Executive Summary
The purpose of this data review project is to examine the diabetes management practices applied by Anthem through a data review of key indicators and compare this information to the benchmarks set by the AHQR. The focus is on diabetes as a chronic condition because it requires specific attention when addressing comorbidities and interventions that target a person’s lifestyle, which has to be done outside a clinical setting.
The rationale is reflected in two major trends – the fact that the population in the United States is aging, meaning that the percentage of people who have some chronic condition will increase in the following years and the costs associated with the mentioned care. To examine the data, information was gathered from Anthem, AHQR, and authoritative literature and compared using a histogram for visual presentation.
Metrics for performance include readmission rates, quality of life, denial, the aging process, and socioeconomic conditions. Specific outcomes of this project reveal a significant number of readmissions, satisfactory quality of life reported by patients, and a need to pay additional attention to socioeconomic factors such as education and age.
Overall, the data summary revealed the need to address diabetes management at Anthem by using evidence-based programs since the current performance indicators are unsatisfactory when compared to benchmarks. The rationale for this is the fact that chronic conditions affect individuals continuously, and some can significantly impair an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks. With diabetes, it is essential to monitor blood sugar levels and adhere to a specific diet to remain healthy.
Abstract
Diabetes is a chronic condition that severely affects a person’s health and impairs the overall quality of life. From a perspective of a health insurer Anthem, individuals with diabetes require constant monitoring and health services to ensure that their health state is not compromised, which results in chronic conditions management spending accounting for 75% of the overall reimbursements. Another problem that highlights the urgent need for addressing this issue is the current population trends that require a strategy change from both providers and insurers.
It can be hypothesized that Anthem will be dealing with a more significant number of patients requiring chronic condition care in the following years, and identifying the issues that already exist and addressing them using evidence-based practices can help the insurer prevent adverse consequences of such changes. This data review project determined that Anthem’s readmission rates within 30 days are 23.2% higher than established by a national organization.
Additionally, the self-reported quality of life and socioeconomic assessment provides an understanding of the issues that may contribute to the problem. The evidence-based practices reviewed in this project suggest dedicating more time towards two innovational strategies – telemedicine for educating patients and mHealth for monitoring vital health-related indicators. The assessment of the balanced scorecard developed for Anthem suggests that this approach will help enhance performance in all four domains and improve the bottom line of the company.
Data Review Project Report
This report is written for the executive team at Anthem to notify them of the current issues that affect the insurer’s revenue in the field of chronic disease management. The critical issue examined in this data review project is the increasing number of people affected by chronic diseases in the US, which accounts for a large portion of costs, and with the current population trends, this problem addressing this problem will be more difficult in the future. Poor management practices and lack of support for self-management contribute to a large number of readmissions that exceed 80% with a benchmark of 56,8% and comorbidities as a result of diabetes progression (AHQR, n.d.).
Review of the Literature
In general, most resources provide substantial evidence arguing that diabetes is an increasing problem in the US. Combined with other issues that the healthcare sector in the state is experiencing, such as increasing costs, understaffing, and aging population results in a severe problem that needs to be addressed (Ostling et al., 2017). As an insurer, Anthem can benefit from implementing programs that efficiently reduce the number of patient visits to hospitals through self-management and self-monitoring, since unlike acute conditions, chronic diseases can be successfully addressed at home. Munshi et al. (2016) state that the most common comorbidity that affects diabetes patients is hypoglycemia, which is a condition caused by low blood sugar levels. The authors argue that the care procedures and recommendations should be simplified for better results and emphasize the importance of goal setting based on a specific complication that an individual has.
For Anthem, this implies that providers have to alter their current practices of classifying patients, and value-based care that focuses on the results of treatment, in this case, improvement of a patient’s health concerning particular comorbidity, should be applied. Next, Wallace, Smith, Fahey, and Roland (2016) argue that organizations should focus on community-based interventions to improve the management of diabetes.
Since this is the overall of Anthem’s work, the interventions suggested by the authors can be used to develop a solution for disease management issues. Hamine, Gerth-Guyette, Faulx, Green, and Ginsburg (2015) and Wood et al. (2016) examined the impact of mHealth and telemedicine programs, which are smartphone applications developed to help people track their health status; can have a beneficial effect on the diabetes management and treatment. Based on the findings of this data review, Anthem can apply these solutions to target patients with diabetes and decrease care costs.
Data Review
Currently, the hospital readmission rate within a 30 day period for patients with diabetes is 85% at Anthem, which is the main focus of this project. As for the context, the recommended benchmark set by the is 56.8%, indicating a significant issue that Anthem has to address. Therefore, the goal of the insurer should be to lower the readmission rates by 23.2% to achieve satisfactory quality outcomes. In order to align the problem with the needs of Anthem, it is necessary to examine the organization’s strategic direction. Organizational considerations include the insurer’s mission to improve the lives of communities and use innovation to introduce advanced care to its patients (“Mission, vision, and values,” n.d.). The business model under which Anthem operates implies the need to reimburse providers for services.
In the context of chronic condition care, this means that each visit to a medical expert has to be paid for by Anthem, regardless of the actual impact on a person’s health. Moreover, the healthcare industry’s problems and increasing costs worsen the issue. Therefore, the rationale for engaging in this project is that similarly to any business, Anthem aims to be more cost-effective while providing excellent care services to its patients. Therefore, this data review project will allow Anthem to examine the issue of diabetes care and locate evidence-based solutions that can be implemented to reduce the burden of chronic conditions and improve the quality of patients’ lives.
The balanced scorecard developed for this project highlights the system-wide impact that this initiative can have on a system-wide level. Most importantly, the domain of finance will be affected because lower readmission rates and improved care would result in fewer reimbursement payments for the providers. Additionally, the evidence-based recommendations provided in this paper consider the strategic objectives of Anthem because they allow integration a program that utilizes innovation as a core element of interaction with patients.
The main impact that this project will have on Anthem’s operations is reflected in the fact that approximately 75% of costs in healthcare are dedicated to reimbursing providers for chronic condition management (Raghupathi & Raghupathi, 2018). By addressing the diabetes care and improving current performance indicators to match the benchmarks, Anthem will be able to increase its revenue, by decreasing expenses associated with this problem. Alongside this, the company will benefit from improved client satisfaction and process improvement. Table 1 presents the balanced scorecard developed for this project that outlines key benefits for Anthem.
Table 1. Balanced Scorecard (Created by the Author)
Data Measured
Performance indicators include self-reported quality of life and age group data because it can enhance the company’s understanding of the problem from a community-based perspective. The primary outcome measure is the number of successfully managed cases under the new policy introduced by Anthem. Next, additional information that can be used to strengthen this alignment is the results of the programs that Anthem already launched targeting diabetes care. These initiatives are currently active in some states and target a limited population and understanding whether the chosen approach is practical would help strengthen the focus of this data review project.
Data Review and Discussion
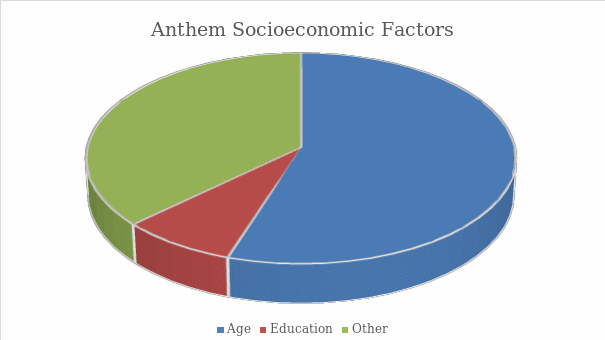
One new insight that emerged as a part of this data review is the fact that education level can significantly impact the likelihood of having diabetes, which is a factor that requires additional attention from the insurer. Graph 1 displays the hospital readmission rates within the 30 day period for Anthem’s patients diagnosed with diabetes. The histogram reveals that the rates are very high, meaning that the majority of patients who initially visited the hospital because of their condition had to return because the issue was not addressed correctly or due to complications.
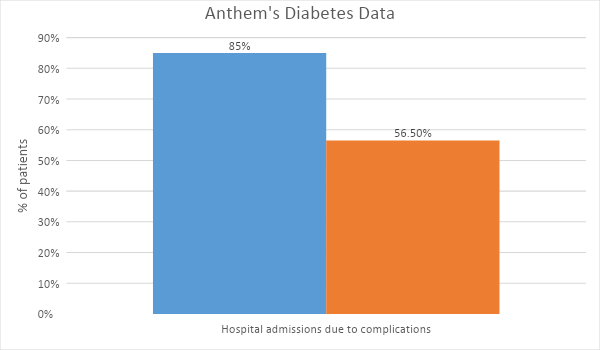
Next, patient satisfaction rates were included in this analysis to determine the impact of the disease and its management on the well-being of the individuals. The self-reported data indicates that most patients have a satisfactory quality of life. However, most individuals do experience inconveniences because of their condition. Prajapati, Blake, Acharya, and Seshadri (2018) use the Self-Administered Quality of Well Being index (QWB-SA) to assess this element, and their findings suggest that the benchmark for this indicator is 64,57. Graph 2 displays the comparison of this data, including the results from Anthem.
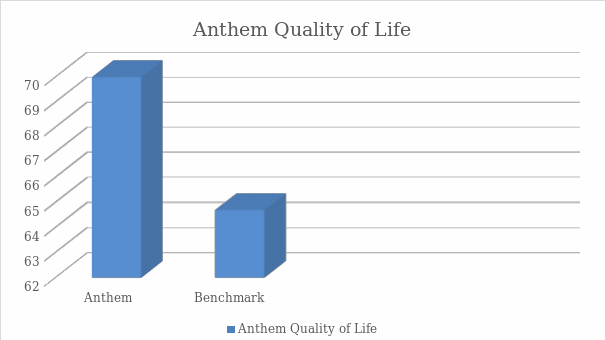
The age group assessment reveals that older individuals are more likely to have diabetes, which is consistent with the evidence found in the scholarly literature.
Suwannaphant, Laohasiriwong, Puttanapong, Saengsuwan, and Phajan (2017) argue that the socioeconomic status of a person has a significant impact on the outcomes of treatment for him or her, and Graph 3 reveals the relationship between socioeconomic status, educational attainment, and diabetes. The findings of this data review project indicate that Anthem’s readmission results and other indicators are significantly worse than those set by the national health organizations or those reported in the literature, and that additional attention should be dedicated to socioeconomic determinants of health.
In the context of recommendations that will be presented next, all solutions should be developed considering the capabilities and skills of this population. Also, the analysis reveals that Anthem may be losing revenue because of comorbidities and complications due to high readmission rates. The limitations of these findings are reflected in the fact that it was conducted using different populations, and self-reported measures lack objectivity. In addition, some bias can be present since data collected from Anthem can poorly present the population’s health. Overall, the data is valid because it is collected and interpreted using scholarly resources and statements by national healthcare organizations.
Recommendations for the Future
The literature review conducted for this project revealed that Anthem should focus on providing accessible and easy-to-use tools to its diabetes patients, which will allow them to successfully self-manage their condition. Currently, the healthcare sector’s primary trend is a shift towards telemedicine, which incorporates the use of communication devices in issuing appointments with patients, diagnosing, and treating conditions. The implications of this approach in diabetes management are significant because using such strategies Anthem will be able to provide expert support to its patients while addressing other issues.
The implication is that patients will be able to receive advice regarding management faster, without a need to drive to a provider and meet a medical professional face-to-face (Wood et al., 2016). Thus, patients will be able to make changes to their management strategies, for instance, alter their dietary preferences or incorporate more exercise, which should lead to an improvement in health. Consequently, this will result in a better quality of life and mitigate the need for frequent hospital admissions and readmissions. Additionally, this strategy addresses the issue of low income that can impair the ability to manage a condition adequately.
Telemedicine is thought to be a significant new development that will help treat a variety of healthcare problems in the US market. However, this approach only targets a part of chronic condition management since individuals who have these conditions require continuous monitoring, guidance, and support. This approach should improve access and enhance support by providing an easy-to-access resource for diabetes clients
The second recommendation is to develop a mobile phone application that allows tracking a patient’s well-being. This is consistent with the findings of the data review project suggesting that socioeconomic conditions have an impact on disease management, requiring a cost-effective solution. Additionally, a study by Hamine et al. (2015) reveals that most studies that are evaluating the efficiency of mHealth report an improved adherence to provider recommendations. These accessible tools can help patients change their behavior and track progress, which is vital in diabetes management. Thus, Anthem should focus on developing a comprehensive tool that addresses exercise, diet, and blood sugar management needs of patients.
Conclusion
This project added value and aligned with the Anthem’s strategic plan by providing implications for improving current diabetes management standards applied by the insurer. The main focus is on diabetes because the condition results in a number of complications and can lead to frequent hospitalizations if not appropriately managed. In addition, it requires continuous monitoring because of its impact on the levels of blood sugar and requires behavioral intervention as a significant component of management.
References
AHRQ. (n.d.). Diabetes quality measures compared to achievable benchmarks. Web.
Hamine, S., Gerth-Guyette, E., Faulx, D., Green, B., & Ginsburg, A. (2015). Impact of mHealth chronic disease management on treatment adherence and patient outcomes: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 17(2), e52. Web.
Mission, vision, and values. (n.d.) Web.
Munshi, M., Florez, H., Huang, E., Kalyani, R., Mupanomunda, M., Pandya, N.,… Haas, L. B. (2016). Management of diabetes in long-term care and skilled nursing facilities: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care, 39(2), 308-318. Web.
Ostling, S., Wyckoff, J., Ciarkowski, S., Pai, C., Choe, H., Bahl, V., & Gianchandani, R. (2017). The relationship between diabetes mellitus and 30-day readmission rates. Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology, 3(1), 1-8. Web.
Prajapati, V., Blake, R., Acharya, L., & Seshadri, S. (2018). Assessment of quality of life in type II diabetic patients using the modified diabetes quality of life (MDQoL)-17 questionnaire. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 53(4), e17144. Web.
Raghupathi, W., & Raghupathi, V. (2018). An empirical study of chronic diseases in the United States: A visual analytics approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(3), 431. Web.
Suwannaphant, K., Laohasiriwong, W., Puttanapong, N., Saengsuwan, J., & Phajan, T. (2017). Association between socioeconomic status and diabetes mellitus: The national socioeconomics survey, 2010 and 2012. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research: JCDR, 11(7), LC18–LC22. Web.
Wallace, E., Smith, S., Fahey, T., & Roland, M. (2016). Reducing emergency admissions through community-based interventions. BMJ, 352(6817), 1-7. Web.
Wood, C. L., Clements, S. A., McFann, K., Slover, R., Thomas, J. F., & Wadwa, P. (2016). Use of telemedicine to improve adherence to American Diabetes Association standards in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 1(1), 1-8. Web.