Research Motivation
Good leadership is vital in both the performance and success of education. However, there is an urgent need to understand the challenges facing school leadership. Various leadership models are being implemented by organizations or institutions today to achieve their goals (Barth, 2001). This study will focus on the application of the Participatory Leadership Model (PLM) within the Saudi Arabian education system by evaluating the extent of its implementation and success whose evaluation is often done primarily by the national level of literacy to check on the ability of students to integrate and contribute to the society’s development (Bush, 2003). Barth (2001) states that people believe that leadership plays a vital role when implementing working solutions for schools thus it is the responsibility of leaders within institutions utilizing PLM to produce a favorable learning environment for children.
Research Background
School leadership is an effective team performance that comprises individuals who must be motivated towards achieving specific goals even though they may have different roles hence any challenge may distract performance. Evolution in leadership styles has seen a shift in institution leadership from autocratic to consultative approach where school leaders are not only expected to oversee the management but also to create an ideal and democratic learning environment for both staff and students (Barth, 2001). Saudi Arabia’s institution’s education system has faced a lot of challenges hence the need for PLM, which will enhance sharing of information to both parents and children (Gronn, 2003).
Research Problems
The education system in Saudi Arabia gives little priority to leadership as the government provides no incentives for education policy planners consequently leading to little input by administrators in achieving quality education due to operation under the General Administration Education in all the provinces of Saudi Arabia. Centralized power makes school heads powerless and without a definite role plus poor knowledge of PLM.
Literature Review
Leadership in an educational context influences the quality of instructions provided to students in school hence it is a social issue that should be assessed to avoid detrimental impacts on an education system. It is a channel that links teams to their broader working environments hence the need for the Participatory Leadership Model, which holds that the behavior of a leader determines the success of the entire education system (Gamage, 2009). Yukl (1994) states that participatory leadership involves engagement with colleagues as well as a delegation of duties and according to Sergiovanni (1984), it is about positive work relations as this helps in easing the pressures placed on leaders. Collective responsibility allows members to own their ideas without fear plus permits the involvement of multiple stakeholders (Miskel & Hoy, 2005). Participatory leadership gives a chance for the collaboration of parents, teachers, and government education officials in the process of policy formulation and implementation in the education context (Mulford, 2008). It is also an avenue for numerous ideas for team progress through discussions and brainstorming sessions over problems (Miskel & Hoy, 2005).
PLM allows for specialization among staff as they utilize particular staff strengths for overall success thus fostering their confidence and trust, as well as boosting their morale (Leithwood & Day, 2007). Ultimately, the leader decides on the applicable solution. Mulford (2008) lists the prerequisites for achieving success in school leadership as the provision of high-quality teaching to students, engaging parents in children learning and progress, as well as excellent leadership. Successful leadership ensures harmony amongst these three aspects thus enabling teachers, parents, and students to unite and jointly generate a golden era for erudition and schooling (Mulford, 2008). The education sector needs good leadership as it is entrusted with the mandate of grooming future generations to equip them with the skills necessary for the realization of a nation’s development goal (Bush, 2007). The focus on leadership of learning institutions is, therefore, of utmost importance in identifying the appropriate leadership style or ensuring success is a continuous endeavor (Leithwood & Day, 2007).
Research Approach
This paper will adopt both primary and secondary sources of data. Secondary data will be collected in the library on educational policies plus a literacy study to assess the success of the leadership model in use at each period in time. Primary data will be collected using structured questionnaires and will seek to measure both facts and opinions of a cross-section of educational counselors within Saudi Arabia. A written questionnaire will allow the respondents’ time to formulate their answers and also gives room for expanding the sample population. The target group in this study will be approximately 500 educational counselors within the different educational levels in Saudi Arabian education system, and this is due to the prominent role they play as the link between the student population and the institutional leadership and between parents and the institutional leadership.
Conclusion
Qualitative analysis will be used for this study to help relate theories on the efficacy of PLM with experiences within the Saudi Arabian education sector. The presentation will be done with the help of visual aids such as data tabulation, charts, and diagrams to enhance clarity.
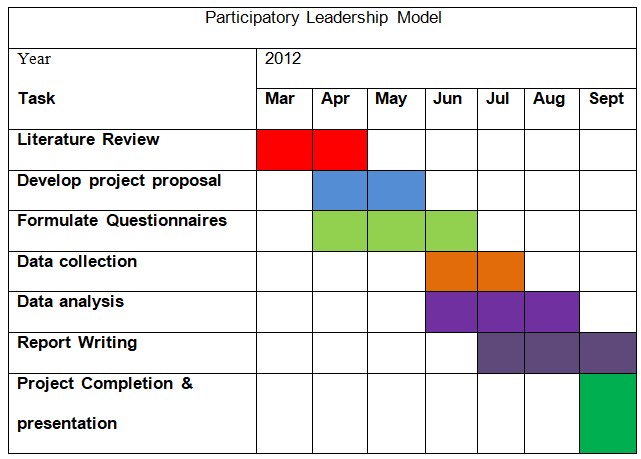
Research Schedule
References
Barth, R. (2001). Learning by heart. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Bush, T. (2003). Theories of educational leadership and management (3rd ed.). London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Bush, T. (2007). Educational leadership and management: theory, policy, and practice. South African Journal of Education, 27(3), 391-406.
Gamage, D., T. (2009). Leading and managing the 21st century schools for improved student performance. Australia: McGraw-Hill.
Gronn, P. (2003). The new work of educational leaders: Changing leadership practice in an era of school reform. London: Paul Chapman.
Leithwood, K., & Day C. (2007). Successful school leadership. London: Sage Publications.
Miskel, C., G., & Hoy, W., K. (2005). Educational administration: Theory, research, and practice. New York: McGraw Hill.
Mulford, B. (2008). The leadership challenge: Improving learning in schools. Victoria: ACER Press.
Sergiovanni, T., J. (1984). Handbook for effective department leadership: Concepts and practices in today’s secondary schools. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Yukl, G., A. (1994). Leadership in organizations. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.