Industry and Company Overview
Based in Britain and with its headquarters located in London-Luton airport, Easy Jet Airline was inaugurated in 1995. The company had a workforce exceeding 8000 people by September 2012. The main mode of expansion of the company is through acquisitions (Sumberg 2011, Para.5). Its main secret of growth is the capitalisation of low-cost air transport demand. According to Easy Jet plc (2011), “the airline, along with subsidiary airline Easy Jet Switzerland, now operates over 200 aircraft, mostly Airbus A319” (p.13). Easy Jet comes second to Ryan airlines in terms of costs of travel.
With regard to Easy Jet plc (2011), in the fiscal year 2011, the company flew more than 55 million people (p.8). In need of enhancing competitiveness in comparison with other competing airlines, in February 2011, the company “painted eight of its aircraft with a lightweight, thin revolutionary nanotechnology coating polymer” (Sumberg 2011, Para.4). This coating reduces debris drag across the planes’ surfaces and the amount of power required to propel aircraft. Also, it has the implication of reduction of fuel bills (Sumberg 2011, Para.5).
Marketing Mix
Introduction to Marketing Mix
Marketing mix embraces the various choices that organisations make to ensure that their products or services are availed to the market place at the right price using the appropriate promotional strategies (Menon et al. 1999, p.19).
Marketing mix for Easy Jet
Place
Easy Jet specialises in service delivery. The place for the service offering is dependent on the preferred destination of its clients. This means that place is an essential factor for the company to consider in the derivation of the marketing mix for the company. In fact, according to Millward (2011), “…it serves 500 routes and a total of 118 airports in Europe, North Africa, and West Asia” (p.16). Therefore, for the success of the company, it has to choose the destination that will attract clients who are willing to pay all costs for the delivery of such services without making it encounter losses.
Promotion
Over the years of operation, Easy Jet airline has developed a number of ways of effectively communicating with clients to ensure that it retains the existing ones besides attracting new ones. One of the tactics of doing this is by promoting Easy Jet’s products through “making flying as affordable as a pair of jeans” (Jones 2007, p.34). Also, this can be done by requesting its customers to “cut out the travel agent” (Jones 2007, p.35).
Arguably, this is a more innovative promotion technique since, in a decade ago, the company only advertised through painting a booking telephone number on the side of its aircraft. The filming of airline TV series (1999 -2007) had the impact of making the Easy Jet appear like a household name within the UK. Although this film never portrayed the name of the company positively all the time, the company was highly promoted. Moreover, as part of promotional strategies, the company has changed from one business slogan to another. First, it was “‘the web’s favourite airline’ followed by ‘come on, let’s fly’ and later to ‘to fly, to save’” (Jones 2007, p.47: Armstrong 2006, p.83).
Price
Easy Jet capitalises on low fares as the main means of gaining more clientele and maintaining market share for the company. According to Easy Jet plc (2011), the company saved about 1 to 2 per cent of the total fuel costs (p.10) through this strategy. This saving amounts to about 14 million Euros. Consequently, in comparisons with other airlines, low fares give the company a competitive advantage.
Positioning
In terms of passenger carriage capacity, both internationally and domestically, the company has positioned itself as the biggest airline in the UK (Jones 2007, p.35).
SWOT Analysis
Introduction to SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis involves a strategic planning approach for evaluating the strengths, limitations, and opportunities coupled with threats that business establishment encounters (Hill & Westbrook 1997, p.47).
Strengths
Strengths are the traits that enable an organisation to have an advantage in comparison to other organisations. One of the strengths of Easy Jet is that it is a low budget and a leading service provider. Also, it offers services to many destinations, including Barcelona, Berlin, Prague, and many more (Hill & Westbrook 1997, p.46). The company offers incredible quality services at customer-friendly prices. Moreover, it has managed to build a magnificently recognisable brand name across the UK air travel industry. Customers are able to access all price breakdowns in the user-friendly website of the company.
Weaknesses
Although Easy Jet has incredible strengths that have made it remain competitive in the UK’s air travel industry, it has some weaknesses. Weaknesses, or limitations, are the traits of an organisation that places it at a disadvantage in comparison with other organisations in the same industry (Hill & Westbrook 1997, p.47). Firstly, one of the subtle weaknesses of Easy Jet is attributed to the fact the company declines from offering food services free of charge in case of flights taking more than two hours. Moreover, there is also intense competition from other service providers such as BMI Baby, Jet2, and Ryan. The competitive forces influence the company’s pricing policies making some of the routes operated by it less profitable.
Opportunities
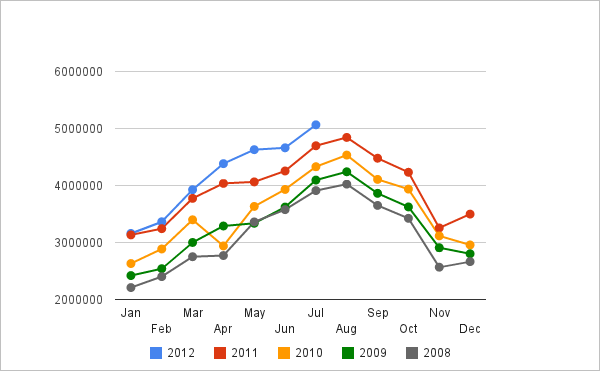
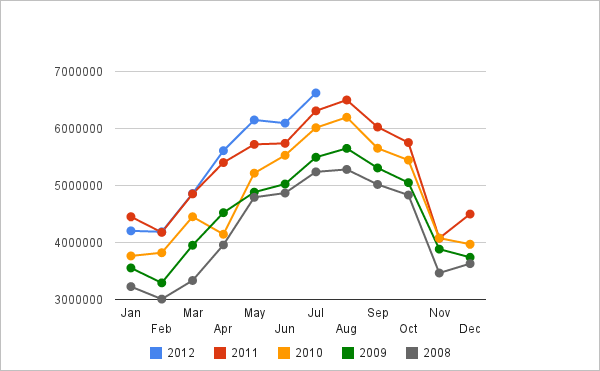
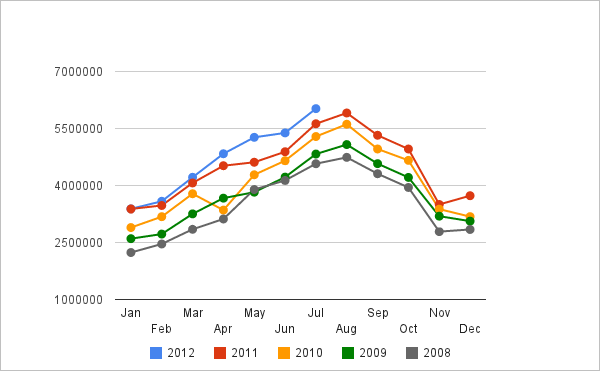
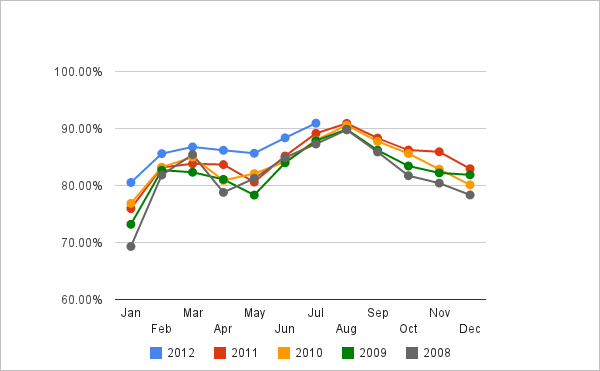
Opportunities are the existing external chances, which, while utilised, make an organisation improve its performance (Hill & Westbrook 1997, p.49). One of the opportunities for Easy Jet is the possibility of opening new routes such as Dublin to the UK. This route has the probabilities of increasing the clientele levels due to the potentially large number of air travellers attending soccer matches. Another opportunity is to offer free food services to passengers taking flights for more than two hours. Consequently, this can increase customers’ experience with the company. The increased pool of passengers, as shown below, has led to the need for new routes.
Threats
Threats are the external chances that impair the performance of an organisation (Hill & Westbrook 1997, p.49). One of the threats of Easy Jet is the external competitive market forces. This creates pressure on the profit margins of the company, especially in some of the most popular routes. Amid the strategies deployed by the company to cut the cost of fuel, the escalating international price of fuel is another major threat to the company. Moreover, there are instances of employees’ union pressures, often leading to strikes. This paralyses the operation of the company. The repercussion is the poor public image of the company.
PESTLE Analysis
Introduction to PESTEL Analysis
A number of factors influence the decisions of managers of any organisation. From the PESTEL organisational analysis approach, these factors are political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors (Gerry, Kevan & Whittington 2005, p.105).
Political Environment
Political environment influences the operations of the Easy Jet via taxing policies. The company must pay charges while landing in various nations (Easy Jet plc 2011, p.37). The management must also comply with environmental regulations, tariffs, and employment laws established within the UK besides complying with trade restriction policies.
Economic Factors
The operational economic environment of the Easy Jet is characterised by rapidly fluctuating prices (Easy Jet plc 2011, p.37). For instance, the increasing cost of fuel puts barriers to the margin of profits that the company can use to reinvest in its growth or CSR.
Social Factors
The social factors act as immense success factors of the company because the passengers and the staff of Easy Jet are promised compliance with safety standards. Hence, enhancing the security of all flights helps in retaining and attracting new clients since people having a first time experience with the company always send an impressive message to other potential clients (Easy Jet plc 2011, p.38).
Technological Factors
Easy Jet Company deploys the internet to accomplish tasks such as booking and checking services. With regard to Easy Jet plc (2011), Easy Jet’s painted her planes with a nanotechnology polymer coating to reduce frictional drag and hence the amount of fuel consumed (p.39). This is also an attempt to keep on par with technology.
Environmental Factors
Easy Jet is incredibly concerned about its environmental impacts. In this end, Easy Jet plc (2011) asserts, “environmental concerns have a significant impact on public policy towards aviation from restrictions on airport expansion to passenger taxes” (p.38).
Legal Factors
In the recent past, the UK has introduced legislation on minimum wage and another one requiring firms to recycle their wastes as a measure of being environmentally green. These two legal legislations have influenced Easy Jet’s profitability levels since extra costs are encountered (Easy Jet plc 2011, p. 10).
Competitive Analysis: Porter’s 5 Forces
Introduction to Porter’s 5 Forces
Several forces shape any industry’s competition. These forces include “threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threats of substitute products, and rivalry among existing competitors” (Porter 2008, p.57). The relationship between these forces is as shown schematically below.
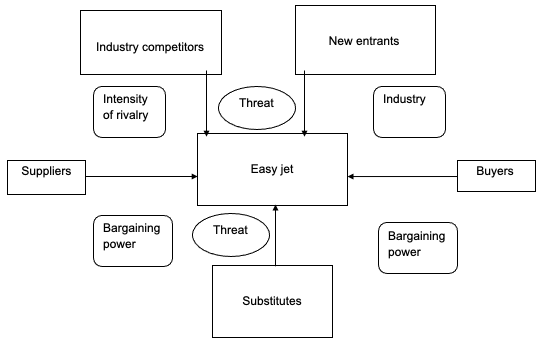
Threat of New Entrants
Easy Jet has a low threat of new entrants because there are both industry and low fare barriers. Starting up the new airline industry is capital intensive. For a new company, large amounts of capital are required to either lease or buy new aircraft (Porter 2008, p.56). Working capital is also required to take all the losses encountered within a short period of operation.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Easy Jets’ bargaining power is moderate in relation to the suppliers. Since the establishment of the company in 1995, Easy Jet has seen its aircraft increase from two to several hundred (Porter 2008, p.58). Consequently, Easy Jet aircraft’s deal means quite a lot to suppliers who can indeed benefit immensely from it. On the other hand, the suppliers of petrol have a significant impact on the company’s operations. This means that petrol has a central role to play in affecting the competitiveness of the company in terms of creating shortages. However, the company has enormous storage capacities of fuel reserves to absorb temporary shortages.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
The bargaining power of Easy Jet clients is moderate. By utilising the weapon of low fares, the company is able to prevent its clients from seeking alternative service providers. In an economic sense, the lower the prices, the higher the demand. This effect is more effective for the case of Easy Jet since the company intensively creates price awareness through the internet (Porter 2008, p.59). Hence, whenever service consumers think of switching from one airline to another based on fair prices, the alternative is always the Easy Jet.
Threats of Substitute Products
Easy Jet’s threat from substitutes is very low (Porter 2008, p.61). In the first place, although vehicles may provide convenience and flexibility in terms of enabling the passengers to manage their journey better, it is a time-consuming mode of transport. Therefore, especially in the case of international routes, vehicles are not an alternative to air transport. The other alternative is rail transport. With the introduction of high-speed trains, air transport is threatened due to the competitive nature of rail transport in terms of prices.
Rivalry among Existing Competitors
Easy Jet faces a moderate extent of competitive rivalry. While it is the biggest intra-UK airline, it is also the fifth-biggest airline operating within Europe. Therefore, it is highly competitive while compared with rival companies. The traditional low-cost airlines target different market segments in comparison to Easy Jet (Porter 2008, p.63). This makes them non-competitors to the company. In terms of low-cost business strategy, Ryan is the only company that has succeeded in reporting continuous profitably each fiscal year.
Conclusion
Since its establishment in 1995, Easy Jet airline has encountered tremendous growth. This growth has been realised amid the various challenges such as increasing fuel costs. This paper has focused on discussing the growth success factors and barriers from the contexts of Competitive Analysis: Porter’s 5 Forces and SWOT analysis. Some of the crucial statistics for Easy Jet airlines have been given in the appendix section.
References
Armstrong, M 2006, Management Processes and Functions, CIPD, London.
Easy Jet plc 2011, Annual report and accounts 2011. Web.
Gerry, J, Kevan, S, & Whittington, R 2005, Exploring corporate strategy: text and cases, Prentice Hall, London.
Hill, T & Westbrook, R 1997, ‘SWOT Analysis: It’s Time for a Product Recall’, Long Range Planning, vol. 30 no. 1, pp. 46–52.
Jones, L 2007, Easyjet: the Story of Britain’s Biggest Low-Cost Airline, Aurum Press, London.
Kentleton, R 2011, Monthly Traffic Statistics easyjet. Web.
Menon, A et al. 1999, ‘Antecedents and Consequences of Marketing Strategy Making’, Journal of Marketing, vol. 63 no. 2, pp. 18–40.
Millward, D 2011, ‘Easy Jet to open new base at Southend’, The Daily Telegraph, vol. 1 no. 1, p. 16.
Porter, M 2008, ‘The five forces that shape strategy’, Harvard business review, vol.3 no. 1, pp. 56-63.
Sumberg, J 2011, Easyjet paint job makes fuel bills less of a drag. Web.
Appendix