LEGO
A Case Study
Problems and Issues Faced by the Firm and Leadership
- The Lego Company faced its first financial crisis in 1998 and addressed the largest internal economic decline by 2004.
- The Lego Group’s supply chain did not manage to follow the changing dynamics within the market and timely manufacturing. The issue of complexity affected the design, production, service supply of retailers, forecasting, and inventory control.
- The restructuring program targeted at the cost-cutting strategy resulted in a staff reduction of about 10% of the total employees.
- The company has a poor organizational strategy since there was an evident lack of monitoring of the engineering, manufacturing, and production costs processes.
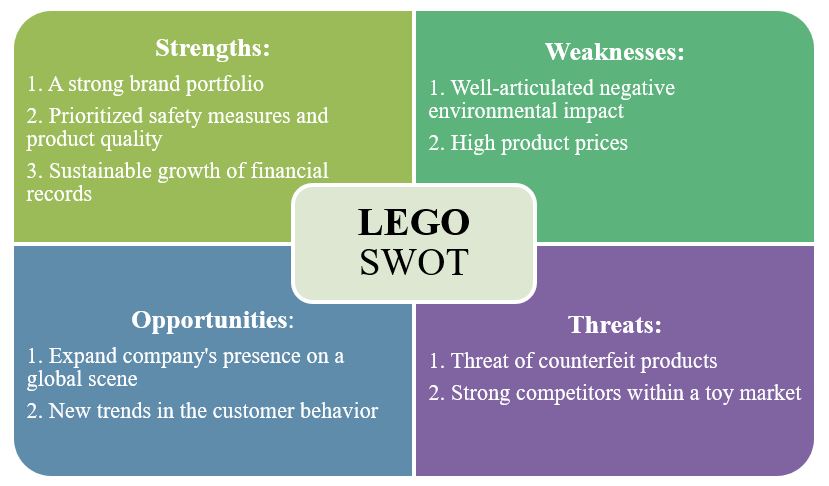
SWOT Analysis of Strategy
Marketing Strategy
Four P’s
PESTEL Analysis
Recommended Courses of Action
Improve Online Communication
The first step toward an improved organizational strategy would be to work on LEGO’s social communication, both online and offline. It is vital to include more initiatives aimed at the ability to increase customer engagement and build a stronger community with a focus on the parents’ population. LEGO might create a database of parents who would establish a community of loyal customers and engage in open discussions concerning the development of creativity, new ideas, and effective ways of applying LEGO blocks in education and other spheres of children’s development. Such a strategy can enhance the company’s relationships with customers and validate the existing price tags.
Focus on Supply Chain and Cost
Considering the company’s failure with supply chain management, cost-cutting should be the primary objective of the Lego Company. This step might involve the assessment of the general procurement process, as well as the reduction of the suppliers. Therefore, this strategy can reduce costs significantly and provide high-level savings for the company annually. In addition, the Lego Group can implement an outsourcing approach in order to save production costs. Finally, referring to the seasonal nature of Lego’s toys, it should have a flexible supply chain to manage its international manufacturing process more efficiently and focus on the association with Flextronics. Hence, this can help in avoiding the staff reductions that happened during the restructuring program.
Reconsider the Organization Strategy
The manufacturing and distribution sites should be located close to the biggest markets of the company. This would reduce the delivery period and have a beneficial impact on delivery costs. The complexity issue that Lego faced can be eliminated by the removal of a niche market. The flexible and eased level of products’ complexity might promote using more common Lego’s parts in terms of the product range. The company should reorganize its purchasing norms, lessen the number of suppliers, improve business communication, and advance the management of innovation costs and product development. To conclude, the Lego Company should not participate in supplementary and not-profit-making enterprises and prioritize the production that makes a profit. Lego can re-establish its leading position in the market by implementing a reliable and innovative business strategy and critical changes based on the analyzed weaknesses and issues that led to the financial crisis.
Reference
Rivkin, J., Thomke, S., & Beyersdorfer, D. (2013). Lego (A): The Case. Harvard Business School. Web.