Introduction
The population of the elderly people in the United Kingdom and many other developed countries in Europe and North America has been in a consistent rise over the past decades. Improved healthcare systems, technological development among other human development index factors have extended life expectancy in these countries (Goodwin 2016). An increase in the population of the elderly people in the society means that there is an increased need to have systems and structures that can be used to support them. The number of care homes meant to provide shelter, healthcare, and social support for these people have been increasing because of the increased demand. These institutions need the support of the government and other stakeholders to ensure that they can offer effective services to their clients.
In this business proposal, the primary goal is to deliver healthcare services in a care home of 50 vulnerable residents. These elderly individuals are considered vulnerable because they do not have the capacity to earn a living on their own and they also have no direct support from their family members. The institution receives a weekly rental income of £1,200 every week from social services. The problem is that this amount of money is not enough to meet all the needs of the residents in this institution. As such, this plan seeks to help the institution by providing healthcare services needed by the vulnerable residents. The team intends to embrace integrated working framework to ensure that all the relevant stakeholders are involved when delivering the relevant services to the targeted population. This service delivery approach helps in ensuring that all the stakeholders are involved to enhance teamwork, avoid duplication of tasks, and to improve the overall performance. The goal of the programme is to ensure that the elderly who are living in the selected care home lead a long and fulfilling life, free from various illnesses.
The Proposed Services to Be Offered
The healthcare sector within the United Kingdom has been working on various programs to help support the elderly, especially as their population continues to increase. As a senior manager working in this sector, the researcher understands the need to offer this vulnerable group basic care to help prevent the development of serious medical conditions. The team intends to offer laboratory and x-ray imaging services to the vulnerable group. The decision to offer these services to the selected care home was based on the initial research that had been conducted at the institution. The study had revealed that the limited budget made it impossible for the management to pay for specialised screening of their clients despite the need for these services.
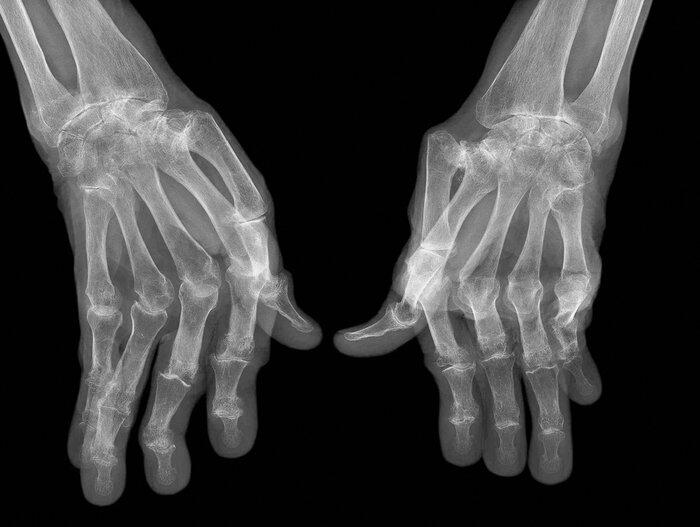
A significant majority of these residents could not afford to pay for the services on their own, and the institution’s limited budget could to support such specialised treatment services. As such, most of these patients had to visit public healthcare institutions to have access to such services. As Maruthappu et al. (2015) note, sometimes long distance movement among the elderly is a big challenge. As such, it helps when these services are brought closer to them. Figure 1 below shows an image of a patient’s hand who suffers from rheumatoid arthritis. This condition is common among the elderly. When it is detected at the right time, corrective measures can be taken to ensure that it does not worsen.
The Demand for the Planned Service among the Target Group
Laboratory and x-ray imaging are some of the most important medical services that the elderly people in home care need. According to Baxter et al. (2018), the aging people are highly susceptible to various medical conditions. For instance, a report by Harris et al. (2016) show that about 1.3 million Americans are affected by rheumatoid arthritis, most of who are the elderly women. Other common medical conditions among this vulnerable group include adult onset diabetes, arthritis, dementia, bladder and kidney problems, and Parkinson’s disease, cataracts, glaucoma, and lung problems. The more one advances in age, the more they become susceptible to these conditions. These conditions can only be managed effectively if they are diagnosed in time and the patient taken through proper medication as soon as possible.
The care home that is targeted has expressed their concern about their limited capacity to offer these services because their limited budget. Some of the screening services that they need are expensive. The fact that some of them may need regular screening means that there is a huge demand. According to González-Ortiz et al. (2018), managing the health of old people may be a challenge, especially if there is misdiagnosis. It is critical to ensure that their conditions are correctly diagnosed to ensure that the right medication is administered. It was noted, with great concern that the institution has been struggling to have access to these services for their clients. If this proposal is approved, the problem will be solved at this institution. All the residents of the care home will be receiving specialised laboratory and x-ray imaging services for free within the next five years that the programme will be running.
The Relevance of Integrated Working Framework in This Plan
The primary goal of this programme is to offer laboratory and x-ray imaging services to the elderly in a selected care home within the United Kingdom. To achieve the intended goals, the researcher, as a senior manager who has worked in the healthcare sector for years, understands and values the need to have an integrated working framework that will help improve service delivery. The care of these elderly individuals is a responsibility of many stakeholders in the society. The management and all employees of the care home, the local authority, family and friends, donors, and medical officers all play a central role in ensuring that the vulnerable group gets all the services and the attention that they need. As a team that will be offering screening services to these people, it is important to work closely with all the other relevant stakeholders.
The management and employees of the care home will play a critical role in enhancing activities that will be carried under this program. These stakeholders are involved in the daily care for the targeted group. They will help the screening staff to select individuals who are in need of urgent x-ray or other laboratory services. They will provide historic medical records of patients that will enable the staff to understand the nature of each patient’s medical condition. The screening staff will also work closely with the physicians and other medical officers who will be offering various specialised treatments for these patients. Once the screening is done and a specific medical condition is diagnosed, the next step is to provide relevant treatment for the patient.
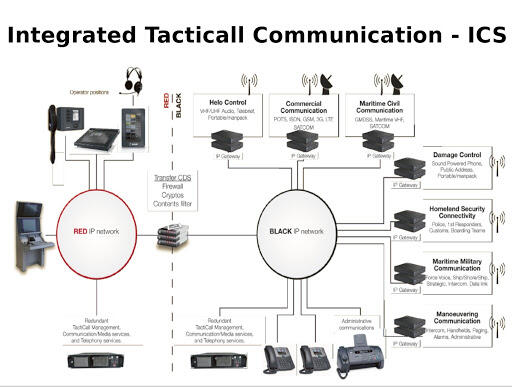
In this programme, there is a plan to have an integrated communication system, such as the one shown in figure 2 below. The system is meant to ensure that there is a seamless flow of information from one medical staff to another. Once the screening staff have made their diagnosis, they will make the information available in the central server. Doctors can easily find this information for each of the patient. They can request further laboratory services for each of the patients whenever it is necessary. The integrated system will enable the medical staff to make direct phone calls to specific staff members whenever there is an emergency. The goal is to ensure that all the medical needs of these patients are met effectively and within the shortest time possible.
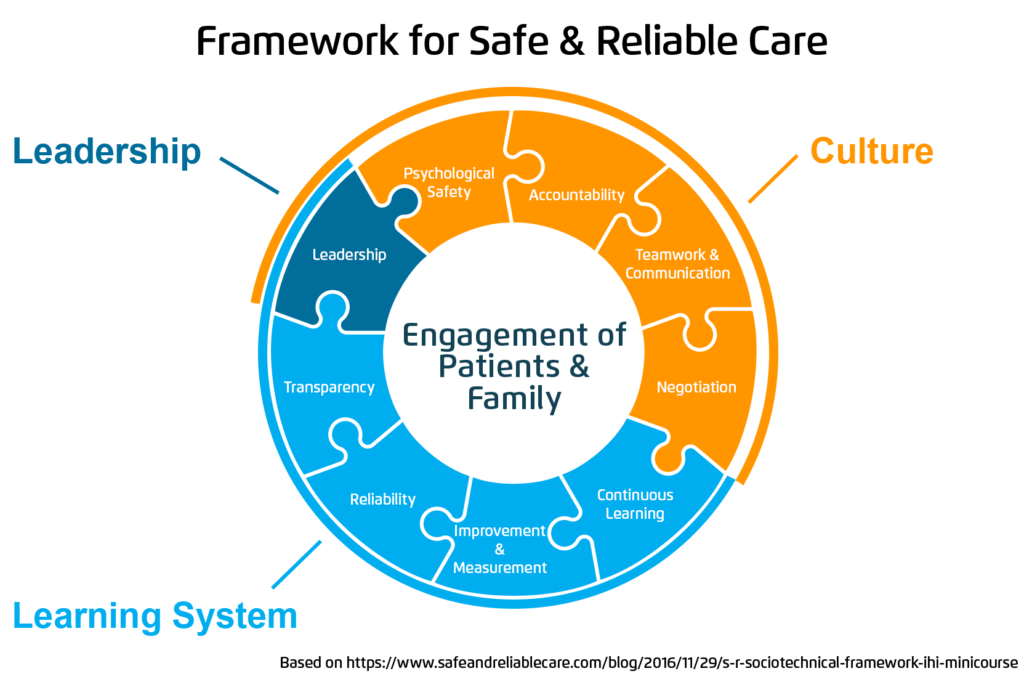
Family members of the residents of this care home are the other group of stakeholders in this integrated working framework. According to Binder (2016), there are cases when it becomes necessary for family members to accompany a patient when conducting some major medical tests. These patients would need reassurance that all will be okay. The screening staff may need the patient to be calm and composed to ensure that the test can be done accurately. Family members can help in calming a patient down. Where necessary, there should be a clear communication between the staff and these family members when their patient is going for a test. The staff can explain to the family member the role that they need to play to ensure that the process is a success. Donors are indispensible member of this integrated framework. The programme manager will ensure that all donors are briefed of the progress of the programme, challenges faced and how they are addressed, and the level of success. The local authority also needs regular updates. As the body that is responsible for the approval and monitoring of the proframme’s progress, the local authority officers will need to work closely with the staff involved with screening of these patients. Figure 3 below shows three factors that should be considered for a framework for safe and reliable care.
An integrated working framework requires leadership. Under this programme, the researcher will be the project manager. As the leader of the team that will be involved in offering the needed screening services, it will be important to demonstrate leadership. That involved motivating team members and enabling them to appreciate the significance of the role they will be playing. The project manager is the link between the team and other external stakeholders (Raydugin 2017). As such, the programme manager will ensure that there is an effective communication system with all the other relevant external stakeholders.
The figure below emphasises the need to have a learning system in an integrated working framework. Members will need to learn about the relevance of transparency and how it helps in achieving specific goals. They also need to know how to be reliable in every responsibility assigned to them. Improvement and measurements are also critical aspects of the learning system as shown in the figure. The model also emphasises the need to embrace continuous learning among all stakeholders involved in the project.
An integrated working framework can only be a success if the stakeholders embrace the right culture. In a medical environment, psychological safety is one of the most important factors that should be considered when defining the right culture. All those who are involved in the programme, including the patients, should feel that they are safe. Accountability is another factor that should define the culture under which this project will run. Donors to this programme expect their contributions to be used specifically for tasks they are meant to finance. A regular update should be made available to all the stakeholders showing how the resources are utilised and the progress made in improving lives of this vulnerable group. Teamwork and communication is another important aspect of the culture. As discussed above, the team will ensure that there is an effective communication system with all the relevant stakeholders. Negotiation should also be a culture that the team should embrace. Whenever it is necessary, team members should feel free to share their ideas about how best these patients should be served. In such engagements, members should be willing to take the best ideas and abandon their own when they are convinced that the chosen alternative would be more beneficial to a patient.
Policy Landmarks of Initiatives that Promote Integrated Working
The government of the United Kingdom has demonstrated its willingness to have an integrated working environment through various policy landmarks of initiatives. The United Kingdom Co-ordinating Body is one such entity that is meant to promote integrated working. The body is a unit within the executive arm of the government that works closely with national government bodies to facilitate the implementation of agricultural policies set by the European Union (Alam and Gühl 2016). Although the United Kingdom has officially moved out of the European Union, this body may continue playing a critical role in coordinating different arms of the government to help promote development in the agricultural sector.
The government has also established various institutions to help facilitated close coordination and inspection of activities within the healthcare sector. The General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC) is the body responsible for coordinating activities of pharmacists in the country (Ekanem 2017). It creates a platform where these medical experts can share their research findings and overcome common challenges they face at work. The General Medical Council (GMC) is the regulatory body for doctors in the country (Hawkey 2017). It not only registers qualified doctors but also ensure that they have a platform where they can coordinate their work and share new ideas. The Nursing & Midwifery Council is the institution that registers and coordinates activities of nurses within the United Kingdom (Morris 2017). These institutions work closely together to ensure that they promote an integrated working environment within the healthcare sector.
Types and Purpose of Data Required When Implementing the Plan
When implementing this programme, the team will need data that will inform their decision to ensure that the set goals are achieved. The team will use two types of data, which are the internal and external data. Internal data will be obtained from the direct x-ray and laboratory tests that will be conducted on the patients to determine their health condition. Historic medical records of these patients will also form part of the internal data. The second source will be the external data. They will come from external sources such as the prevailing medical conditions in the country. For instance, currently there is the threat of corona virus that started in China. In the United Kingdom, two cases have been reported. Such information may help in defining the laboratory tests that a patient needs when they present signs and symptoms similar to that of a corona virus patient.
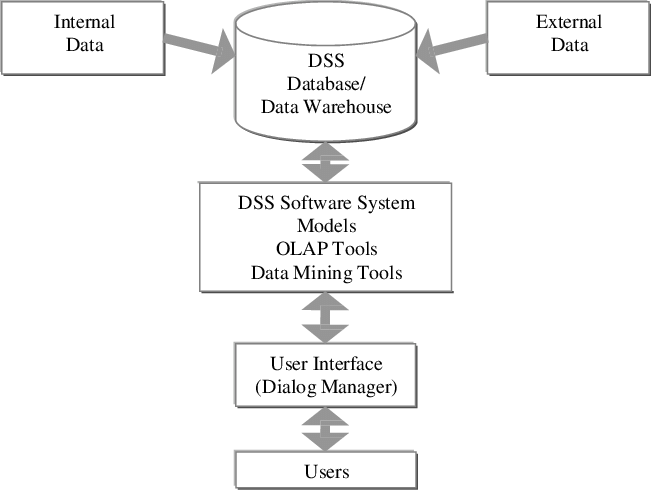
Decision support system (DSS) is software that the team can use in making decision during the process of implementation. The system can be human-powered, computerised or a combination of the two. This system can be used in the management, planning, and operational activities, especially when making decisions based on data. As shown in figure 4 below, the system uses both internal and external data, which are fed into the database. The DSS software system then processes the information, based on the data fed into it and the variables desired, to produce processed information in the user interface. The dialogue manager can then process the information to reflect what can be done in specific contexts based on the information that is presented. The system will then present possible options of decisions that can be made to undertake a given duty, ranking them based on suitability and identifying pros and cons in each case. The information will then be presented to users so that they can understand the appropriate path towards undertaking a given duty.
The Necessity of Working with Partners and Stakeholders
The concept of integrated working framework has gained massive relevance in the healthcare sector. According to (Evans and Lindsay 2017), it is evident that medical practitioners need the support of and close coordination with other stakeholders to ensure there is a success in improving the health of their patients. In this programme, the team will be working with elderly members of the society who are residing in care homes. As discussed above, it is not possible for this team to achieve its goals without working with various partners and stakeholders. Donors are critical partners that will define the success of the project. Conducting laboratory services is a costly process that the targeted vulnerable group cannot afford.
The team will need to have these machines at the facility. There will be the option of either buying these equipments or leasing them as may be necessary. Donors will provide the funding needed to make this project a success. The local authority will be a partner in this project. Authorities from the body will help in ensuring that quality of services offered during this programme meets national standards. These officers will be required to engage the screening staff actively and identify weaknesses that they feel should be addressed to enhance the level of success. Having an external evaluation team eliminates any form of bias and ensures that what these patients get meets the set national standards.
Advantages of User Engagement
User engagement has various advantages and disadvantages which are worth discussing at this stage of the report. The project team members will consist of a contingent of laboratory technicians who may not have vast knowledge of culture and the role that it plays in the medical sector. Most of them are always focused on taking and testing various samples presented to them or taking their clients through other screening processes. However, Goodwin (2016) explains that when handling the elderly, one should not ignore issues such as their emotions, cultural practices, religious beliefs, and such other related factors. User engagement creates a system where these medical experts can understand how to deal with these challenges. Working closely with employees of the care home can help the technicians to understand unique traits of each patient and what to expect from them. Sometimes family members can accompany them to the screening rooms to help calm them down so that a proper diagnosis can be conducted. These relatives and care home staff can also help the technicians to know when a patient has phobia towards specific medical procedures. The teamwork enhances chances that the programme will achieve the set goals within a specific duration.
Theory and Ethical Considerations
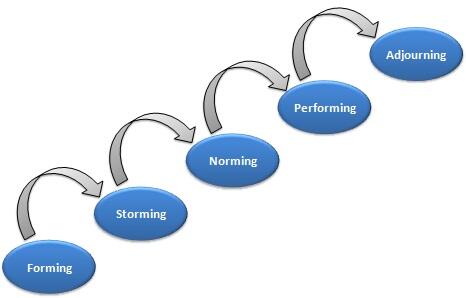
It is necessary for the all the stakeholders to work as a team when implementing this programme that is meant to benefit the elderly members of the community living in the selected care home. Tuckman’s model of group development identifies five stages that should be followed to ensure that the desired success is realised. The first stage is referred to as forming. It involves members meeting and learning of the task that they need to perform within a given period. The second stage of storming is often characterised with polarisation and conflicts as people try to bond despite having varying characteristics. The project manager is expected to have the capacity to overcome the conflicts that would emerge. Norming is the third stage where team members start to understand one another. They start to embrace their position and the need to work as a unit to achieve specific goals.
The performing stage is the situation where members of the team are comfortable with one another and are committed to performing specific tasks to realise the desired goals. In an ideal environment, performing stage should be the longest period in the entire development process because it involves undertaking specific functions of the project. The last stage is known as the adjourning phase. Upon the completion of project activities, the team will be adjourned. In this case, the team will be adjourned after five years as set in the programme. Figure 5 below summarises the five stages of group development.
It is important for the medical staff to understand and embrace ethical considerations when offering the screening services to the elderly. According to Morris (2017), one of the main ethical requirements that medical staff have to embrace is the protection of patients’ data. In the United Kingdom, it is a legal requirement for healthcare workers to avoid sharing patients’ information with unauthorised parties. In this integrated system, the screening staff will have to ensure that the results of their tests are only made available to the patient and the specific medical staff who requested for it. The information can only be shared with other parties when the patient authorises so.
In some cases, it is often advisable to share sensitive information with family members so that they can help the patient to overcome the shock, possible denial, and even depression (Raydugin 2017). However, that would be the responsibility of the medical staff that will need to find a psychologist to undertake such a responsibility. The screening staff will strictly limit their responsibility to conducting reliable and accurate testing of the condition of their patients. The staff under this problem will have the ethical responsibility of explaining to each patient the nature of the test that is to be conducted. The patient should know why the diagnosis is needed, the possible outcomes of the tests, and if it is a painful process.
The Budget
One of the most important aspects of this business proposal is the budget. According to Lock (2016), the budget helps in clearly outlining the expenses that in the programme, funding expected, and sustainability of the project within a specific period that it will be active. Before issuing the necessary approval, the local authority will need to be convinced about the relevance of this project and its value to the selected group. They need to review the budget to evaluate the programme. Donors also need to review the budget to determine if their investment will be used in the right way. In this section, the researcher breaks down the five-year budget for the screening programme at the selected care home. The project will rely on a donation of 2 million pounds, which will be the primary funding of all the activities. The team will not rely on the £1,200/week that the care home receives from social service. Table 1 below shows the proposed 5-year expense plan for the project.
Table 1: Proposed 5-year expenses for the project.
It is important to note that most of the heavy screening equipments will be leased from the local hospitals. Other lighter instruments will be purchased to help cut cost. The team has a deal with the leasing firm and the one selling the consumables to reduce the cost on the fifth consecutive year, as shown in the budget above.
Conclusion
The growing population of the elderly members of the society has led to an increase in the demand for care homes. However, most of these homes are often unable to meet all the needs of their clients. Specialised medical care is one of the main concerns of these institutions because of the associated costs. As such, this programme focused on providing specialised laboratory and x-ray services to help manage medical conditions that these patients have. The project has a budget of £ 2 million and will last for five years. Within this period, a team of highly specialised laboratory technicians will offer a wide range of screening services to the vulnerable population within the selected institution. The team will embrace the concept of integrated working framework to ensure that all the relevant stakeholders are brought in to work as a team. The goal will be to ensure that the targeted vulnerable population has a long and fulfilling life free from various illnesses.
Reference List
Alam, M., and Gühl, F., 2016. Project Management in Practice: A Guideline and Toolbox for Successful Projects. Berlin: Springer.
Baxter, S., Johnson, M., Chambers, D., Sutton, A., Goyder, E., and Booth, A., 2018. The Effects of Integrated Care: A Systematic Review of UK and International Evidence. BMC Health Services Research. 18(350), 1-28.
Binder, J., 2016. Global Project Management: Communication, Collaboration and Management across Borders. 2nd Edition. New York, NY: Routledge.
Ekanem, I., 2017. Writing a Business Plan: A Practical Guide. New York, NY: Routledge.
Evans, J., and Lindsay, M., 2017. Managing for Quality and Performance. Boston, MA : Cengage Learning.
González-Ortiz, L., Calciolari, S., Goodwin, N., and Stein, V., 2018. The Core Dimensions of Integrated Care: A Literature Review to Support the Development of a Comprehensive Framework for Implementing Integrated Care. International Journal of Integrated Care. 18(3), 10-25.
Goodwin, N., 2016. Understanding Integrated Care. International Journal of Integrated Care. 16(4), 6-10.
Harris, J., Roussel, L., Thomas, P., and Dearman, C., 2016. Project Planning & Management: A Guide for Nurses and Interprofessional Teams. 2nd Edition. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Hartley, S., 2018. Project Management: A Practical Guide to Planning and Managing Projects. 4th Edition. Melbourne: Allen & Unwin.
Hawkey, J., 2017. Exit Strategy Planning: Grooming Your Business for Sale or Succession. New York, NY: Routledge.
Lock, D., 2016. Project Management in Construction. 2nd Edition. New York, NY: Routledge.
Maruthappu, M., Hasan, A., and Zeltner, T., 2015. Enablers and Barriers in Implementing Integrated Care. Journal of Health Systems & Reform. 1(4), 250-256.
Morden, T., 2016. Principles of Strategic Management. 2nd Edition. London: Taylor & Francis Group.
Morris, D., 2017. Scrum in Easy Steps. London: Easy Steps Limited.
Raydugin, Y., 2017. Handbook of Research on Leveraging Risk and Uncertainties for Effective Project Management. Hershey, PA: IGI Global.
Turner, R., 2016. Gower Handbook of Project Management. 4th Edition. London: Routledge.