Introduction
Coca-Cola Inc. is one of the most respected firms who have celebrated more than a century of sustained business excellence, the company was incorporated in September of 1919. The 53 billion beverages consumed worldwide that bear the company’s trademark in which Coke owns or licenses accounts for approximately 1.5 billion.
Coca-Cola Inc., goal is to use its company’s assets- brands, financial strength, unrivaled distribution system, global reach and accelerate growth in a manner that creates value for its shareholders. However, sustaining their leading edge position in the non-alcoholic beverage market has not gone without its challenges. The firm’s outlook for 2008 fell well below the initial expectations.
The purpose of this paper is to examine the effect Coca-Cola’s brand new financial initiative to reduce their price on 16 ounce plastic bottles of coke will have on stock prices, cash flow, and market share. It will also compare and contrast the various outcomes as well as discuss the financial impact.
Financial Initiative – Coca Cola Reduces Price on 16 ounce plastic bottle of coke to $.99
On January 21, 2009, Coca-Cola launched a new global marketing campaign in an effort to draw consumers back to soft drinks. The company used the Super Bowl to introduced its “Open Happiness” campaign to announce its “recession-friendly price initiative. Beverage Digest Editor, John Sicher, noted that soda sales fell about 4.8 percent in the U.S. during the first nine months of last year. Coca-Cola soft drink sales fell 4.4 percent in the same period, but the company did gain 0.1 percentage points of market share.
As part of its marketing campaign, Coke announced it will sell 16-ounce plastic bottles of Coke, Coke Zero, Diet Coke, Sprite and Fanta for just 99 cents. It is anticipated that the lower price will appeal to recession-weary consumers. The company hopes that the ad campaign will help bring old customers back who stopped consuming soft drinks and attract new consumers to their product line.
For purposes of this analysis, it is suggested that the price reduction will notably increase sales by 10%. The financial outcomes resulting from the anticipated increase in sales will affect not only profitability, but the value of stock in addition to increasing its market share of soda products.
Outcome 1 – Profitability
The goal of any firm is to maximize the wealth of the investors. One step to maximizing wealth is by increasing profitability. To examine the impact of a 10% increase in sales revenue, we used a percent of sales based pro forma income statement.
One would anticipate that an increase in sales would result in an increase of profitability, but such is not the case with this endeavor. The financial initiative of Coke was to increase sales by 10%, but did not include any initiatives to eliminate or reduce expenses. Thus, based on the pro forma projections, Coke is projected to reduce its profitability by 9.8%. The chart below compares the revenue and expenses from 2007 to those associated with the 10% increase in sales revenue.
Profitability Pro Forma
Outcome 2 – Stock Valuation
With a 12% growth in stock in 2007 the following calculation proposes an additional 10% increase in 2008.
ATLANTA, February 21, 2008 – The Board of Directors of The Coca-Cola Company today approved the Company’s 46th consecutive annual dividend increase, raising the quarterly dividend 12 percent from 34 cents to 38 cents per common share. This is equivalent to an annual dividend of $1.52 per share, up from $1.36 per share in 2007. The dividend is payable April 1, 2008, to shareowners of record as of March 15, 2008 (The Coca-Cola Company, 2008).
Market Share
Market share is not only how the company is doing in sales but how they are trying to in creases their sales by cutting their cost to produce more for less. Coca-Cola decreasing the cost of their 16-ounce shows they are trying to increase their sales across the nation due to economical impact in the economy. Market share is determine by calculating sales for the year, then divided by the total market sales. In an article by Greg Guenthner states “The Beverage Marketing Corp. has the carbonated soda pop business pegged at $65.9 billion in total annual sales last year. But traditional soda growth has been spotty and lackluster for many years this decade” (Guenthner, 2008, p8) The total market sales have been decreasing at a rate of 0.2% each year. With this information Coca-Cola should attract more the current consumer with the low cost beverage.
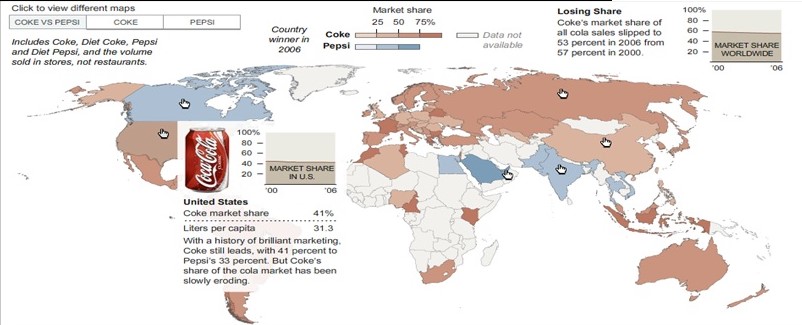
The map above shows a clear view of Coca-Cola’s market share in 2006 with comparison with sales in 2007 and the number of total market sales Coca-Cola showed a very little increase in their total market share.
- Compare & Contrast – Evaluate your findings to determine the most likely outcome – Holly
Additionally, be sure to include your calculations which support your analysis of the various financial outcomes.
Conclusion – Discuss impact – Elka Brown
The recession the world economy, especially that of the United States, first touches those categories of products that consumers evaluate not as indispensable. The Coca-Cola Company that we are discussing offers such category of products. The soft drinks industry is something people can do without if they have less money to spend. This is the reason the company launched its latest initiative of serving 16 ounces bottles of its products for 99 cents.
But, the problem the company has is that the soft drinks market, which it is in, has been shrinking by 0.2% per year the last years. This means that the companies in this market have been doing 0.2% less total sales per year the last years. This means less revenue for these companies, which in return means less possibility for profit. As we see from the profitability analysis their net profit after taxes (which is the ultimate amount of money that the company earns per year) is going to have a variance of -9.8. This means that the company with have earned at the end of the year an amount of money 9.8% less than the previous year. In this respect this is not good news and, since we almost have a double digit percentage loss, the company has to think seriously of its future. The launch of the latest 99 cent initiative can be seen as effort in this direction.
In order to respond to the shrinking market sales, another important initiative was that of increasing the share dividend. This effort was made, I think, in order to attract more capital toward the company in a difficult time. In this situation of market sales going down regularly it is important to have investors put trust (and ultimately) money in your company. This would give you the necessary liquidity to cover expenses of strategies like the one we are discussing.
Finally, I would say that the market share increase in percentage is a positive factor for company’s future. It is true that it was increased only to 45.8% from 41.52% and that is not an important increase. But, in the current conditions where the total sales of the market are shrinking, and the recession ahead, to have an increase, even this small, means that you consolidate your position on the market. At the moment the 99 cents strategy major impact is that of strengthening the market position of the company. This market position consolidation would guarantee a steady flow of cash to the company and would ultimately serve for the future when the recession will pass. At this time, this strategy can guarantee the “survival” from the recession to the company and when the market will re-begin to expand-grow (in a future time) the company would be in a much better position to start-off than the competition.
Reference
Gitman, L (2006). Principles of Managerial Finance. Boston, Mass: Addison Wesley.
Coke announces ‘Open Happiness’ campaign. The Atlanta Journal-Constitution (2009) Web.
Guenthner, G. (2008) Investing in Beverage Stocks. Penny Sleuth. Web.
The Coca-Cola Company, (2008). THE COCA-COLA COMPANY INCREASES ANNUAL DIVIDEND BY 12 PERCENT; 46th CONSECUTIVE ANNUAL INCREASE. Web.
The New York Times, (2007) I’d Like to Sell the World a Coke. Web.