Introduction
The digital camera is a commonly utilized hardware device that enables users to capture and store photographs as data on a memory card. To master the art of photography, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the technical aspects of a modern digital camera. It consists of several integral parts that capture and preserve images.
The lens, composed of high-quality glass, plays a crucial role in focusing light and capturing the picture. The camera features a screen that allows users to preview and adjust settings before taking a photo, providing a convenient interface for customization. Moreover, a flash enhances the camera’s functionality, ensuring proper lighting in dim or dark environments, resulting in more precise and well-lit shots.
The digital camera serves the primary purpose of capturing valuable moments and landscapes, while also offering the ability to record videos of varying durations. It offers a convenient means of immortalizing visual content for personal and professional purposes. This comprehensive technical description will explore the dimensions, materials, operational principles, functions, and interconnections of each camera part, including the lens, screen, and flash, providing a detailed understanding of its inner workings and potential benefits.
Detailed Description of the Digital Camera
Lens
As mentioned, the lens is the primary component of a digital camera, playing a critical role in capturing images. Its dimensions depend on the model and its intended use. Made of high-quality orthotic glass, it is characterized by perfect transparency and smoothness. The camera lens’s operation principle is based on one of the main optical properties of light — refraction (Bonk, 2022). This property is visible when stirring sugar in a cup of tea.
In a digital camera lens, light is refracted as it passes through the clear surface of the lens glass. As a result, the lens projects a sharp image of the objects being photographed onto the “matrix” or photosensitive element. The lens’s primary function is to capture and direct light, allowing one to create photographs with different focal lengths, depth of field, and clarity levels. Its relation to other camera parts involves its alignment with the image sensor and cooperation with its autofocus system to ensure accurate focusing.
Display
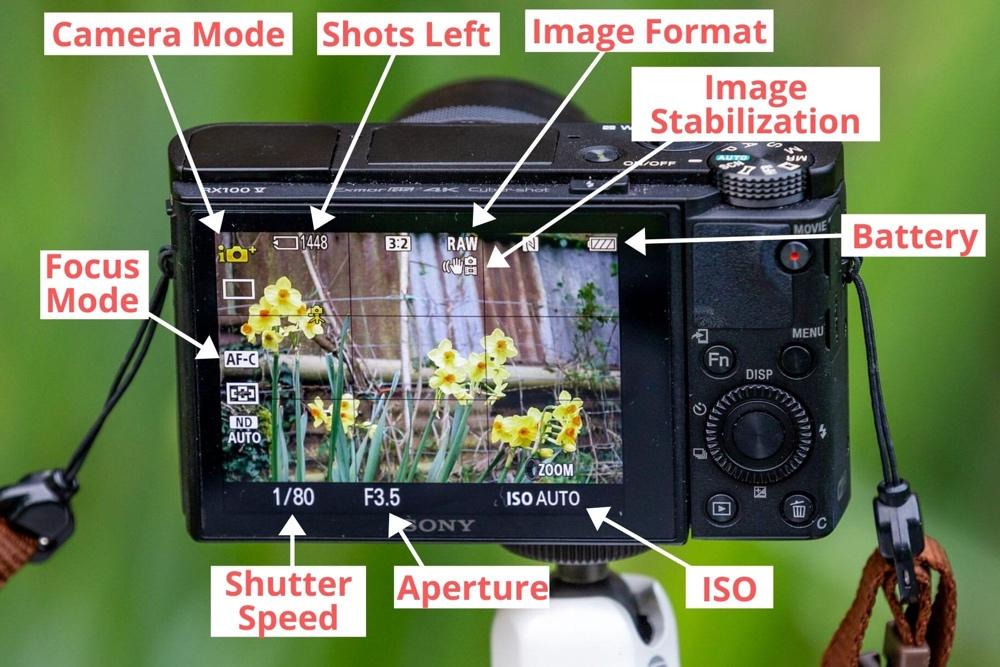
The screen, also known as the liquid crystal display (LCD), is an integral part of a digital camera that provides visual feedback to the user. The LCD takes up most of the camera and helps adjust aspects such as exposure, the sensitivity of the camera’s sensor, and shutter speed (Fig. 1). It is usually a high-resolution panel, varying in size from a few inches to several inches diagonally.
The screen displays a live scene preview and presents various personalization settings and options. Its function allows users to compose shots, view captured images, navigate menus, and customize camera settings. In terms of interconnectivity with other parts, the screen is electronically linked to the camera’s internal processor, providing a visual interface for interacting with camera functions.
Flash
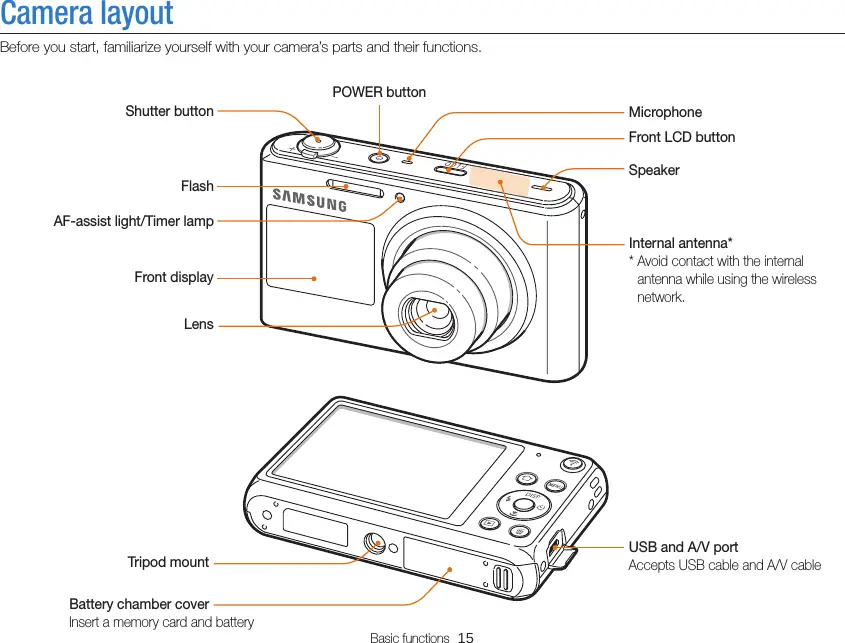
The flash is an essential component of a digital camera that provides additional illumination when shooting in low-light conditions or to fill in shadows. It is a part located at the top of the camera that emits light briefly (Fig. 2). The shutter button triggers it, and then it exposes the subjects to be photographed. The size of the flash may vary depending on the camera model.
The primary function of the flash is to supplement the available ambient light, resulting in well-lit photographs with accurate colors and details. The flash is synchronized with the camera’s electronic shutter and exposure control to ensure optimal lighting conditions at the right moment. It works in conjunction with the camera’s metering system to determine the optimal amount of light for balanced exposure.
Conclusion
With its lens, screen, and flash, the digital camera is a powerful tool for capturing and preserving visual memories. These components interact to capture light and convert it into a picture using lens elements, sensors, and technologies included in the camera display. The camera’s versatility caters to a wide range of photography needs, from capturing fleeting moments to documenting significant events.
References
Bonk, L. (2022). What do different digital camera lens do? Gadget review. Web.
How to use a point and shoot camera – A detailed guide to compact camera photography. (n.d.). Finding the universe. Web.
Samsung galaxy digital camera manual. (n.d.). Ihongtortai. Web.