Over the recent years, profitability for firms has decreased progressively due to the impact of COVID-19, fuel prices, and associated factors like inflation rates. The economic slowdown has influenced firms’ profitability and fear of firms because earnings per share decline when the economy turns into a recession. Currently, firms are consolidating to maximize profit and maintain market share. Low tax and interest rates have contributed to profit growth over the past two decades (‘‘Have profits peaked at American businesses?’’ n.d.). However, there are rising tax and interest rates, which are prospected to impact company profitability as it will be costlier to service debts. Therefore, to increase profitability for American businesses, it will be essential to cut down on rising tax and interest rates and consider other factors contributing to profit growth.
Supply and demand are essential elements that affect the profit margins of any organization. Considering shortages of parts at Ford plants, it can be depicted that the company’s profit is likely to be affected (‘‘Have profits peaked at American businesses?’’ n.d.). Shortages of parts affect the demand for the products such that when there is high demand for the commodity, and its supply is low, the company will incur losses (see figure 1). Demand and supply are significant because it affects pricing, competitiveness, expansion, marketing, inventory, financing, and salaries.
The demand and supply graph affects the pricing of services and products a business offers. A lack of market demand forces a company to lower its prices to move products off the shelves, while a supply shortage can increase prices. Shortage of parts at the Ford plant has implication on the supply, which result in a low-profit margin as the company will produce less for the market. Supply and demand also influence the competitiveness of an organization. In this scenario, loss of supply by the Ford plant can result in unsatisfied customer needs risking the company to lose potential customers to its competitors. A drop in demand for a product offers an opportunity for competitors to provide an alternative to consumers and take market shares.
A business’s ability to expand depends mainly on supply and demand since an organization with higher demand for products and services receives more significant growth opportunities and makes more profit. However, oversupplying and low demand can result in business collapse due to low profits earned. Organizations must attain the appropriate balance for sustained and consistent expansion. At the Ford plant, a shortage of parts can affect marketing because the firm cannot satisfy the needs of all customers (‘‘Have profits peaked at American businesses?’’ n.d.). Marketing is one way a business drives demand for its services and products. A good marketing campaign makes customers aware of commodities and creates a desire for them, increasing profitability. Strong demand and supply increase an organization’s attractiveness to shareholders to offer financial assistance that expands and improves the business. A lack of solid demand or supply to satisfy customers’ needs can result in the company making less profit and a lack of interest in investors.
Consolidation is a phase in the industry life cycle where competitors merge. The main reasons for the companies seeking consolidation are to gain a more significant portion of overall market shares and gain competitive market advantage. Consolidated companies can increase top-line revenue and business valuation to improve corporate fundamentals and make shares of their stocks more attractive to investors. However, during consolidation, some businesses can find their synergies well-suited for consolidation, but it might backfire when one of the companies has too much debt. Therefore, consolidation can increase the debt load of the new company and, if not adequately addressed, become problematic for the management of the business and shareholders. Business consolidation can lead to cost-cutting increasing revenue and profit. However, it can have a negative economic effect as it can potentially cause redundancies in the workforce that mostly end in unemployment and layoffs.
Tax changes impact the behavior of businesses and individuals through substitution and income effects. Tax rate cuts have positive effects as lower tax rates raise the after-tax reward for investing, saving, and working. Any change in taxes has a potential effect on a business. When income tax is increased, it reduces the disposable income of consumers, which consequently makes them have less money to spend on services and goods. As a result, it lowers demand and sales revenues causing a decline in business profit (See figure 2).
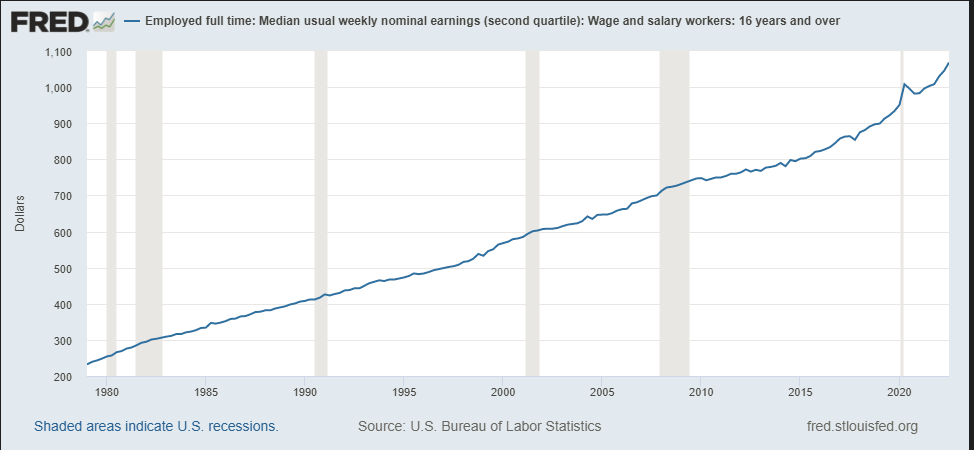
In the U.S., labor costs have risen as a tight jobs market boosted wage growth, keeping inflation elevated and hiking interest rates. High costs for gasoline and a range of goods and services have accelerated consumer spending, with monthly prices surging. Increased inflation has led to economic contraction, risking the global economy to enter into a recession. As shown in figure 3 below, the nominal wage growth shows rising labor costs from years ago.
To gain control over profit margins and reduce rising labor costs requires an organization to provide employees with predictable work schedules, reduce pay overages, optimize schedules, incentivize performance, increase productivity and reduce turnover. Providing shift workers with fair and predictable schedules leads to cost-savings and other associated benefits, such as increasing employee morale and decreasing stress. The practice can be implemented by giving advance notices, providing ample rest time, and reducing schedule changes. Cutting avoidable pay overages is one way of reducing labor costs. It can be done by using stress profiles to alert overtime, ensuring appropriate rest time between shifts, and confidently recording accurate timesheets. Schedule optimization helps a business understand better trends and make prompt decisions that benefit the business. It is also more costly to replace an employee that to retain one. Investing and keeping staff happy empowers them to achieve company objectives. Providing employees with job security helps reduce labor costs, and it can be achieved through team empowerment, prioritizing their well-being, and practicing a sense of inclusivity. Employees who perform well should be provided with commissions and bonuses as incentives.
In conclusion, profitability for American businesses has been influenced by various factors, including tax rates. Increasing tax rates results in a company being unable to service its debts. For the business to become profitable in the future it will be essential to control rising labor costs and taxes. Supply and demand affect profitability as they affect pricing, competitiveness, expansion, marketing, inventory, financing, and salaries. Companies have opted for consolidation to gain a more significant portion of market shares and maintain a competitive advantage.
References
Employed full time: Median usual weekly nominal earnings (second quartile): Wage and salary workers: 16 years and over. (n.d.). Federal Reserve Economic Data | FRED | St. Louis Fed. Web.
Have profits peaked at American businesses? (n.d.). The Economist. Web.