Introduction
Organizational development depends on multiple factors that are interconnected and illustrated through the overall outcomes of the company. While employee satisfaction, customer demand, and competitiveness on the market are vital factors that highlight how the business operates, specific negative implications may affect all these essential concepts. The identification of the adverse outcomes and the implementation of possibly effective solutions are two of the main organizational development aspects that can drastically improve the company on multiple levels and contribute to a more favorable external and internal environment. First, it is crucial to identify the exact problems and the levels in which these issues occur. A diagnosis will highlight what areas need improvement and illustrate what needs to be done in order for these concerns to be mitigated. The diagnostic approach will include the identification of stakeholders, relationships, and contracting. Moreover, the first step will allow for a better understanding of the exact focused area that needs to be analyzed.
The second step that is directly linked to the diagnostics phase is the intervention. This includes identifying the issues that will be addressed after the organizational diagnosis creates a transparent overview of the situation. The solution will require a design and an identification of desired outcomes. Moreover, the new implementations will be justified and explained in terms of the levels they will affect and the overall results that the strategy will generate. Such an approach will include both an analysis of the organizational structure and potential issues. Furthermore, the decision-making process in regards to how the problems in questions can be mitigated will be illustrated.
Diagnostic Approach and Structure
Organizational diagnosis involves an in-depth analysis of how the company operates, what levels do not meet the required standards, and which areas need improvement. First, it is vital to collect data and valuable information that will be then examined and scrutinized. Such data includes productivity rates, revenue during several months/years, and subjective information gathered from employees. The workforce is an essential factor that can compromise organizational productivity, which is why it is vital to receive feedback in regard to personal experiences within the company. Such information can be obtained through questioners, interviews, written/verbal feedback, etc. This will allow for clear visualization of the overall job satisfaction among team members and areas that need intervention.
Weisbord’s six-box model is one of the models that allow leaders and consultants to operate a diagnosis within their organization. According to researchers, this method examines the purpose of the company, the structural characteristics, the reward systems, leaders that operate the main tasks, cooperation, and coordinating mechanisms (Adebayo et al., 2021).
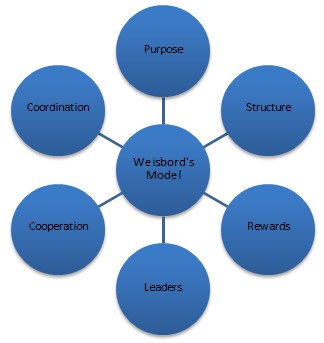
The first step is identifying the purpose, which highlights the aim of the business, its ideas, and the market area in which it operates (Figure 1). Moreover, the diagnosis has to include an analysis of the structure, which touches upon how responsibilities are divided within the workforce. This is linked to another concept within the model, which is cooperation. Cooperation is the notion that explores relationships in the team, whether the communication is effective, and how conflicts are being mitigated. Furthermore, the next factor that focuses on employees is the rewards system. According to researchers, unsatisfying salaries correlate with low productivity (Vinod, 2017). A lack of an adequate rewards system is a significant risk factor that may lead to adverse organizational outcomes.
Since team members rely on their leaders for guidance, motivation, and inspiration, it is vital to examine the leadership style. Researchers point out that an effective leadership style such as the transformational one correlates with team productivity (Buil et al., 2019). This evidence proves that an effective leader can drastically improve organizational outcomes. On the other hand, autocratic leadership styles have opposite results in terms of employee satisfaction and the overall internal environment of the company.
Coordination (supporting mechanisms) is the area that illustrates all the connections between departments and supply chain actors. This includes communication, systems that control budgets, plans, and specific procedures requiring collaboration between more than one entity. A lack of an efficient mechanism of cooperation may lead to adverse outcomes in terms of production, deadlines, coordination, and professional relationships. It is vital to have a system that supports such measures so that the work process is smooth and risk-free.
Stakeholder Identification, Relationships, and Contracting
The diagnosis is redundant without identifying the stakeholders. The stakeholders are all the parties that are affected by the business, how it operates, and the outcomes that it generates. Moreover, the relationships between the stakeholders and the company illustrate the extent to which this impact will be noticeable.

The stakeholders can be divided into internal and external (Figure 2). Internal stakeholders are the individuals who directly contribute to the organization as active members. The external ones, on the other hand, are only impacted by the organization without actively involving themselves in the corporate structure. Stakeholders are not always economically affected by the business (media, unions, etc.). Considering only centralized parties financially involved in organizational processes leads to a significant lack of information regarding other essential entities (Fritz et al., 2018). Moreover, all the individuals and institutions have different relationships among them and with the business in question. Another aspect that contrasts is how the parties are involved in the organizational structure and whether there is a direct or indirect participation.
Identifying the correlation between the business and the internal stakeholders is unchallenging due to the fact that all the individuals in this category are active in the company’s work process. Employees, contractors, managers, and business owners are directly affected by the company’s outcomes in terms of wages, investment, profit, etc. External stakeholders are not directly related to the organization. The government’s relationship with the business is established by the regulations that need to be followed. Moreover, consumer demand influences what types of products or services an organization provides, which is also related to what the general population desires from a business.
Suppliers are in charge of raw materials, and they are responsible for ensuring high quality and a reasonable price that will not cause the business to experience financial losses. Media and unions have a powerful voice that can impact the reputation and the overall branding, which can influence consumers’ perception of the company. Investors and creditors have a financial interest in the business, and this is why low productivity adversely affects them.
Interventions may or may not require third parties involved in the problem-solving decisions. Contractors are usually the consultants who have expertise in diagnosing an organization, pointing out the areas that need improvements, and designing solutions before implementing them. Having an outside opinion can be beneficial because it minimizes the risk for subjective bias. In case an organization relies on the judgment of the leaders, there is a chance of a lack of perspective and an emphasis on personal goals. However, hiring an outside expert can be a catalyst for change and reforms.
Potential Diagnostic Areas of Focus
It has been established that the significant organizational issue is productivity which does not meet the required standards. There are several aspects that may lead to such outcomes. This is why it is important to examine the areas that need improvement for the production levels to increase. The first aspect is the type of leadership. Researchers point out that effective leadership is one of the fundamental forces that encourages beneficial organizational changes (Griffith et al., 2019). Transformational leaders are considered the managers who are able to build a strong workforce that is motivated to be effective and proficient in the domain in which they operate. On the other hand, ineffective leadership creates a hostile environment that does not allow team members to activate their full potential, productivity, and innovative mindset.
As mentioned prior, leadership directly affects the employees, which is why it is vital to assess job satisfaction. Low satisfaction within the workforce can lead to low productivity. A strong team consists of individuals who want to improve and cooperate for the sake of the company. Instead of focusing on individual goals, a united workforce achieves greater organizational objectives and works towards a more prominent organizational structure. This is why the workforce is another domain that potentially compromises organizational productivity.
A business with a motivated, innovative, and hard-working team is less likely to experience failure. Since employees’ morale is high, they are able to externalize their skills through their work and allow the company to reach high levels of productivity, competitiveness, and consumer satisfaction. However, a team that lacks inspiration, desire to contribute to the workflow, and will to be active is a burden for the company in which they operate. While managers approve or build structural concepts, come up with essential ideas, and control organizations, the human resource is the one that has to keep the production levels high. This is why the workforce is one area that needs to be focused on when trying to create a productive environment and a higher chance for the company to improve.
Approach to Identifying Solutions
The diagnosis allows for a more in-depth understanding of the organization and the possible issues that affect competitiveness, the internal environment, and other significant business areas. After examining the stakeholders and the possible areas of focus, it is essential to analyze the solutions that can mitigate the problems. First, it is crucial to consider the areas of focus highlighted in the diagnosis phase. Since employee morale and leadership are two of the critical aspects that impact productivity, the solutions have to address these particular issues. If the intervention focuses on the workforce and the leaders in terms of their managing approach, the objectives will be to improve job satisfaction and address the leadership style. Advancing in these domains will lead to healthy professional communication within the workforce, relationships based on trust and understanding, and motivation that will encourage all parties to address the productivity issue effectively.
Design Approach
There are two possible problems that have to be considered when designing the interventional approach. Since leadership directly impacts organizational outcomes, leaders will receive adequate tools for learning about effective methods of managing a team. First, it is crucial to directly assess how the managers view their position, what the challenges are, and how they usually address conflicts. The information can be received through personal interviews and questioners addressed specifically towards leaders. After gathering data, it is important to give them the knowledge regarding certain organizational situations and solutions that have been beneficial for other companies in the same position.
Courses, training, and meetings with other leaders are excellent ways of creating open discussions. Moreover, managers will be able to share their personal experiences of mitigating conflicts within their departments, dealing with crisis situations, and consolidating their leadership styles within their work environments. Third-party contractors can be hired to expand on specific topics that current managers are less familiar with. Meetings with such experts are helpful in terms of new knowledge designed towards improving production levels and managing employees efficiently.
When it comes to addressing employee morale, several policies can be implemented. First, it is important to focus on team-building exercises. Team building is an excellent tool used within organizations to create a positive atmosphere that motivates individuals to improve their productivity and effectiveness. Employee satisfaction directly correlates with the company’s overall performance (Al Kurdi et al., 2020). Similar to the intervention for leaders, employees can benefit from communicating with each other and attending courses to learn new information and create a collective mindset.
The first improvement that managers tend to apply is an increase in wages. However, this is an issue for multiple businesses that are not financially able to significantly increase salaries (Shan & Tang, 2020). Researchers point out that subjective measures such as moral support can be just as effective as monetary rewards (Leitão et al., 2019). If the organization can remunerate excellent performances, a possible solution will be implementing a reward system. This will ensure high productivity since bonuses depend on the effectiveness of a particular employee. Such rewards positively affect job satisfaction and high morale (Ahn & Kwon, 2018).
In order for such financial bonuses to be implemented, it is important to have certain performance management measures that will highlight the amount of work each team member does daily. Monitoring employees gives managers an opportunity to assess how the workforce operates, deals with professional tasks, and copes with stressful situations (Pestana et al., 2020). Moreover, performance management strategies are redundant without keeping track of the effort put towards the organization’s goals. Bortoluzzi et al. (2021) refer to such performance measures as KPIs tables as effective ways of controlling the workflow. Since the company aims to achieve a higher level of productivity, there needs to be an implementation that would control the team in terms of actively contributing to the everyday tasks.
Job satisfaction is interconnected with how team members are being treated by their colleagues and leaders. This is why it is crucial to consider the psychological aspect of being in an organization. Stress, burnout, mental health issues, or having problems connecting with other individuals within the workforce can drastically change one’s perspective on their job. Moreover, it is imperative to offer support during crises or any other organizational issues that may lead to low morale. According to Kour et al. (2019), implementing concepts that address one’s psychological well-being has been found to be beneficial for organizational performance. This includes moral support, motivation, transparency, praise for good work, and open discussions with team members who meet difficulties within their work environment.
Design Criteria
Precise objectives have to be examined and illustrated in order for the solutions to be implemented and for the intervention to be successful. Researchers mention interventions often being unsuccessful due to the lack of desire to change and improve (Achterbergh & Vriens, 2019). However, by having a direct aim towards a greater goal, such risks are being minimized.
The first objective is to improve the leadership styles and ensure the leaders are proficient in managing their teams. A precise goal is to ensure managers are able to verbalize their thoughts and ideas in an efficient way. This will be achieved through training and exercises with professional speakers, other successful managers, and experts in the field. If leaders have the ability to verbally illustrate their ideas, motivate employees, and highlight certain organizational goals by the end of the training, the aim will be achieved. Moreover, another objective is teaching leaders how to build and implement a long-term plan. Researchers mention that a focus on productivity without addressing quality is redundant (Thorat & Mahesha, 2020). This is why leaders will have to present a plan in which multiple organizational outcomes are predicted, and a strategy towards achieving said objectives is constructed.
One more goal is examining whether leaders have learned to interact with other team members in a way that they feel empowered and inspired to be more productive. This will be achieved through monitoring such interactions, questioning team members about how they perceive the recent changes, and having discussions with the leaders themselves. As mentioned prior, transformational leadership is the style that has recommended itself as most effective for improving productivity (Mahmood et al., 2019). Giving managers an understanding of what the implications of this concept are and how to externalize them within their organizations is the primary goal of improving leadership.
The design criteria for improving job satisfaction among employees includes several significant objectives that the intervention aims to fulfill. As mention before, the first design approach is building a solid and united team. The criterion for this implementation is creating specific team-building courses and events where team members will be able to interact outside of their usual work environment. Weekly professional meetings and monthly events where individuals will communicate can contribute to the consolidation of a collective mindset. This will promote the idea that each employee is a part of a bigger team rather than an individual with personal goals as a primary concern.
To motivate the workforce even further, a reward system will be implemented. Each employee is to be monitored in terms of productivity, work hours, and effectiveness. This can be done through KPI tables and digital systems to analyze the amount of work and the number of tasks each person has achieved within a month. The best results have to be rewarded with bonuses, which motivates colleagues to become more proficient and achieve the same results. This will contribute to a more active workforce and be less financially expensive for the company compared to an increase in wages. Moreover, this method is designed to reward efficiency rather than solely use the money to increase satisfaction without any additional measures.
Furthermore, low employee morale must be address. Since effective leadership strategies directly correlate with job satisfaction, implementing the measures aimed at managers is the first step towards high morale. Moreover, psychological support can be accentuated by allowing team members to have honest and transparent discussions with their superiors. In case an individual is unsatisfied with the position, wage, work environment, or other conditions, they should be able to give feedback without any repercussions. Every leader has to inform the workforce that commentary is welcomed and their offices are safe spaces where every issue can be openly addressed. This will give team members the empowerment to speak up, a sense of validation, and an understanding that they are being appreciated and valued in their professional setting. Since this is one of the primary needs within every organization, empowered individuals tend to be more satisfied, which leads to better outcomes and higher productivity.
Desired Outcomes
The intervention touches upon two different areas that are interconnected, which means that the desired outcomes are linked to the domains that are to be improved. The general objective is to improve organizational productivity in order for this measure to reach standard levels. It has been established that in order for the productivity levels to increase, two possible areas that need to be focused on are leadership and job satisfaction. In terms of leadership, the desired outcomes would be to establish an effective leadership style, focus on transformational concepts to motivate employees, and establish close relationships between managers from different departments to promote sharing information and advice in challenging situations. The implementation can be considered successful if the managers use techniques based on the transformational style to operate the team in a way that the outcomes illustrate productivity and efficiency while maintaining high motivation. Moreover, monthly executive meetings attended by all leaders are other excellent portrayals of the intervention being maintained within the business structure.
Several desired outcomes focus on employees, their job satisfaction, and high morale. First, the team-building addition will create a more positive atmosphere where colleagues will feel like they are all aiming for the same goals. Collegial relationships have to be professional yet close and based on trust and unity among team members. Such a close-knit community with the same organizational culture and long-term objectives will be a strong force towards productivity and positive outcomes.
Another goal is to observe a strive towards proficiency in each individual working for the company. If a reward system is put in place, the results will have to show an increase in productivity in every team member. The results will most likely show that employees are less likely to take unauthorized breaks, come in late, and leave the office early. Moreover, the digital system has to illustrate that the time each person spends fulfilling professional tasks is longer compared to previous measures. Positive competitiveness is the objective that will allow individuals to perform better and aim for higher results to receive the monthly performance bonus.
Moreover, a key objective that is focused on mental well-being and mitigation of burnout and stress is creating an environment where the workforce is valued, listened to, and supported by superiors and colleagues. The desired outcome is for employees to frequently visit managers with discussions and concerns in regards to their professional environment. Moreover, the weekly meetings within the organizations have to be the platforms that people use to express their feelings, doubts, or satisfaction in regards to a particular change or reform in the company. Such implementations will hopefully encourage employees towards being transparent and verbalizing their worries before the management decides how to mitigate them or compromise with the person expressing said concerns.
Solution Decision-Making
The diagnostic approach allows for an in-depth understanding of how an organization operates, its structure, stakeholders, and potentially problematic areas that need improvement.
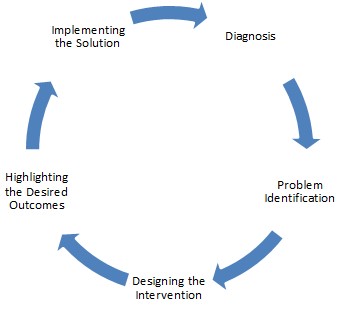
After analyzing data and collecting information about the business in question, it is important to find out what the issue is and what domains need to be addressed to mitigate this concern (Figure 3). Identifying the problematic structural areas is vital for the following steps in which these risks are addressed. After examining the business and identifying the issue and why it occurred, the intervention is designed. The design must address all the areas mentioned above in order for the outcomes not to be compromised. Furthermore, planning the desired objectives will allow for a better understanding of the future organizational changes followed by the implementations. This strategy improves long-term interventional goals and allows managers to be ready for possible shifts within the work environment.
All these steps contribute to the primary goal, which is the implementation of the solution. As highlighted prior, the decision-making process is based on objective data and strategies formulated after an extensive process. This process includes examining, planning, and considering all the factors that may influence the business before, during, and after the solution is applied. It is crucial to mitigate risk factors such as adverse outcomes for stakeholders. However, since the organization is inefficient in terms of production levels, the decision is based on the main goal, which is improving productivity.
Conclusion
Organizational development directly depends on productivity. In case productivity is below the standard levels, the company experiences problems on all levels, including financial profit, consumer satisfaction, internal environment, and negative implications for the stakeholders. There are several possible areas that affect the efficiency to which a business operates. Some of the most eminent domains are leadership and job dissatisfaction. Both leaders and followers directly influence how the company operates, which is why it is vital to address these concepts during the diagnosis process.
Inefficient leaders are not able to manage the workforce efficiently, promote motivation, and improve organizational outcomes. On the other hand, an unmotivated team with low morale and no strive for innovation is most likely to cause the entire business to suffer financial losses. In order for the managers to be able to change the situation into a more favorable one, a transformational style is recommended. Moreover, leaders will benefit from having weekly meetings, attending courses, and communicating with other individuals in similar situations. Employees will benefit from receiving rewards for hard work, being supported by superiors and colleagues, and having a system that will monitor their performance and support them based on the results. Open discussions, feedback, and praise for good work will empower individuals and create a positive environment that promotes high-quality products and services, productivity, and effectiveness.
Reference List
Achterbergh, J. and Vriens, D. (2019) ‘Designing episodic interventions’, Organizational Development. doi: 10.4324/9781315695228.
Adebayo, O. P., Worlu, R. E., Moses, C. L., Ogunnaike, O. O. and Salau, O. P. (2021) ‘An organisational diagnostic model for a sustainable organizational performance’, IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 655(1), doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/655/1/012026.
Ahn, H.-Y. and Kwon, S.-B. (2018) ‘Effect of organizational diagnosis, job satisfaction and organizational commitment of a single-grade Korean medicine hospital using six-box model’, The Korean Journal of Health Service Management, 12(1), pp. 35–46. doi: 10.12811/kshsm.2018.12.1.035.
Al Kurdi, B., Alshurideh, M. and Alnaser, A. (2020) ‘The impact of employee satisfaction on customer satisfaction: Theoretical and empirical underpinning’, Management Science Letters, pp. 3561–3570. doi: 10.5267/j.msl.2020.6.038.
Bortoluzzi, B., Carey, D., McArthur, J. J. and Menassa, C. (2021) ‘Measurements of workplace productivity in the office context: A systematic review and current industry insights’, doi: 10.32920/14638242.
Buil, I., Martínez, E. and Matute, J. (2019) ‘Transformational leadership and employee performance: The role of identification, engagement and proactive personality’, International Journal of Hospitality Management, 77, pp. 64–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.06.014.
Fritz, M. M. C., Rauter, R., Baumgartner, R. J. and Dentchev, N. (2018) ‘A supply chain perspective of stakeholder identification as a tool for responsible policy and decision-making’, Environmental Science & Policy, 81, pp. 63–76. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2017.12.011.
Griffith, J. A., Baur, J. E. and Buckley, M. R. (2019) ‘Creating comprehensive leadership pipelines: Applying the real options approach to organizational leadership development’, Human Resource Management Review, 29(3), pp. 305–315. doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2018.07.001.
Kour, J., El-Den, J. and Sriratanaviriyakul, N. (2019) ‘The role of positive psychology in improving employees’ performance and organizational productivity: An experimental study’, Procedia Computer Science, 161, pp. 226–232. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2019.11.118.
Leitão, J., Pereira, D. and Gonçalves, Â. (2019) ‘Quality of work life and organizational performance: Workers’ feelings of contributing, or not, to the organization’s productivity’, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), p. 3803. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16203803.
Mahmood, M., Uddin, M. A. and Fan, L. (2019) ‘The influence of transformational leadership on employees’ creative process engagement’, Management Decision, 57(3), pp. 741–764. doi: 10.1108/md-07-2017-0707.
Pestana, M., Pereira, R. and Moro, S. (2020) ‘Improving health care management in hospitals through a productivity dashboard’, Journal of Medical Systems, 44(4). doi: 10.1007/s10916-020-01546-1.
Shan, C. and Tang, D. Y. (2020) ‘The value of employee satisfaction in disastrous times: Evidence from covid-19’, SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3560919.
Thorat, R. and Mahesha, G. T. (2020) ‘Improvement in productivity through TPM Implementation’, Materials Today: Proceedings, 24, pp. 1508–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.470.
Vinod, H. D. (2017) ‘Can low payroll growth cause low productivity growth?’, SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3015965.