The aim of this report is to evaluate the appropriateness of AIG’s strategic proposals, as well as the justification driving its current strategy, with recommendations and considerations based on findings. The information provided will be based on independent evidence and research into the organization. The analysis will be based on a series of theoretical tools that look at the internal and external environment that considers the competition within the industry. The evidence is developed by utilizing outside data and analyzing it through key frameworks, such as SWOT, PESTEL, and others. These will be reviewed, taking into consideration the core competencies, organization culture, structure, people, and the development processes within AIG.
Background
To allow the reader to understand the findings, it is necessary to understand AIG as a company. Founded by Cornelius Vander Starr in 1919, AIG, at the time known as American Asiatic Underwriters (AAU), was established in Shanghai. AAU re-established itself in 1968 as American International Group Inc., otherwise referred to as AIG.
Today, AIG’s holding company is based in New York, USA, and it employs 46000 people internationally across 80 countries. AIG offers a diverse range of insurance products covering general and financial services as well as consumer insurance, such as life & retirement business. It offers services to 90 million commercial and individual customers worldwide, with notable firms, such as Shell, HSBC, and more than ninety percent of all aerospace products. Its mission statement reads, “Reducing fear of the future and empowering our clients through our risk expertise and financial strength” (American International Group, 2019, para. 3). In other words, the organization positions itself as a potentially negative outcome preventer for the clients.
Case Study
It is important to note that AIG was once known as the world’s largest insurance firm. However, it has struggled to make a strong comeback in the market since its 2009 bailout of $185bn from the US Government as part of a rescue package during the height of the financial crisis[1] (Garthard, 2020). AIG’s main strategic priorities for recovery were to pay back the government and focus its objectives around reputational issues and maintain a presence in the market. From 2005 until 2017, AIG has had no less than seven CEOs, were each with very different strategies. AIG’s revenues declined year-on-year from their ten-year peak in 2010, of 78.33 billion U.S. dollars down to 49.75 billion U.S. dollars by 2019 (Garthard, 2020). Thus, there was a significant decline in the key numeric metrics within the company.
The AIG Strategy is based on four core objectives:
- Achieving underwriting excellence focusing on the development of products and building its medium-sized portfolio.
- Exiting non-profitable business, partner with competitors to manage larger risks
- Modernizing its operating infrastructure,
- Enhancing both is internal user and customer experiences. [2]
Based on lessons learned, shifting markets, and disruptors such as technology that are continuing to change customer expectations and behavior, how appropriate is AIG’s latest strategy. For example, these goals were set in order to match the contemporary shifts in the market (“AIG plans to make changes to organizational structure,” 2017). In other words, one should note that AIG is aware of the flaws of its system of corporate strategies.
Internal & External Factors
In order to develop a strategic plan, a company needs to understand both the internal[3] and external[4] factors of its environment. A common methodology used is SWOT, which is comprised of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats[5]. SWOT analysis is used because it allows one to observe key internal and internal forces. This information can be used to form the basis of the most appropriate strategy, and the analysis can be seen in Table 1 in the Appendix section. Other methods are PESTEL, which looks at the external strategic environment in which a company operates. The main reason is that the given instrument is highly useful for understanding the influences of the macroenvironment. The PESTEL analysis is conducted and shown in Table 2 in the Appendix section, and it demonstrates that AIG’s strategy needs to consider the strongest asset of its company. The argument is based on the fact that the company’s strongest assets can be useful in overcoming major challenges. The key Through providing a clear plan will help define the organization’s goals and priorities.
AIG’s strength is based on the following elements
- Strong capital position.
- Brand name and presence supported by skilled underwriters.
- Ability to meet customers’ demand through the diversity of products.
- Response to market conditions and offsetting risk business through reinsurance.
Analysis and Considerations of the Related Organization Factors
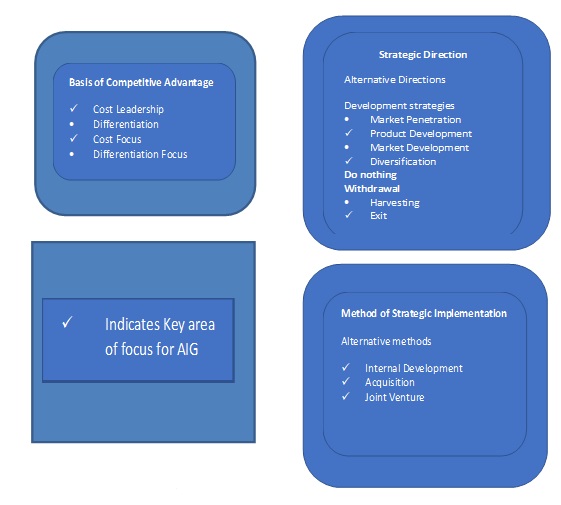
In order to develop a strategic plan, several theories such as Porter’s diamond, VRIO analysis, Johnson and Scholes Cultural Paradigm, J&S DIY/Buy/Allyas well as others can be considered. The Cultural Web developed by Johnson and Scholes in 1992, is a tool that can be used to understand the organization’s cultural assumptions and practices[6]. To develop the right strategy the new Management team needs to consider past issues and realize that the internal strategy is equally important to the external[7]. The Cultural Web is formed of six interrelated areas of the organization which are based on a set of ideas and beliefs. The information on the concept and the corresponding assessment can be seen in Table 3 in the Appendix section. For AIG to consider some of its strategic options, it should note Johnson and Scholes’s methodology. It has been linked to other theories, which can be accessed in Figure 1 of the Appendix. In other words, it widens the understanding of strategic directions as well as its competitiveness factors.
Current Organizational Strategy from Different Perspective
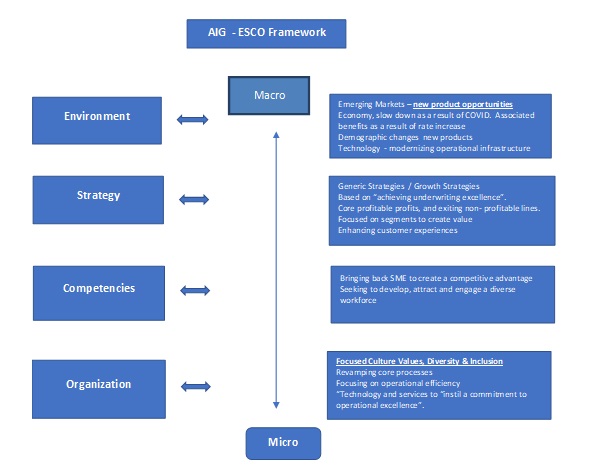
The ESCO Framework, Environment, Strategy, Core Competencies & Organizational culture looks at how the strategic plan is aligned to each area as can be seen in Figure 2 of the Appendix. The closer aligned AIG strategy is aligned to each area the better the company is likely to perform. In the case of macro-influences, the environment plays the central role, where the key factors are the newly emerging market. They create novel market opportunities, which is true even in the conditions of the pandemic. Although the overall economy is slower, AIG’s products and services remain valuable. Strategy is another macro-force, which focuses on both generic and growth strategies. AIG primarily focuses on customer experience and market targeting due to the slow down limiting the increase of the clientele base. The company’s core competencies are viable only through a diverse workforce, which can realize these objectives. The micro-influence is based on the notion of the organization, which focuses on cultural values and inclusion.
Future Directions of the Organization
AIG has significantly overhauled its strategy since the appointment of its latest CEO Brian Duperreault 2017, and in 2019 reported a $12000000 underwriting profit compared to a more than $1 billion loss in the 2018 fourth quarter, showing already that it is on the road to recovery (American International Group, 2019). It has now put together a multiyear strategy to address past leadership outcomes with the focus on addressing internal issues in order to take the company forward. This section reviews the strategies considered, rationale, and their future direction, which can be seen in Table 4 of the Appendix.
Recommendations & Conclusions
Based on AIG’s strategy there are several gaps have been identified that need to be considered. The formation of the definition of the strategic potential of AIG, as well as the analysis of the conditions, results of its functioning, and goals, is largely influenced by the systems approach. AIG’s strategic potential is the sum of the internal resources available and the organization’s ability to develop and implement an enterprise strategy. An important point in the study of strategic potential is to ensure its consistency, when not a single aspect of it is ignored, ensuring the complexity of the strategy itself.
An important step in AIG’s strategic planning process is assessing the strategic capacity of the organization. It should be carried out both in the process of realizing a mission and goals and in choosing a strategy. In the first case, the assessment of the strategic potential is carried out at the stage of analysis of the external and internal environment, during which information about the potential of the economic entity is formed. It is evident that the company needs to utilize its brand name, worldwide presence, and strong capital in order to gradually expand its clientele base by market fragments. At the same time, the study of the influence of the external environment is one of the stages of designing the organizational structure of AIG, which corresponds to the conditions of the enterprise’s functioning. The company should use its technology infrastructure in order to limit the disruptive effect of COVID-19, which facilitates the cyber-insurance expansion. In the second case, the potential of the organization must be tied to a specific goal. It represents the ability of an enterprise to achieve accurate results, which are formulated as a specific set of goals. At the same time, the strategic potential of an organization is understood not only as a static value but also as a dynamic one. As a rule, any strategy is aimed at improving the performance of the organization, and the consequence of this is to build up its strategic potential. Therefore, not only the existing potential should be assessed, but also the possibilities for its development.
In conclusion, AIG seems to have a strong strategy, focusing on underwriting excellence, tools, and expansion of product development and customer excellence. The current direction of the organization is an effective one because it utilizes its internal strength and competencies. However, on the basis of multiple assessment instruments used in the given evaluation, AIG needs to deliberately seek out opportunities within the market despite the economic impact of the pandemic. Assessment of strategic potential is one of the important stages of strategic planning. The basis for the selection of criteria for assessing strategic alternatives is a competently performed AIG diagnosis. At the same time, there is no single method or algorithm for carrying out the procedure for assessing strategic potential. The set of methods by which the potential assessment is carried out is determined by the requirements for the speed of its implementation, the past experience of strategic planners. It can also involve the qualifications, intuition, and experience of the leaders and owners of the business, the resources available, and other factors.
References
AIG plans to make changes to organizational structure. (2017). Web.
American International Group. (2019). Annual Report 2018 [PDF document]. Web.
Garthard, G. (2020). Falling giant: A case study of AIG. Investopedia. Web.
Hyken, S. (2015). Drucker said ‘culture eats strategy for breakfast’ and enterprise rent-a-car proves it. Forbes. Web.
Ralph, O. (2018). AIG: The long struggle to repair its reputation. Financial Times. Web.
Wright, A. (2012). Chartis name dropped in return to AIG. Insurance Times. Web.
Appendix
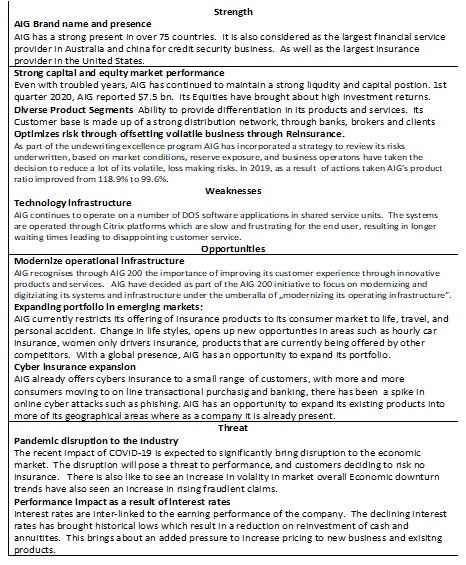
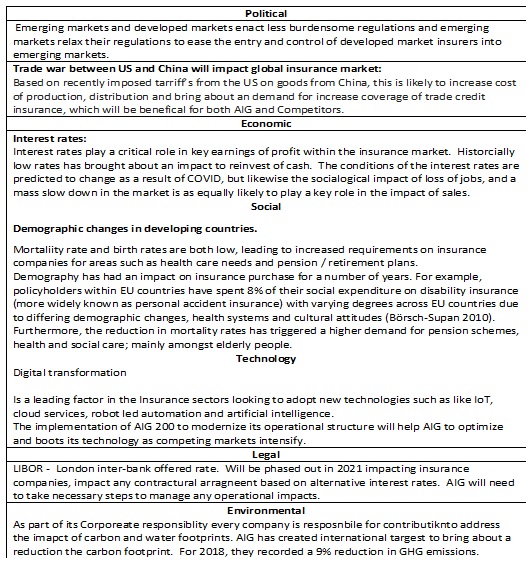
Table 2. PESTEL.