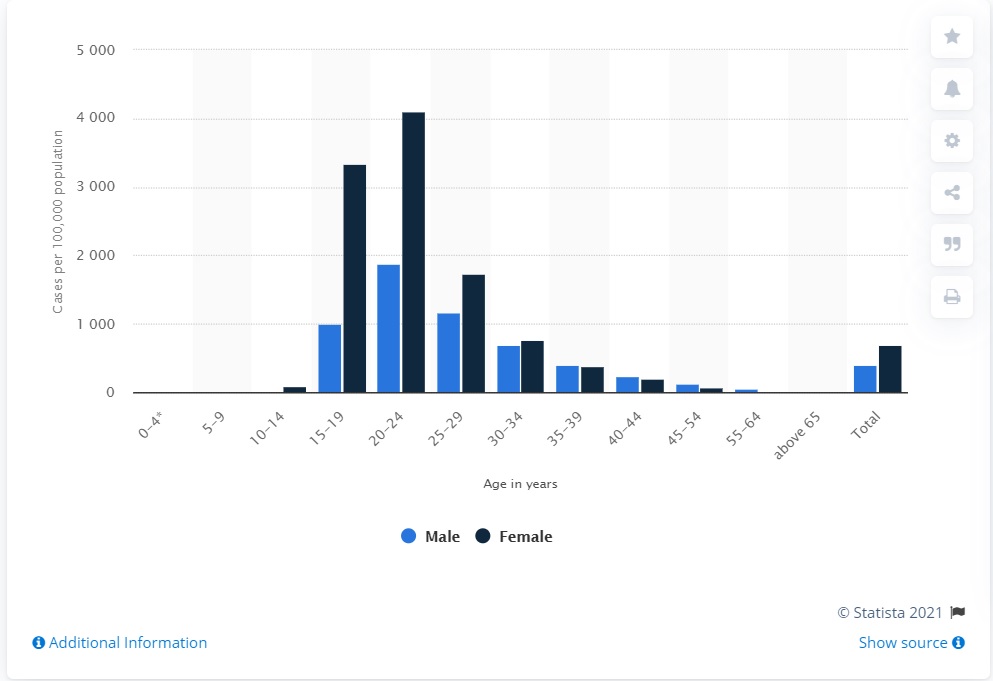
One of the most common sexually transmitted infections in the United States is chlamydia triggered by the bacterium called chlamydia trachomatis. Chlamydia infection is asymptomatic and can be easily cured with the help of antibiotics (Fig. 1). However, this infection might lead to long-term health consequences if it is not identified in time. Therefore, it is highly crucial to emphasize sexual health education and all the potential outcomes that can affect anyone. In the United States, the chlamydia cases statistics are overwhelming. More specifically, both Elflein (2021) and National Overview (2021) revealed that, as of 2019, rates of reported chlamydia cases have increased by 2.8% compared to the previous year. The numbers increase among males and females; however, the highest rates were noted for the group aged between 20 and 24 years: men – 1,871.5 and women – 4.109.5 (per 100,000 population) (Fig. 2). The overall figure of 1,808,703 cases of chlamydia in the United States in 2019 made it one of the most prevalent conditions in the region.
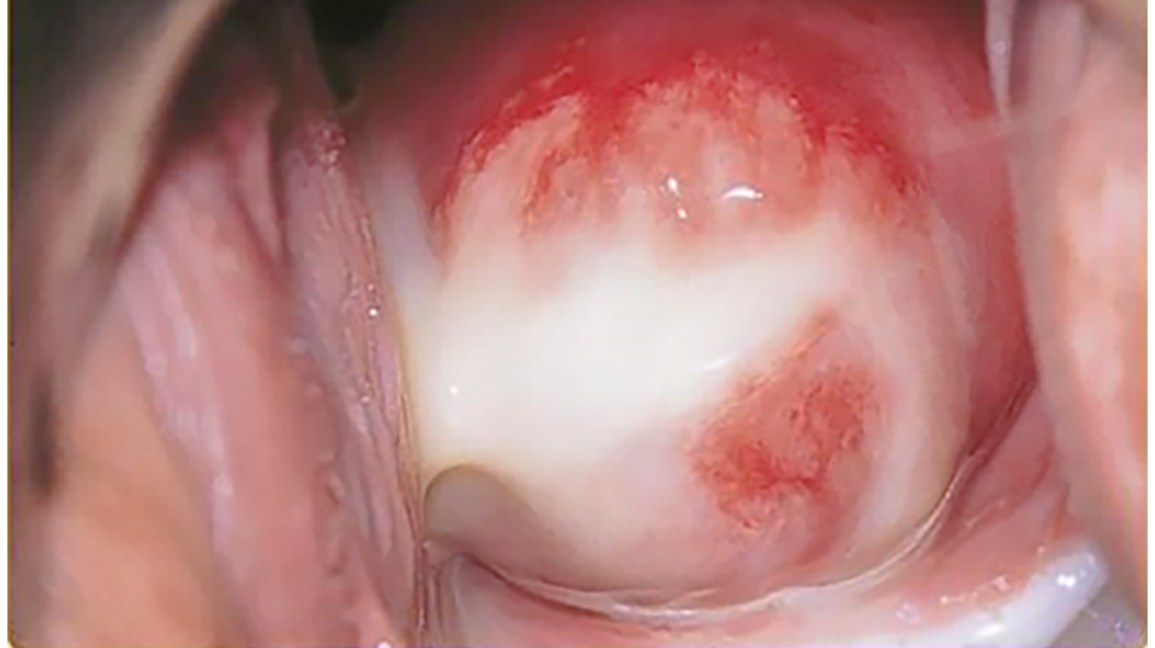
As a rule, chlamydia is transmitted through genital contact, including unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex. A person can also become infected through contact with infected semen or vaginal fluid (Seladi-Schulman, 2020). The most crucial preventive measure is using condoms to protect partners from getting infected and regularly check one’s health status. Despite being an asymptomatic disease, there might be some similar symptoms to other STIs. Chlamydia in men is characterized by a burning sensation during urination, pain in the lower abdomen and testicles, and yellow- or green-colored secretions from the penis. In women, the symptoms include dyspareunia, vaginal discharge, cervicitis, bleeding, burning sensation during urination, and pain in the lower abdomen (Seladi-Schulman, 2020). Moreover, some women might encounter the risk of infection spreading to the fallopian tubes, provoking pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
As mentioned above, chlamydia can be easily treated by antibiotics, which must be prescribed by a doctor. However, in case of lingering condition, more radical measures have to be applied. For instance, PID is a severe and life-threatening illness that must also be timely treated with antibiotics. On rarer occasions, chlamydia might be the leading cause of infertility in men. Most importantly, when discovering any STIs, a person must be urgently tested for HIV and responsibly lead his/her sexual activity and think about the health of other people with whom one interacts.
References
National Overview – Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance, 2019. (2021). CDC. Web.
Elflein, J. (2021). Rates of reported cases of chlamydia in the United States in 2019, by age and gender. Statista. Web.
Seladi-Schulman, J. (2020). Everything you need to know about chlamydia infection. Healthline.