The contribution margin per unit, total fixed costs, the breakeven point in units, and total expected profit
The contribution margin per unit, total fixed costs, breakeven level, and total expected profit of Dewqas Limited based on its decisions of reducing the selling price of its product and installing new machinery are calculated in the following table:
Table 3: CVP Analysis.
The expected profit at various sales levels
The profit-volume analysis of Dewqas Limited is given in the following table:
Table 4: Profit-Volume Analysis.
The profit-volume charts of ‘no change’ and ‘decisions’ scenarios are given in the following:
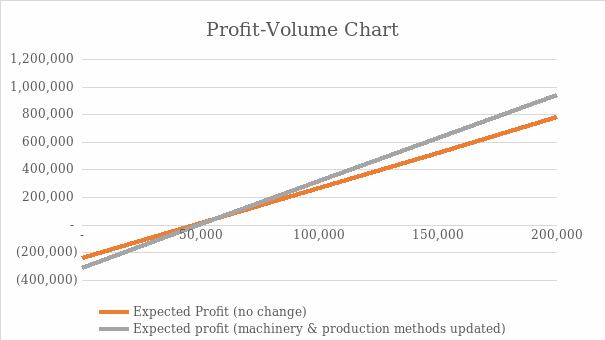
A brief recommendation to management advising on the recommended course of action
Dewqas Limited is considering different options to improve its profitability, including reducing the selling price of its product and updating its existing machinery and production methods. These two decisions are independent of each other and can be implemented together. Lowering the selling price can increase the company’s sales from 150,000 units to 157,500 units. However, the company will earn less revenue from its marginal sales as the price will reduce from $9.8 per unit to $9.65 per unit.
The decision to update machinery and production methods will also reduce the variable cost of production from $4.7 per unit to $3.4 per unit. The Cost-Volume-Profit analysis shows that the company could generate a higher contribution margin by implementing these decisions. This means that the profitability of the company could improve by selling more units. However, the decision to update machinery and production methods will increase the company’s fixed costs from $243,000 to $311,000. This implies that the breakeven level (units) will increase from 47,647 to 49,760 if the company makes the proposed changes in its selling price and production.
A high breakeven level is not recommended as the company needs to cover its high fixed costs before achieving a profit. However, the profit-volume analysis shows that the company will have a profit of $626,500, which is more than the current profit of $522,000 by selling 150,000 units. This shows that these decisions could improve the business’s profitability, and the management should accept these decisions.
Reference
Pilbeam, K 2018, Finance & financial markets. 4th edn, Macmillan International Higher Education, New York.