Introduction
Financial performance of an entity changes from one period to another period depending on a number of factors. Some of the factors are economic (such as fluctuations in exchange rate, stiff competition and recession), social (such as people’s perception about the product), and climatic factors (adverse weather changes such as drought and constant snow flow) among other factors (Vance, 2003). Therefore, an institution should closely monitor how both internal and external factors affect various attributes of the financial statements (Haber, 2004). It is of essence to analyze financial performance of a company. This treatise analyzes the financial statements of Coca-Cola Amatil using ratios.
Ratio Analysis
Various ratios were computed to ascertain profitability, efficiency, leverage and liquidity of the company. A summary of the results of the ratios computed is in appendix. The trend for Liquidity ratios has been erratic. Current ratio, quick asset ratio and cash flow ratio declined in 2009 and thereafter increased in 2010. The trend for the ratio is shown in the graph below.
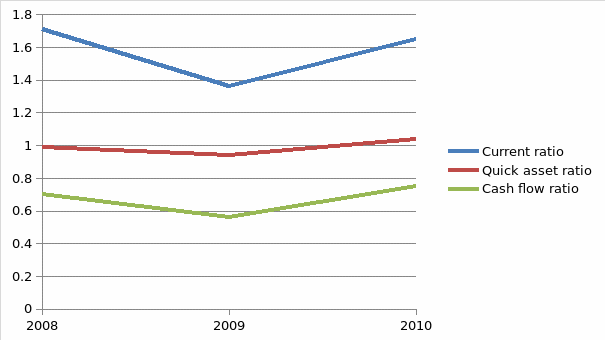
- Graph showing trend of liquidity ratios
- Vertical axis represents the ratios
- Horizontal axis represents the year
Profitability ratios
Gross profit margin has increased over the three year period from 17.54 in 2008 to 19.28 in 2010. Return on equity increased in 2009 thereafter it declined in 2010. Therefore, no trend can be observed. Return on assets has increased over the three year period. The diagram below shows the trend of profitability ratios.
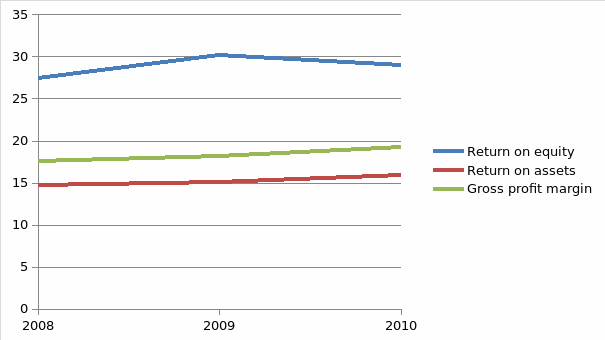
- Graph showing trend of profitability ratios
- Vertical axis represents the ratios
- Horizontal axis represents the year
Cause of decline in performance
In 2009, the net profit after tax of the company grew by 11.1%. While in 2010, the rate of growth declined. 2010 annual report indicates that the company experienced unprecedented number of natural disasters across the major markets. There were floods in “Queensland, Victoria and New South Wales, Cyclone Yasi. In addition, Christchurch experienced earthquakes” (Sydney Morning Herald, 2011). These natural disasters affected over 4,000 key customers. This led to reduction in sales for 2010. Besides, the company donated plenty drinks to the affected areas.
Other than natural disasters, there has been “colder and wetter weather across the Eastern seaboard compared with the previous years” (Sydney Morning Herald, 2011). The wet weather caused by the floods weakened trading condition throughout summer. This affected consumption significantly. Another factor which led to decline in performance is the global recession experienced in 2010. The recession caused reduction in consumers’ disposal income. This led to changes in consumption patterns. More specifically, there was a decline in demand for the company’s products. This resulted to lower actual sales than forecasted. Further, the industry faced a lot of competition from imported cheap drinks. High Australian dollar contributed to importation of cheap drinks. Also, rising popularity of other drinks impacted negatively on Coca-Cola products. Therefore, competition and exchange rate fluctuations played a role in poor performance reported in 2010 (Sydney Morning Herald, 2011).
Remedies
The company should explore new markets and new products. This will be a long term measure. Management should target markets which are not prone to natural disasters. Also, Coca-Cola Amatil should avoid overreliance in one market or a few markets for revenue. Currently, the company manufactures, distributes and markets carbonated soft drinks, still and mineral water, fruit juices, coffee, fruits, vegetable, and various brands of beer. Therefore, there is a need to reach for new markets across the globe. To achieve this, the company should come up with new products. The products should target specific markets. They should also have a variety of products which will have demand in all seasons.
Appendix
References
Haber, R. (2004). Accounting dimistified. New York: American Management association.
Sydney Morning Herald, (2011). CCA lowers guidance for 2nd half of 2010. Web.
Vance, D. E. (2003). Financial analysis and decision making: Tools and techniques to solve. United States: McGraw-Hill books