Executive Summary of Etisalat Business Plan
Etisalat is a telecommunication company, and it has been in operation for 39 years. Its remarkable performance has facilitated the expansion into emerging markets coupled with acquiring over 160 million subscribers in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. The strategic management of its operations necessitates investigation into the environmental factors that have shaped up the company’s growth. In this essence, an application of various strategic analysis tools would aid this study in coming up with valid and reliable conclusions regarding the company in its quest to be amongst the top players in the industry. An evaluation of the strategic choices and alternatives regarding the expectations of the stakeholders would facilitate the formulation of recommendations to boost the growth of the company in the global market
Etisalat Strategy: Introduction
The telecommunications industry has experienced new developments and trends that mainly portray the players’ drive towards attaining competitiveness. Companies implement strategic plans to gain a competitive edge by securing a sizeable market share. Therefore, conducting a strategic analysis of a particular organization in the industry is essential for the identification of the environmental factors, strategic capabilities, cultural beliefs, and the stakeholders’ expectations. In this regard, focusing on Etisalat as one of the key global players in the telecommunications industry is relevant considering its continued growth in emerging markets. This analysis will use analytical tools like PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, SWOT, and the TOWS analysis. Analyzing the stakeholders that influence the operations of Etisalat is also essential to determine the implication of the strategic choices.
Company Overview Branded
The Emirates Telecommunications Corporation, which is also known as Etisalat, was incorporated in 1976 in Abu Dhabi. International Aeradio Limited, which is a British company, and local partners in the UAE constituted the formation of the corporation as a joint-stock. In 1991, Etisalat was given the right to provide wired and wireless telecommunication services by the UAE government. The issuance of the government Federal Law number 1 implied that Etisalat would create a monopoly in the telecommunication market.
Currently, Etisalat has subscribers in 19 countries located in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Besides the data and voice calls services, the company’s innovative strategies are depicted in its association with telecoms entities in providing services that include SIM card manufacturing, staff training, payment solution, submarine, and land cable services, voice and data transit, and peering.
Etisalat has recorded impressive financial reports spanning nearly four decades of its operations. Etisalat has a current market capitalization of $ 23.8 billion that is accountable for its consideration as a leading telecoms company in the emerging market niches. In 2014, Etisalat attained total revenues of $13.3 billion that translated to a net profit of $ 2.42 billion (Etisalat, 2015a). The gains were due to its innovative strategies, which are attributed to its investment in the first-ever 5G Internet services in the UAE (UAE TRA, 2015).
Vision, Mission, and Values
The company’s vision, mission, and vision formulated the organizational culture that fosters its strategic management systems geared towards goal attainment. The company’s vision is to achieve a world whereby matter or distance does not hinder communication. The implication is that Etisalat strives to enhance communication across boundaries as individuals travel internationally to foster their social and economic aspects of life.
The mission that Etisalat seeks to achieve is the extension of people’s reach. The mission is pursued through the creation of advanced networks that seek to promote an individual’s development, learning, and growth.
The core values that drive Etisalat towards the realization of its goals mission and vision include energy, openness, and enablement. To achieve transparency, Etisalat favors fairness, honesty, sociability, and a welcoming heart to all the stakeholders. The value of enablement is facilitated by the provision of opportunities that would fulfill people’s goals (Etisalat, 2015b).
Purpose of the Study
The motive for studying the strategic attributes that are accountable for the company’s performance is to identify the internal and external environmental factors that trigger its status. This paper seeks to investigate the company’s strategic analysis that considers the application of various analytical tools that facilitate its evaluation and make recommendations for its continued success and sustainability.
Etisalat Corporate Plans: PESTEL Analysis
Political
- Environmental concerns over radioactive emissions that are associated with the telecommunications mechanism have raised the eyebrows of the governmental agencies in different regions that Etisalat provides its mobile services. However, Etisalat has observed ethical operations by engaging governments in environmental conservation (Management Guru, 2015).
- Public policy participation has been an advocacy strategy for Etisalat that seeks to influence positive change at the national and international levels. In this respect, Etisalat engages political bodies in the formulation of policies that enable people to attain their goals as a value upheld by the organization.
- The UAE government provides corporations like Etisalat with an enabling environment through incentives that include the provision of quality industrial facilities, red tape reduction, and business support services. Political stability and favorable tax laws have also been influential for the Company’s growth.
- The UAE government has imposed restrictions to protect Etisalat from competition from new players in the industry by ascribing the corporation control via the TRA (UAE TRA, 2015). However, the case is a little different in other countries in which it operates.
Economic
- Etisalat has attained desirable financial results, which have characterized its profitability. In 2014, Etisalat made a net profit of $2.4 billion, which was an improvement compared to the previous fiscal year that made gains of $2.1billion.
- Etisalat boasts of capital injections from various stockholders who see the potential of the company.
Social
- Etisalat seeks to connect social individuals and groups through the provision of mobile calls and Internet services that enhance communication regardless of matter or distance. In this respect, the organization focuses on the integration of more than 160 million subscribers based in the Middle East, Asia, and Africa (Etisalat, 2015b).
- With the Company’s operations in diverse cultures, the organization is committed to corporate social responsibility initiatives that seek to elevate social, political, and environmental factors of various communities.
- The shift towards the information society in the 21st century has subjected Etisalat to be innovative as it embarked on 5G LTE Internet connectivity, a milestone in the telecommunications industry.
- The culturally diverse workforce at Etisalat enjoys an environment that values them as their opinions and ideas are highly regarded. The fair treatment of its employees on three continents ensures their motivation towards the success of the company.
Technology
- Etisalat has been at the forefront of technological advancements in the telecoms industry. An upgrade of its mobile and Internet services has seen high-speed connectivity and unmatched precision in the delivery of products and services thus enhancing its competitive advantage.
- Etisalat has engaged in the innovative application of telecommunications technology to combat HIV/AIDS after collaborating with the United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) through their mobile network platform (IT & Telecom Digest, 2015). This movie portrays its CSR initiatives that employ technological advancements.
- The company’s completion of the VoWifi (Voice over WiFi) trial ensured that the company pioneers the technology in the region giving it a competitive advantage (Qualys, 2015).
Ecological
- The Company’s environmental stewardship initiatives have enhanced its competitiveness given the environmental threats imposed by the industry. The M2M (Machine-to-Machine) initiative was recently unveiled to whereby mobile applications could be used to foster environmental sustainability.
- The presence of Etisalat in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia implies that its workforce is situated in diverse climatic conditions that facilitate its adaptation in different regions thus enhances its sustainability.
- Various CSR initiatives facilitated by Etisalat ensure its positive impact on environmental protection and the empowerment of the communities in which it operates.
Legal
- Regular liaison with the UAE’s legal authorities like the Consumer Affairs Authority, Local Authorities, Municipal Councils, and the Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA)
- Compliance with constitutional provision ensures that Etisalat facilitates its streamlined activities in the UAE and 18 other countries.
- Etisalat protects and respects the privacy of its subscribers by ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the information provided to them.
The Five Forces Analysis of Etisalat Group
The Threat of Entry
- The threat of new entrants into the market dominated by Etisalat is a threat to its competitiveness. However, the UAE government has levied restrictions on new entrants to enhance its survival in the telecoms industry (+).
- The global collapse characterized by the recession may force the UAE government to allow the entry of new players in the telecoms industry to create economic equilibrium needed for sustainability thus creating stiff competition (-).
- The operations of Etisalat in 19 countries enhance its economies of scale thereby hindering new competitors’ ease of entrance (+).
- The Company’s drive towards the provision of new technology services such as 5G networks in the Middle East may not result in cost advantage since the initial stages of the adoption of the technologies might be expensive. However, the cost may be canceled by the existing infrastructure implying that new competitors may find it difficult to enter the market (+).
Overall – High
The Threat of Substitutes
- The threat of new substitutes is relative since Etisalat has safeguarded its presence in the telecoms by providing wired and wireless services to its subscribers. The innovation adopted by the organization ensures the provision of communications services that are regarded as substitutes through various partnerships with related industrial players like Bharti Airtel to expand its coverage (+).
- The image created by Etisalat through the provision of quality services led to the development of customer loyalty thus diminishes the likelihood of switching to new mobile service providers (+).
Overall – High
The Bargaining Power of the Buyers
- The bargaining power of the Company’s subscribers is relatively low due to the few competitors in the UAE market and its operations in other countries like Nigeria. Despite the low switching cost in the UAE market, Etisalat plans to foster its services thus preventing the clients move to Du, the immediate competitor (+/-).
- In other countries outside the UAE, the bargaining power of the buyers might be higher considering the number of mobile service providers in such regions. For instance, Mobinil, Orange, Vodafone, and Etisalat make up Egypt’s telecommunications market implying that the customers have a greater bargaining power due to the multiple mobile service providers (-).
Overall – Moderate
The Bargaining Power of the Suppliers
- In the UAE, the bargaining power of the suppliers is considerably low since only two players, viz. Etisalat and Du, dominate the market. In this regard, the suppliers depend highly on the demands of the mobile service providers led by Etisalat (+).
- The Company’s operations other regions including Africa and Asia implies some countries have multiple competitors that translate to higher bargaining powers of the suppliers. Consequently, Etisalat has been affected by the interns of bargaining capabilities in foreign markets (-).
The Extent of Rivalry between Competitors
- Despite the duopolistic market in the UAE environment, Etisalat tends to possess a competitive edge over Du since it had been ascribed monopolistic powers in the past thereby having a better foundation as compared to its competitor. Etisalat utilizes promotional strategies to gain a sizeable share of the UAE telecoms market thus enhancing its competitiveness (+).
- In the global market, Etisalat has made its impact to be felt by its close competitors that include Vodafone, Telenor, Three Mobile, and AT &T with its aim of becoming one of the top ten mobile services providers globally (-).
Overall – Medium
Internal Forces on Etisalat Company: Analysis
Strategic Capabilities
An analysis of the internal environment at Etisalat would be successful through the assessment of its strategic capabilities considering its resources and competencies, benchmarking, an analysis of its value chain, and the VRIO analysis.
Resources and Competencies
Etisalat possesses various facilities, assets, and competencies that facilitate its competitiveness as industrial players intensify the competition while targeting new subscribers to provide their mobile network services.
- Physical Facilities: The Company’s physical assets comprise all the tangible resources that facilitate the operations that lead to the delivery of mobile network services. The tangibles include transmitters, computers, fiber optic cables, and other equipment required for the Internet and voice services.
- Intangible Assets: The intangible assets at Etisalat include telecommunications software, the diverse culture workforce, the Etisalat brand name, computerized databases, proprietary software, technology, sharing agreements, subscribers’ lists, and customer relationships. The intangible assets are instrumental for the Company’s success in the telecoms industry.
- Human Resources: The human resources aspect is a valuable input for the Company’s success as it seeks to improve its employee’s relations by promoting the organizational culture through the values of energy, enablement, and openness. The workforce of over 400oo employees strives towards the attainment of the organizational goals.
- Financial: The positive financial outcomes realized at Etisalat have enhanced positive feedback from the shareholders who envision a positive future for the company as it continues its operations in emerging markets. The total revenues attained in 2014 were $13.3 billion portraying its valuable financial resources (Etisalat, 2015a).
- Marketing and CSR: Etisalat markets its products through promotional approaches that pursue to improve the sales of its mobile, telephone, Internet, landline, and Television services. The CSR initiatives at Etisalat encompass environmental stewardship, customer experience, employee concern, community development, public policy participation, and human rights advocacy (Etisalat, 2013).
Besides the invaluable resources, Etisalat has the following competencies.
- Experience: Operating for 39 years, Etisalat has acquired vast experience in the telecoms industry as it provides its mobile services to various subscribers globally. The experience has enhanced its competitive advantage as its managerial team formulates and implements strategies that are necessary for growth. The Company’s position at number 13 worldwide is partially accountable for its success.
- Diverse and skilled workforce: The employees situated in 19 countries have abilities that have spread the organizational culture that aims at linking people regardless of their distance or conditions. The skilled workforce handles streamlined operations that have steadily improved the organization’s customer relations.
- Customer Relations: Etisalat practices efficient customer service, which meets the subscribers’ satisfaction. The organization has won awards like the Honorary Mention in various categories including customer service.
Etisalat Group VRIO Analysis
An assessment of the aspects of value, rareness, imitability, and organizational support concerning the Company’s resources is significant for the evaluation of its strategic management. Below is a VRIO framework table that facilitates the assessment of the Company’s tangible and intangible resources.
The VRIO framework above portrays different strategic functions and capabilities of Etisalat that utilize the resources required to deliver quality voice and data services to over 160 million subscribers. The organizational culture influenced by the able leadership of the CEO, Ahmad Abdulkarim Mohd Julfar. The skilled and diversified employee base situated in the Middle East, Asia, and Africa adds value to the functions of this promotes the sustainability of Etisalat. The internationalization strategies are strategic and costly to imitate due to the resources needed to expand to various regions regarding the resources required.
Etisalat is a global brand due to its presence in 19 countries making it the 13th largest telecommunications organization in the world. The company invests in low-cost strategies characterized by cross-channeling approaches that seem to reduce its operational costs in emerging markets. The finance and purchasing functions depict influential approaches that require innovation to foster its rarity. The aspects of innovation, creativity, and technology promote the Company’s sustainability that coincides with the organization’s expectations.
Benchmarking
An analysis of the Company’s performance concerning its competitors is appropriate for gauging the impacts of its strategic initiatives. In this essence, benchmarking portrays a multidimensional view of Etihad’s performance-enhancing the study in terms of its competitive advantage, and weaknesses. The following charts highlight the Etisalat and Du’s benchmarking results based on the UAE market.
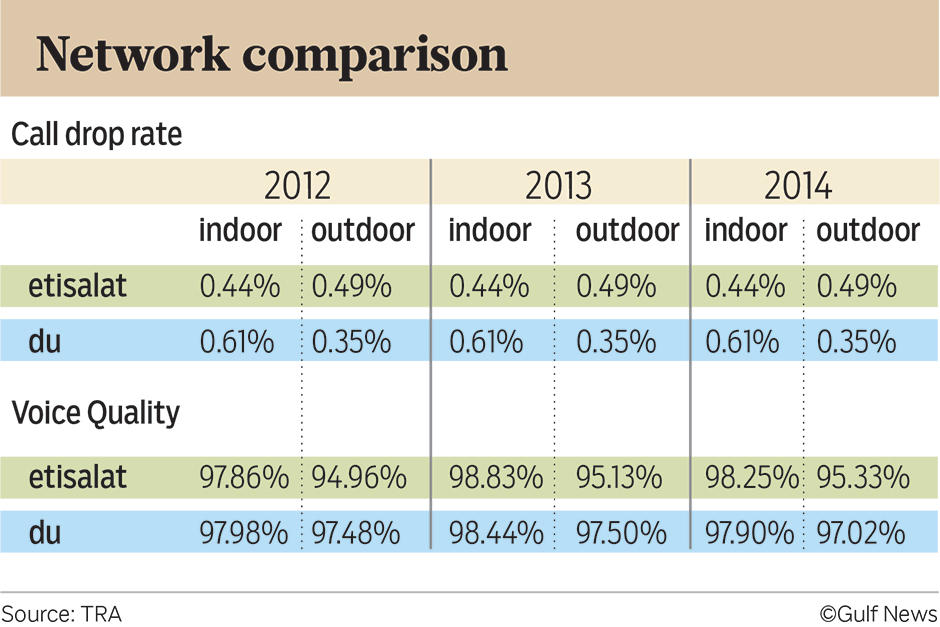
The above figure indicates the call drop rate and voice quality between Etisalat and du between 2012 and 2014. Etisalat has recorded consistency in its call drop rate over the period showing stronger indoor network as compared to du. Du recorded lower drop rates in outdoor environments at 0.35%. The voice quality category depicted inconsistency in the strength of indoor and outdoor, as the outdoor voice quality for Etisalat was poorer as compared to that of Du. This aspect implies that Du exerts pressure on Etisalat to provide quality services in both indoor and outdoor voice services.
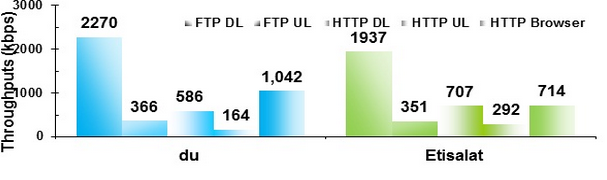
Considering the dual-mode (2G/3G) transfer rates, Du tends to offer faster data transfer rates as compared to the Company’s services. This aspect implies that the entry of Du into the UAE’s telecoms industry brought advanced technology resulted in faster data transfer rates of the dual-mode.
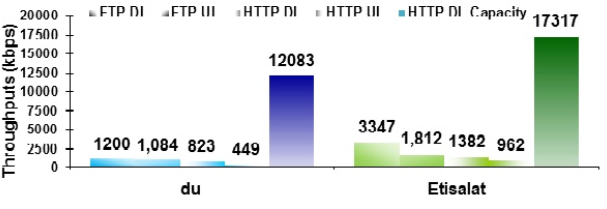
Due to the Company’s innovative strategies that incorporated the deployment of innovations in the industry through 4G networks, the company performed better as compared to Du. Consequently, customers experienced fast data transfer rates in outdoor settings. In this respect, Etisalat gained a competitive advantage considering the data transfer rate on 4G platforms.
Value Chain Analysis
Focusing on the primary and supportive activities within the Company’s operations facilitates the analysis of the value of its processes. In this light, the customers’ value triggered by competitive strategies is the main aspects of concern based on elements like operations, human resource development, marketing and sales, services, technology development, and organization’s infrastructure. Therefore, value chain analysis justifies or refutes the prices at which the Company’s customers pay for the services rendered.
Etisalat Strategy in Management: Firm Infrastructure
Etisalat has invested heavily in its infrastructure over the three decades of operations. The tangible and intangible physical infrastructure is evident due to the satellite transmitters, fiber optic cables, advanced computers, network software, and other complementary facilities. The massive investments in infrastructural developments over the years have been accountable for the organization’s competitive edge enabling it to offer services in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East.
SWOT Analysis of Etisalat
Strengths
- Etisalat is a major telecommunications player in the Middle East providing voice, the Internet, roaming, broadcast, mobile, and corporate data services that cement its domestic market share. Its vast services have stamped its authority in the region thus evoking intense competition to rivals like Du (MBASkool, 2015).
- Huge capital investments facilitate the financial management of the company as it provides services that apply the latest technology.
- Etisalat offers enhanced customer service through a skilled workforce that values customer engagement and empowerment.
- The high growth rate that has seen the company globally ranked at position 13 in the telecoms industry. Its experience spanning over 39 years has enabled it to subscribe to 160 million customers on various continents.
Weaknesses
- There is a high likelihood of new entrants venturing into the industry thus creating more competition, thus affecting the market share that has already been secured by Etisalat
- The Company’s control of operations in various countries might compromise the quality of its products thus creating opportunities to maximize the loopholes. Therefore, managing global operations might prove to be challenging resulting in profit warnings.
- Employees and the customers in countries like Egypt have little knowledge about the technological services provided by Etisalat resulting in cost inefficiencies (Leadership, 2014).
Opportunities
- There is developing demand for voice, the Internet, roaming, and broadcasting services in the emerging markets implying that Etisalat could seize the opportunities through expansion strategies. For instance, the developing African economies have embraced technological advancements that the company could implement in its strategic plans.
- Opportunities for growth would be available if Etisalat embraces service improvement strategies that incorporate improved bucket offerings to customers.
Threats
- The low purchasing power of clients in regions like Africa has subjected Etisalat to lower its voice and data rates resulting in lower profit margins in such regions (Cole, 2013).
- Global economic fluctuations characterized by the recession might pose threats to the sustainability of the Company’s operations in various economic areas thus negatively affecting its profitability.
- The entry of new competitors in the industry will lead to stiff competition.
Etisalat Group TOWS Matrix Analysis
Further analysis of the Company’s operating environment necessitates the move beyond the SWOT analysis. The TOWS Matrix is a strategic analysis tool that facilitates the formulation of plans that seek to capitalize on the Company’s strengths and opportunities while curtailing the weaknesses and threats.
Etisalat Business Plan: Stakeholder Analysis
The Etisalat Group constantly engages its key stakeholders to update them on the strides the company has made towards the attainment of its goals. The stakeholder engagements revolve around consultations, communications, and disclosures concerning the strategic choices the organization has made to satisfy the needs of all the parties. The following table provides an overview of the stakeholder analysis at Etisalat.
Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder mapping for the parties that have an impact on the performance of Etisalat is essential for the evaluation of their significance in consideration of the strategic choices developed by the top management. According to the mapping results, The CEO, Board of Directors and shareholders, employees, competitors, and legal agencies portray high interest and power in the formulation of the organization’s strategies. The customers that subscribe to the Company’s services end up being highly interested in the quality of the services provided, but with limited power despite their numbers. Suppliers show low interests in the formulation of the Company’s strategies, but their implications are powerful since, without them, the telecoms cannot thrive. The communities in which Etisalat carries out its operations tend to be less interested in the activities of the organization despite the CSR benefits thus it is less powerful (Sutherland, 2011).
Etisalat Group – Competitive Advantage
External analysis is of the Company’s environment is inadequate for concluding the functionality of the telecoms company. Therefore, analyzing the internal aspects that drive Etisalat towards its success is suitable for evaluating the unique elements that grant the company a competitive edge.
Efficiency: The Company’s operations hinge on efficiency due to the commitment to deliver quality services to its customers. Its indoor and outdoor voice calls are relatively stable resulting in satisfaction. The LTE 4G Internet network is stable providing faster data transfer rates. The 5G LTE trial portrays the innovative move aimed at improving Internet surfing experiences. The Company’s overall efficiency stands out in the annual financial results that have constantly recorded profits (Gulf News, 2014).
Quality: The Company’s services employ innovation to deliver high standard products and services. The participation of Etisalat in solving social and economic issues in its area of operations creates environments characterized by quality experiences. Since quality services and customer satisfaction is the company’s priority, the organization has been strategizing on improving operational processes that are inefficient to enhance its competitive advantage.
Innovation: The aspect of innovation has been a significant attribute of the Company’s products and services. The company has invested in modern technology to gain a competitive edge over its rivals. For instance, the introduction of the VoWiFi and 5G LTE network in the Middle East, the first one in the region, reveals how the corporate endeavors to incorporate the latest technology in its services (Etisalat, 2015b). The innovative initiatives have led to the organization’s recognition and accreditation for awards in the innovation category.
Customer Responsiveness: The feedback of the customers of a particular business entity is essential for reflecting on the standard of the products and services offered. In regions like Africa through Etisalat Nigeria, over 21 million subscribers have expressed average contentment with the services provided and raise the issues that need to be worked on to improve its services in the region (Leadership, 2014). Etisalat maintains professional customer relations that value the opinions of the subscribers.
Strategic Choices and Evaluation
With the competitive advantage of quality service and customer experiences, Etisalat could employ differentiation strategies that would fortify its position in the telecoms industry. In this regard, a focus on a differentiation strategy, alliances, alternative strategies, and going global could be the valid choices that might facilitate the growth of the company.
Differentiation Strategy
Various differentiation approached could be considered to improve its competitiveness. Cost differentiation could be detrimental since this would elicit the need to impose premiums on the products and services offered resulting in hiked prices that would trigger the exit of its customers. Product differentiation could prove to be strategic, as customers would get quality services that satisfy their communication needs at considerable prices. The standard of services should be highly considered for product differentiation to be successful. Similarly, the cost of differentiation should be in line with the expectations of the customers.
Strategic Alliances or Acquisition and Merger
Alliances, Mergers, and Acquisitions could act as strategic choices that would boost the Company’s competitiveness. The telecom giant has made partnerships with some corporations to improve its competitiveness. As a strategic and innovative move, Etisalat Nigeria partnered with Uber, a global taxi services provider by enabling access to their services instantly (Punch, 2015). This collaboration was strategic since it widened the company’s coverage, especially on its data and voice services. Additionally, Etisalat engaged in a partnership with Bharti Airtel to develop the services offered by the SmartHub facility established by Etisalat implying that the alliance would widen the network of the two telecommunications companies (The National, 2011).
Etisalat Strategy & Alternatives Strategies
The adoption of alternative strategies would facilitate the Company’s growth in emerging and already existing markets. In a bit to circumvent the competitive trends, Etisalat could consider the option of value-added services to its current offers. Enhanced mobile Internet services could improve customer experiences and improve the quality of services delivered. Additionally, Etisalat could venture into specialized media content services that would broaden its scope of roaming, the Internet, and broadcasting operations.
Go-Global
The Company’s goal of acquiring a global ranking among the top 10 telecoms is achievable if it embarks on expansion plans that would see its presence in all the continents. Collaboration with iPass ensured that the Company’s subscribers could access Internet connectivity in over 150 countries thus enhancing its global connectivity and presence. Unveiling the Etisalat GolabalTalk App ensured that the customers could interact with a social platform regardless of their location or distance hence it promoted social connectivity (Ayish, 2013). Therefore, Etisalat needs to venture into the global market by applying innovative strategies to acquire more customers.
Questionnaire Analysis
A questionnaire analysis would facilitate the deduction of the qualitative perspectives of the customers concerning the quality of services, Internet speeds, customer relationships, voice, the Internet, and broadcasting services. In this respect, scrutiny of the data collection materials including the structured and unstructured questionnaires is essential for valid and reliable conclusions about the strategic management of Etisalat.
Etisalat Business Plan: Key Strategic Issues
Some issues tend to inhibit the successful implementation of the Company’s strategic plans. Firstly, the Company’s competitors tend to shift towards its competitors despite the alliances and partnerships that have been formed. For instance, in the UAE, Du has gained almost 40% share of the market posing threats to the Company’s growth.
Secondly, the Company’s competitors are also venturing into the emerging markets that Etisalat intends to dominate thus creating competition that has denied the company a steady growth of the customer base.
Thirdly, the pricing of the products and services offered by Etisalat tends to be unfavorable, thus inconveniencing the purchasing power of the globally situated customers. Therefore, the marketing strategies tend to be ineffective considering the price (Ayish, 2013).
Recommendations to Improve Etisalat Strategy
Considering the critical strategic issues, Etisalat needs to implement the following recommendations for enhanced global operations.
- Etisalat should form alliances and partnerships with key players in the industry to enlarge its economies of scale thereby limiting the competition from new entrants. The effect would broaden and strengthen the network of Etisalat domestically and internationally
- Apart from venturing into emerging markets, Etisalat should consider penetrating the Australian, European, and American economies despite the potential competition from already established players. The strategy would spread the brand name of Etisalat to other markets.
- Fair pricing mechanisms should be implemented to offer an affordable package to customers from diverse economic backgrounds. Minimizing the operational costs would make the price reduction move is successful.
Conclusion
The company’s experience in the telecoms industry stretching over three decades has been instrumental in laying the foundation for its competitiveness in the market. The weaknesses and threats that Etisalat has been subjected to hinder its growth in the market. In this respect, various alternatives such as partnerships, mergers, acquisitions, and enhancing its global presence could be strategic for sustainable growth.
References
Ayish, M. (2013). Media Convergence in the United Arab Emirates A Survey of Evolving Patterns. Convergence: The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies, 9(3), 77-87.
Cole, A. (2013). Analysis of Etisalat. Munich, Germany: GRIN Verlag.
Etisalat: Etisalat CSR & Sustainability Report 2012. (2013).
Etisalat: Business. (2015). Web.
Etisalat: Our Belief. (2015). Web.
Gulf News: Etisalat partners with Bharti Airtel to expand network infrastructure. (2014).
IT & Telecom Digest: Why Etisalat Nigeria is a Success. (2015). Web.
Leadership: Etisalat Expands To 11 African Countries. (2014). Web.
Management Guru: Etisalat: Strategic Analysis. (2012).
MBASkool: Brandguide: Etisalat. (2015).
Punch: Etisalat, Uber keeps customers on the move. (2015). Web.
Qualys: Etisalat Secures Growth. (2015).
Sutherland, E. (2011). International mobile roaming in the Arab states. Info, 13(2), 35-52.
The National: Foreign interests help Etisalat beat forecasts. (2011).
UAE TRA: UAE Cellular Mobile Networks Benchmarking 2013. (2015). Web.