Risk Identification
TransGlobal is a Filipino cargo carrier based at Clark International Airport. The airline offers scheduled and ad-hoc flights to the Middle East and destinations in North Asia. Risk impact assessment of the cargo airline indicates global congestion and rising and unstable fuel prices. An increase in jet fuel prices directly impacts airline companies’ financial portfolios (Georgiadis, 2021). As the Russian-Ukraine conflict continues to influence global oil price variation, the share of fuel in total operational costs for airlines is expected to remain unpredictable.
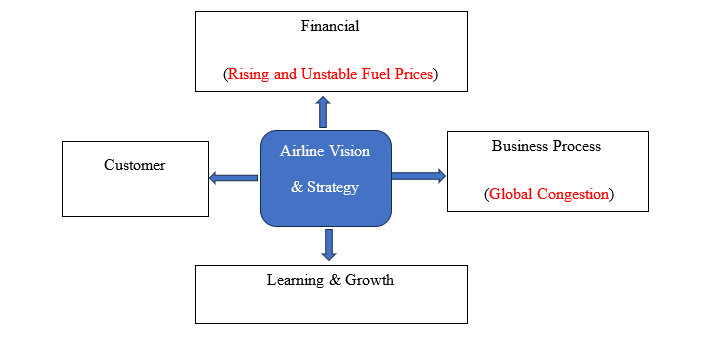
Global congestion, such as airport and air congestion, is another risk factor in the airline’s operation, which appears to have no clear solution, at least in the immediate future. Airports in Asia are frequently overcrowded, and flight delays have become the norm (Asian Aviation, 2023). Most flights appear full, and terminals are always packed, with the rise in air passengers playing a significant role in airport traffic, which subsequently affects cargo planes (Asian Aviation, 2023). Global congestion and unstable fuel prices are operational risks corresponding to the balanced scorecard’s business process and financial measures (see Figure 1).
Risk Evaluation
Global congestion and airport capacity issues are growing problems with the busiest airports reaching capacity. The sector is particularly concerned because airlines have little influence over global congestion and infrastructure capacity issues. Significant delays in handling flights and processing cargo have been caused by staffing shortages on the ground, notably in security, baggage handling, and ramp agents, adding to the persistent airport congestion (Wyman, 2019). Delays in the airline’s operations often cause serious disruptions, logistical challenges, and cargo management plans, amounting to significant financial losses. Although the carrier strives to make cargo transport seamless, congestion continues to create logistical challenges for the aviation industry.
Oil and aviation fuel costs have increased dramatically in recent years. According to some estimates, 30% of an airline’s operating expenses are fuel-related (IATA, 2020). Therefore, any rise could have a substantial impact on profitability. Although airlines continue to pursue tactics to protect themselves from rising fuel prices, this has proven particularly challenging due to unclear future oil prices, fierce competition, and the need to operate as efficiently as possible. An uncertain situation like this is difficult to manage, as it is in many sectors. Table 1 shows the risk-impact category based on the probability and impact of each risk.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Hedging offers a viable solution for airlines to mitigate unstable fuel prices. Airlines use fuel hedging as a financial technique to protect themselves against fluctuating jet fuel prices, particularly during unpredictable geopolitical periods (Georgiadis, 2021). Although this can range from six months to a year, the airline can hedge funds up to two years in advance. The duration is determined by several variables, including the airline’s long-term strategy, its evaluation of the market, and its capacity to withstand prospective price rises. Employing demand management techniques like slot allocation, congestion pricing, or peak-time scheduling can assist in short-term airport congestion control (Wang, 2022). However, the long-term option to increase airplane capacity and potentially reduce delays involves building more runways or expanding airport infrastructure.
References
Asian Aviation. (2023). SITA: More pax headed to the airport despite concerns over congestion and delays. Web.
Georgiadis, P. (2021). Fuel price increase threatens airlines’ recovery from pandemic. Financial Times. Web.
IATA. (2020). Industry fuel costs and net profit. Web.
Wang, X. (2022). Measures for airlines to reduce airport congestion fees: Scheme design and performance assessment. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 1–12. Web.
Wyman, O. (2019). Airlines struggle to cope with rush-hour-style congestion. Forbes. Web.