Basics
- Do not use Wikipedia and other online encyclopedias as a source in a paper, as well as sources like SparkNotes, CliffNotes, etc. BUT: You can still review articles from such websites to understand the topic better.
- You should be interested in supporting your paper only with the most credible and relevant sources. Do not waste your time searching through non-reliable websites. Use Google Scholar and scientific libraries/databases. NB: Newspapers and magazine articles are NOT academic/scholarly/peer-reviewed articles.
- If you need some general information about the topic, you can use Google Books to understand the phenomenon or process, etc.
- If you need a comparison table or graph, search Google Images for examples.
- When you have found the required article or book, search for keywords within the file or on the webpage.
- If the book was published by Pearson or McGraw-Hill – look for their websites that support different editions of books. These sites often include outlines, chapters’ content, and slides on chapters.
Finding Credible Sources
When writing academic papers, it is necessary to use only credible or reputable sources. Credible sources are usually written by authors having degrees in a specific area or specialization, published by universities or well-known publishers, published in peer-reviewed journals, provide accurate information supported by evidence, and they are up to date.
Use the following credible sources in your academic papers:
- Scholarly articles published in peer-reviewed/academic journals (e.g., The American Journal of Nursing).
- Books written by professors or published by reputable publishers (e.g., Routledge, Springer).
- Websites of reputable organizations (e.g., UN, WHO) as well as governmental institutions (e.g., with .gov domains).
- Articles published in reputable newspapers (e.g., The New York Times).
- All sources used in the paper need to be carefully cited and referenced following the rules of a citation style (MLA, APA, Harvard, etc.).
Finding Books and Journal Articles
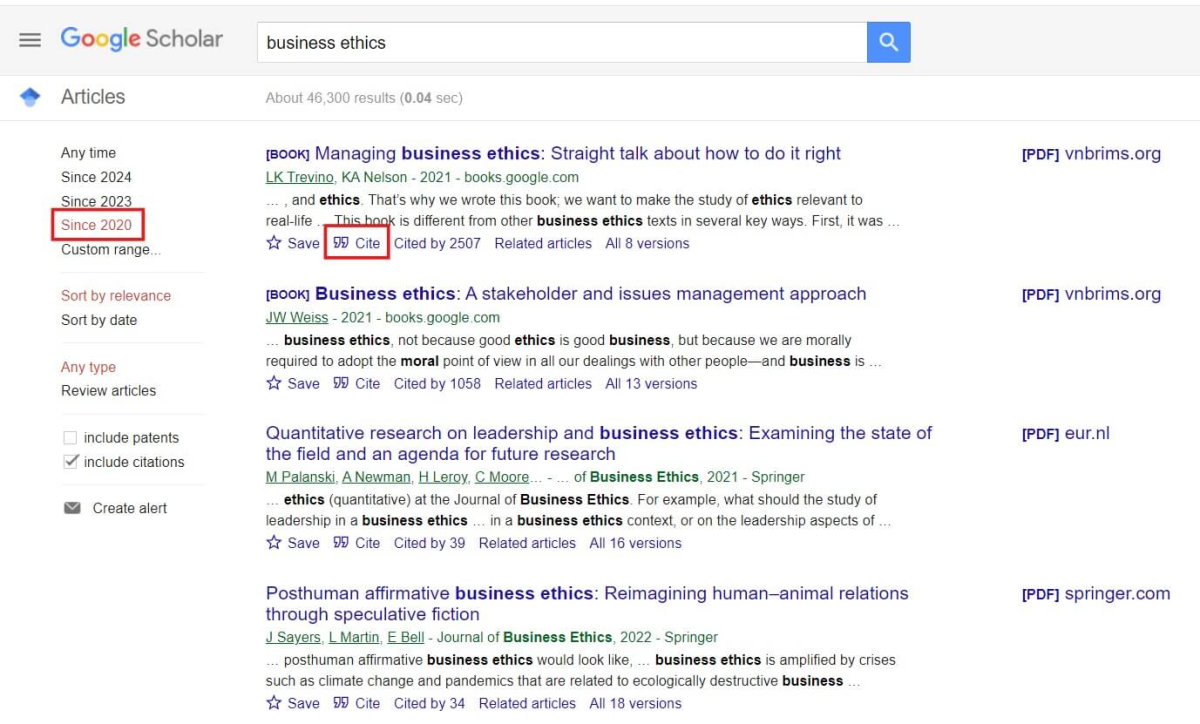
On the example of Google Scholar:
- Type your keywords. You may use quotation marks when searching for exact phrases. Example: “employee productivity,” ”uninsured adults.” To search only available PDFs – type filetype:pdf next to your keywords.
- Select the year: “Since …” (usually, within the past 5 years).
- You can select the time period using “Custom range” and set 2020-2024, for instance.
- Optionally, you may click on [PDF] … next to the source – you will be able to access the full article in a PDF format.
- Make sure the selected source is published in an academic/scholarly/peer-reviewed journal or is a book.
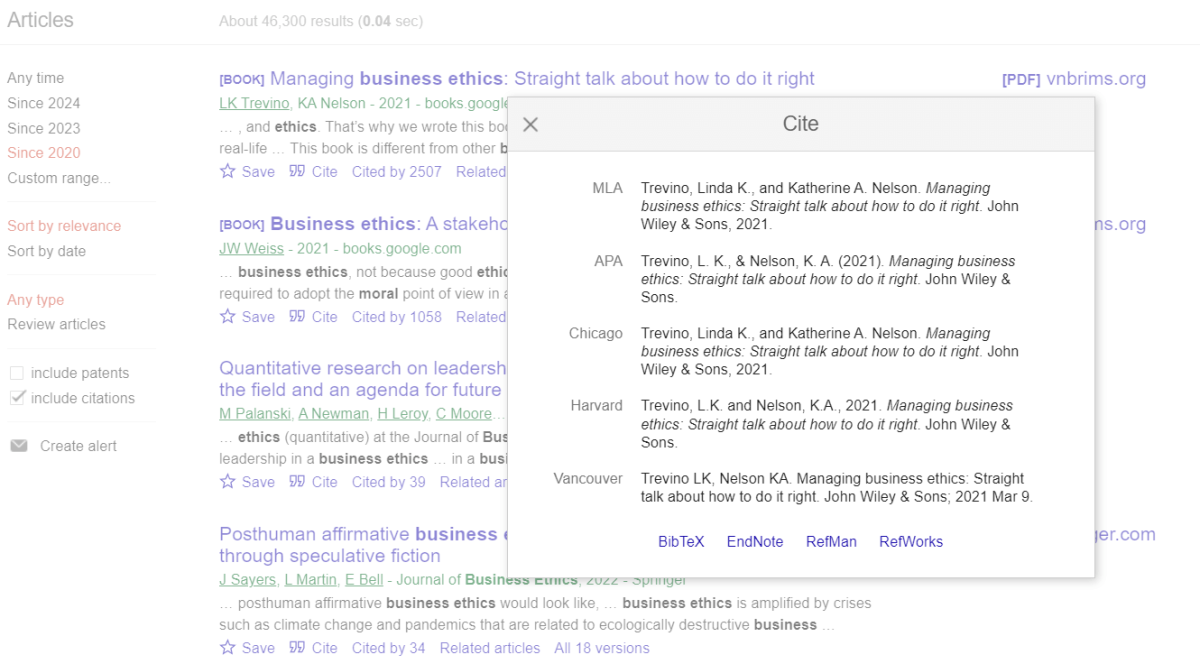
- Pay attention to the “Cite” button under the source.
- The “Cite” button leads to citations formatted according to 5 styles. Just copy and paste the prepared citation.
Using Databases with Credible Sources
When searching sources, it is preferable to use the following databases and libraries:
All sources used in academic papers should be published within the last 5 years.
❓ Searching for Sources FAQ
❓ Sources used in academic papers should be …
Relevant to the paper topic, credible, published within 5 years.
❓ Websites such as SparkNotes, CliffNotes, SlideShare, Wikipedia, and Quora may contain a lot of information on the topic of research. Is it encouraged to use them?
Never use or mention these websites in academic papers.
❓ What databases and resources are best to be used in academic papers? (Some examples)
Google Scholar, EBSCOHost, Jstor, PubMed.