approach the internal analysis in different ways. Therefore, it is essential for the firm to evaluate these factors effectively.
Anything happening within the company or the company’s grasp falls under the category of internal factors. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors as they indicate how well the company copes with managing its internal matters and what should be the focus of the company’s attention. These factors usually refer to matters related to the organization’s various departments, such as finance, marketing, or production.
IKEA’s business strategy mainly focuses on the company’s sustainability and environmental design aims. IKEA has recently launched a tactical plan regarding sustainability, and the company wishes to see it through by 2015 (Times, 2010).
Strengths
Any aspect within an organization that gives it a competitive advantage over other companies is known to be a strength. It could be an excellent ability of the sales team to convince the customers or the infrastructure the company has developed around its premises. The following are some of the strengths which IKEA has:
- A strong brand name to relate to in the global market (Kumar & Kumar, 2010).
- Conscious attitude to cost results and lower prices that blend perfectly with what they call a ‘Democratic Design’ (meaning good quality for lower prices).
- A responsible approach toward market research helps the company be proactive about entering new markets (Kumar & Kumar, 2010).
- IKEA enjoys economies of scale because of its bulk purchasing.
- Wherever IKEA goes, it develops an excellent infrastructure around its location, which makes this company an immediate favorite for the locals (Times, 2010).
- One of its major strengths is delivering products directly from the supplier to IKEA retail outlets. This cuts down the handling costs, lessens the number of road miles, and decreases the carbon footprint.
- Product development and differentiation is considered to be the company’s major strength that gives it a competitive advantage over the others while keeping its costs of operations at a low level. This could be depicted in the following diagram:
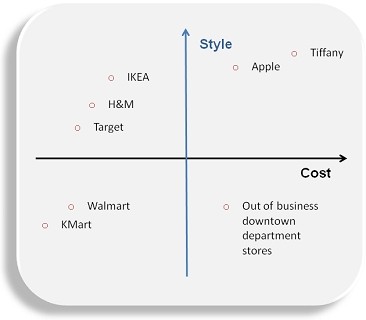
Weaknesses
Problems that any firm may face internally can significantly impact its performance. IKEA is aware of that, so it takes appropriate measures to eliminate such weaknesses (Times, 2010). Often, the plans for overcoming these problems serve as the basis for the company’s short-term objectives. IKEA seems to be facing the following weaknesses:
- The size of the organization is a weakness for IKEA. It manufactures products in different countries, and each country has its geographic constraints, often resulting in the improper implementation of the legislated working conditions.
- Although IKEA spends a lot on research and development, it has problems matching up to one of its primary standards – quality products and low prices. Economies of scale help the company reduce prices, but maintaining a balance between price and quality can be a problem.
- IKEA continuously introduces differentiated products, but its business rivals are catching up with the copies and their own products (Times, 2010).
- Communication barriers are a significant concern. IKEA’s management must maintain healthy communication channels within the organization and with its consumers.
- IKEA has limited advertising and promotional strategies.
IKEA External Environment Analysis of Factors
Factors characterized as uncontrollable and often unpredictable by businesses tend to have severe implications for them. They can affect the direction of the strategy they are pursuing and shape the organizational structure and values within organizations. These factors generally pertain to the external environment of businesses, and therefore they can be divided into two categories. The first group of factors includes the opportunities that involve the necessities in formulating strategies. Secondly, there are external threats that provoke complexities involved in creating the company’s strategies.
Opportunities
A company employs its strengths to benefit from the opportunities that occur. IKEA considers its environmentally concerned business behavior to yield superior returns even in a price-receptive market. IKEA is working on effectual resolutions for customers to help them recycle or reprocess used products (Times, 2010). The opportunities that IKEA takes benefit of through its sustainability outline include:
- An immense opportunity can be seen in a rising demand for environmentally friendly products (Times, 2010).
- There is an increasing demand for low-priced products. Inclinations in the current financial environment may result in consumers visiting less expensive stores.
- It is essential to attract the younger generation, who will be the essential buyers in the upcoming years. IKEA plans to attract the new generation with its low-priced, modern, and stylish products. Due to these characteristics, young people are ready to buy and furnish their homes with IKEA products (Kumar & Kumar, 2010).
- Organizations work on reducing water usage and lowering the usage of carbon footprints. IKEA has set out its plan to cut energy use by introducing alternate sources in its stores and changing its packaging material. Its environmentally friendly transport proposal embraces the aim to reduce business flights by 20% in 2010 and by 60% by the end of 2015 (Times, 2010).
- IKEA is providing social responsibility for the people. IKEA’s strategy includes support for charities such as the World Wildlife Fund, UNICEF, and Save the Children (Times, 2010).
- To attain market value, IKEA can follow the basic marketing strategies of penetrating and scheming the competitive industry to function globally (Kumar & Kumar, 2010).
- The company needs to be open with all its suppliers and stakeholders. It includes creating confidence through good communication with customers, co-workers, vital opinion formers, and the media. Being sustainable is fundamental to IKEA’s image (Times, 2010).
Threats
It can offset potential external threats if a corporation is aware of them. Through creating innovative ideas, IKEA can employ a particular strength to secure its business against threats in the industry. Threats to IKEA may arise from:
- The upcoming social trends can be a threat to IKEA’s business. Most consumers are not ready to try on new products. Therefore, it may result in decelerating first-time purchasers entering the housing market. This is an essential market segment for IKEA items that must be considered.
- The furniture industry has strong market forces that could influence IKEA’s market value. Attracted by the consumer demand and expected returns from household and furnishing markets, many companies have entered these markets. To compete within the industry, IKEA requires strengthening its exclusive qualities (Times, 2010).
- Economic factors are also one of the major threats to all businesses. The downturn of the economy has slowed down consumer expenditure, and disposable income has been reduced.
- Nevertheless, IKEA is concentrating on these threats and trying to overcome them. It is handling weaknesses and threats to generate a positive effect. IKEA is developing an online assistance system to direct customers to a more sustainable life. On its website, it provides customers with information and ideas on how to lessen their influence on the environment. It will also help the business to be more cost-effective. The managers and co-workers are trained on sustainability, particularly on what IKEA is doing and how they can take liability to become responsible for themselves (Times, 2010). IKEA is huge enough to benefit from the economies of scale. The impact of such economies of scale can be seen in lower average operations costs. The company has a team of specialized individuals who have integrated sophisticated technologies, which have helped reduce costs throughout its operations. Because of its ability to derive benefits from high levels of economies of scale and lower business costs, the company can offer highly price-competitive products for consumers. From this, it could be suggested that due to its unique position in the market, the company can establish high barriers for new market entrants.
- Since KEA offers products at a price level that is reasonable and affordable for individuals, it creates a greater demand for its products in times of financial difficulties prevailing in their respective markets. It is imperative to keep prices as low as feasible when the retail sector is dejected. The company should guarantee that it is determined to have the lowest prices in the market in the upcoming years. In order to bring awareness among consumers, it is essential to communicate with the customers through different media channels and promotional strategies (Times, 2010).
Consumer Behaviours Influencing IKEA’s Marketing Strategies
The IKEA world rotates around fashionable design, low prices, madcap promotions, and a passion few organizations in or out of this business can boast. More than any other corporation in the world, IKEA has become a keeper of people’s living standards, if not their lives. At a point when customers face so many alternatives for everything they buy, IKEA offers a one-stop shelter for assurance and self-reliance. It is a reliance-safe zone where people can enter and instantly become members of a like-minded, cost, style, and environmentally-sensitive global tribe (Business Week, 2005).
The IKEA company has plenty of opportunities to run the business successfully. It accounts for 5% to 10% of the furniture market in each country where it manages and sells its products. More significant, says CEO Anders Dahlvig, is that “Awareness of our brand is much bigger than the size of our company. That is because IKEA is far more than a furniture merchant. It sells a lifestyle that customers around the world embrace as a signal that they’ve arrived, that they have good taste and recognize value” (Business Week, 2005). The founder of IKEA, Ingvar Kamprad, is one of the most successful entrepreneurs who has led his business by creating new designs and products to shape consumer trends and tastes.
The company invests a significant amount of costs in opening its new stores, that is, on average, $66 million, to ensure that the location of stores and products offered are feasible for long-term returns. CEO Dahlvig is eagerly enhancing IKEA’s profile in the three fastest-growing markets: the US, Russia, India, and China. He believes the ground is broad open in the US: “We have 25 stores in a market the size of Europe, where we have more than 160 stores” (Business Week, 2005).
IKEA offers exclusive catalogs to attract and fascinate consumers. Pieces address the intricacies of customer traditions. The IKEA catalogs are about uniqueness and personal style. They are distributed worldwide to 175 million people. The IKEA catalogs combine fine arts and marketable production (Christopher, 2008).
IKEA Localisation of Global Market
The company has recognized that most of its market constitutes middle-class customers with typical buying behavior and preferences. The customer expenditure patterns are also similar throughout all countries. Despite these similarities, IKEA comprehends that in order to strengthen its position in the global market, it is obligatory to localize. For example, in China, in 2005, IKEA produced 250,000 plastic placemats to commemorate the year of roosters (ICMR India, 2010).
IKEA’s promotional campaigns are based on exceptional marketing situations and cultural susceptibilities of each country, which differ radically across markets. For instance, European billboards and commercials, particularly in the UK, were more clear-cut than those in North America, which were usually more humorous. For more than twenty-five years, IKEA stores have been available in some countries, such as Canada, Sweden, Australia, and Germany. In contrast, in countries such as the United States, Russia, Britain, China, and Italy, the company has operated for only slightly more than a decade (ICMR India, 2010). During all these years, IKEA has worked with numerous advertising agencies to carry out some of the most inspiring and exceptional television advertisements across the globe.
Conclusion
IKEA is a renowned international brand with hundreds of stores worldwide. Through this research, it is suggested that the company should further evaluate its markets as competitive forces are aligning to impose new challenges for the company. The company needs to make new strategies to keep its strong financial position. It will reveal the essential opportunities it can use and the threats that should be dealt with to retain the market share. IKEA acts by relying on its strengths and cutting down on its weaknesses. With this approach, the company has maintained a strong identity in the market, and over the years, it has continued to promote effective business development strategies.
IKEA’s enthusiasm includes design, low prices, cost-effective use of resources, and accountability for people and the surroundings. The company’s products, progression, and structure reveal its environmental position. For instance, innovative exploitation of packaging and design means that more goods can be stored in a crate, reducing the number of delivery journeys. It basically lessens IKEA’s carbon footprint.
The company also offers support and assistance in furnishing homes and offices. It provides some valuable and exceptional suggestions like which furniture can fit your home according to the space accessibility or which color of wallpaper will go with that furniture. You can obtain the entire home and office-associated information from the professionals at IKEA. The company also offers delivery services for its customers and ensures that the product is delivered to the customer and accepted with the highest level of satisfaction. In addition, there are special offers the customers can avail of to make their shopping experience more enjoyable. IKEA’s wide variety of products has enabled consumers to select and place the finest and most affordable products in their homes and offices. Presently, the organization is renowned for its product development, resourcefulness, and ability to respond and offers a great variety of products across the continents.
Recommendations
IKEA should intend to go further in building prosperity and reputation. In order to create a renowned trademark in Ireland, IKEA’s primary objective should be to become a significant example in raising a sustainable business. It will form an improved everyday life for its consumers. IKEA can retain its market value in Ireland by planning to counteract the threats, especially by using innovative ideas and focusing on the company’s strengths. IKEA’s pricing approach targets customers with restricted financial resources; it should also create products for high-class consumers by providing high-quality designs and extraordinary styles. IKEA has also discovered a new business reality where being sustainable and accountable is not just the best for consumers and the planet, but it is also highly beneficial for the business itself. Therefore, the company should always pay attention to this fact and continue providing functional and innovative styles and products to the people to attain a high market share.
List of References
All Business, 2005. IKEA brings picture to life. Web.
Artisan, 2004. IKEA Furnishing the world. Web.
Business Week, 2005. How the Swedish Retailer became a global cult brand. Web.
Christopher, Y.A., 2008. IKEA idea challenges consumer behavior. The Columbus Dispatch. p.1.
ICMR India, 2010. IKEA’s Global Marketing Strategy. Web.
ICMR, 2010. IKEA’s Cost Efficient Supply Chain. Web.
IKEA, 2003. The Values that characterise IKEA. Web.
Leggett, K., 2009. Service = Brand, Part 2. Web.
Kumar, S. & Kumar, S. 2010. IKEA-Case Sudy. Web.
Miller, M. P. 2010. IKEA with Chinese Characteristics. The China Business Review. p.1.
Times, 2010. IKEA SWOT analysis and sustainable business planning. Web.