Walgreen is a private limited company that operates in the US drug stores industry, which is denoted by the NAICS code 446110. The firm, which was founded in 1901, was incorporated in 1909 in Chicago, Illinois. The firm’s headquarters are located at Deerfield, Illinois 60015. The firm deals in health and wellness services and other consumer products and services through its 8,385 drugstores, which are located in 50 states in the US (Stock Analysis on Net, 2013).
Some of the products that the firm deals in include non-prescription and prescription drugs, candy products, fresh foods, beauty care, convenience foods, personal care, household products, home medical equipments and other health and wellness products. The firm also specializes in managing chronic and complex health problems by offering specialty pharmacy services. Walgreen also operates a number of take care clinics, which provide health care services to such as administering immunizations, treating patients and prescribing drugs to patients. By the end of 2012, the firm had a human resource base of 176,000 employees. The chart below shows a breakdown of Walgreen Co.
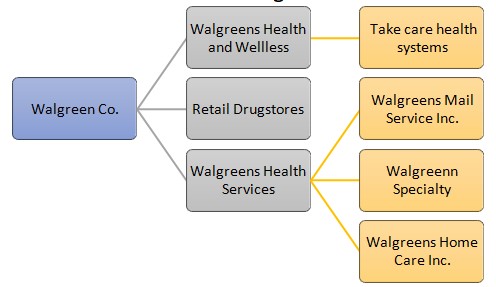
Vision statement
Walgreen intends to position itself as the first choice company with regard health and daily living. The firm also intends to dominate the strategic territory of the consumers’ wellbeing.
Mission statement
The firm intends to establish it as the most convenient and trusted multichannel provider of diverse consumer products and health and wellness solutions. The firm’s operations are also guided by the need to provide US customers with innovative pharmacy services. Walgreen’s operations are guided by the need to position itself as a destination where customers achieve health and wellbeing.
Business model
It is imperative for organizations to adopt an effective business model in order to maximize profit (Mouncey, 2007). Walgreen has adopted the diversified business model. The firm has achieved this by identifying the diverse customer needs. Walgreen has diversified its products and services offering and has managed to attract different customer group.
Customer value and profit proposition
Walgreen is committed towards nurturing a strong customer base. To attain this, the firm has adopted the physical attribute of customer value proposition. The firm maximizes its profit by ensuring its products are of high quality and effectively priced. Moreover, the firm appreciates the importance of ensuring that customers receive products more conveniently. Consequently, the firm has established numerous drugstores in the US.
With regard to profit proposition, the firm intends to maximize its profitability through aggressive marketing. This will ensure that customers are adequately informed about its products and services. Consequently, the likelihood of the firm influencing the consumers’ decision making process is high. Moreover, the firm will develop sufficient competitive advantage to cope with competition emanating from convenient stores such as Wal-Mart.
Financial and strategic objectives
The firm is focused on three main strategic objectives, which include.
- Creating an “efficient and extraordinary global platform through which it can improve its strategic partnership with Alliance Boot GmbH” (Walgreens, 2013, Para.3). The firm projects that the partnership will significantly improve its strategic objective.
- To offer unparalleled, affordable, innovative and high quality health care services to customers.
- Walgreens short-term objectives entail maintaining its liquidity and maximizing the after-tax yields. The firm is also focused towards minimizing the risk faced.
- The firm intends to achieve long-term growth in order to satisfy the shareholders’ investment needs.
Key success factors
Since its inception, Walgreen has successfully attracted customers because of positioning itself as a convenient shop. Consequently, customers can shop for diverse products from the store. The firm’s success also emanates from its effective distribution and interface system that have been developed through e-commerce and the telephone system.
Competitive strategies
Michael Porter argues that strategy is an essential element in a firm’s effort to compete effectively. Developing sufficient competitive advantage requires an organization to formulate effective competitive strategies. Walgreen Company has adopted differentiation has its core competitive strategy.
The firm’s differentiation strategy is based on the uniqueness of its products and services. Moreover, the firm has differentiated itself by positioning itself as a one-stop shopping point from where consumers can purchase diverse products such as health care products, over-the-counter drugs, prescription drugs and grocery products. The firm’s effectiveness with regard to differentiation is because of its commitment towards transforming the drugstore.
The firm’s effectiveness with regard to differentiation is also explained by the fact that it has adopted a customer-centric retailing initiative in order to improve the consumers’ experience. The firm’s effort to develop a unique customer experience is also illustrated by the fact that it has transformed its operations from a traditional model to a modern model by incorporating new e-commerce technologies. Thus, the firm has successfully improved the level of its customer experience. Customers are able to purchase different products from the store online (Mouncey, 2007).
Growth strategies
Walgreen is ranked amongst the fastest growing retail firms in the US. Walgreen has been committed towards improving its market reach. The firm has adopted different growth strategies such as organic growth and strategic partnerships. The firm’s success with regard to organic growth is because of effective selection of sites to locate new stores. Moreover, the firm has been very effective in designing and setting up attractive freestanding store formats. The firm’s ability to develop effective stores is enhanced by its commitment towards continuous improvement and innovation. Through its organic growth strategy, Walgreen has managed to establish a number of stores in the local market.
With regard to strategic partnership, the firm has adopted the concept of acquisition, joint ventures and strategic alliance as its main growth strategies. Over the past few years, the firm has acquired a number of firms. In May 2012, Walgreen completed the acquisition of some assets from BioScrip Incorporation. The acquisition increased Walgreen’s goodwill with a margin of $ 92 million while its intangible assets increased with $50 million.
The firm acquired Crescent Pharmacy Holdings, LLC in February 2012. The acquisition was aimed at improving the firm’s services portfolio in order to penetrate California markets. Similarly, the firm acquired drugstore.com incorporation in 2011. The acquisition significantly improved Walgreen’s online marketing ability. Drugstore.com Incorporation had well established online shopping network in America (Stock Analysis on Net, 2013).
Walgreen intends to enhance its growth by adopting various strategic investments such as acquiring independent health and wellness firms and drugstore chains. The firm has partnered with Alliance Boots GmbH in which it holds 45% investment. Alliance Boots GmbH is one of the leading pharmacy-led beauty and health organization in the world. In March 2013, Alliance Boots GmbH and Walgreen announced their intention to enter into a long-term innovative partnership agreement with AmerisourceBergen, which is the leading pharmaceutical company in North America. The partnership will improve the firm’s economies of scale in addition to enhancing the firm’s market scope, which arises from the fact that Walgreen will market its products in the Euro Zone. The partnership with other firms has led to the development of net synergies. For example, its partnership with Alliance Boots GmbH increased the firm’s net synergy to $ 154 million (Chain Drug Review, 2013).
Ethics and social responsibility
Walgreen has formulated a comprehensive corporate social responsibility policy. The policy takes into account a number of aspects, which include the community, diversity, supplier diversity, environmental sustainability and disability inclusion. The firm is guided by the precepts of supporting and giving back to the people within the society in which it operates. The firm is also concerned about developing its workforces’ career by growing their talent. In the course of its operation, Walgreen is concerned with protecting the environment by investing in green projects, recycling and eco-friendly energy options. The firm does not discriminate individuals on the bases of any variable such as their demographic characteristics.
Porter’s five forces model
Rivalry
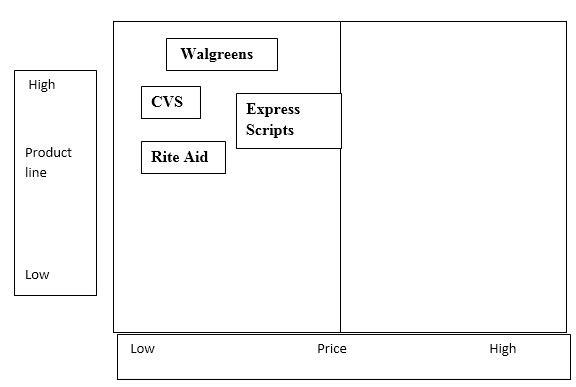
Walgreen’s operations are mainly within the US retail pharmacy industry. The firm deals with a wide range of over-the-counter and prescription drugs and different consumer goods. The firm faces intense competition from CVS, Rite Aid Corporation and Wal-Mart. CVS has over 7000 stores in the US. CVS mainly deals with drugs, which constitute Walgreen’s core product. The firm also faces intense competition from convenience stores such as shopping malls. Thus, the degree of rivalry is relatively high.
Threat of entry
Despite the fact that major players such as Walgreen and CVS dominate the industry, small firms can still enter into the industry. Small and independent pharmacies account for 15% of the total market. Thus, the likelihood of small pharmacies making a profit is high. Establishing an independent pharmacy store in the US is relatively simple. One only requires a pharmacist, an operating license and a storefront.
Substitute
The threat of substitute in the industry is high. The mail order pharmacy business model presents a major challenge to Walgreen’s survival. Moreover, Walgreen faces competition from Pharmacy Benefit Management companies (PBMs), managed care organizations and health maintenance organizations. The PBMs are pushing down the prices of pharmacy products hence attracting customers. To achieve convenience, customers prefer purchasing online for non-pharmacy products hence threatening Walgreen’s competitive advantage.
Supplier bargaining power
Suppliers in the industry have a low bargaining power. Most prescription drugs in the US can only be accessed from the pharmaceutical giant, which holds the patent. Thus, the giant has monopoly power. Small pharmaceutical firms have minimal negotiating power and cannot be able to beat Walgreen’s pricing strategy.
Buyer bargaining power
Individual consumers have minimal buyer bargaining power. On the other hand, institutional consumers such as PBMs and insurance companies have high buyer power. The difference in bargaining power emanates from the fact that institutional consumers are incorporated in drug administration. Thus, Walgreen’s buyer power is moderate.
Driving forces
Several factors stimulate change in the US drugstore industry. Some of these factors include.
- Market and product innovation: Firms in the drugstore industry are adopting online and telemarketing. Development of software robotics is also increasing the rate at which drugstores are delivering products to customers.
- Technological development: The high rate of technological development presents a major challenge to firms with regard to product and service duplication.
- Globalization: Currently, the US drugstore industry is free from international competition. However, the high rate of globalization may attract international players.
- Change in consumer preferences: Consumers are increasingly shifting towards differentiated products. Moreover, change in economic conditions may negatively affect the consumer’s purchasing power and hence the firm’s level of profitability.
- Competition: The industry is experiencing a high rate of consolidation. Firms are integrating the concept of franchising in an effort to develop greater bargaining power.
- Regulatory influences: The drugstore industry is the US is subject to various local, state and federal government rules and regulations. Various government programs for example the Medicare plan are increasingly affecting the industry.
These forces may adversely affect Walgreens competitiveness. To cope with the above forces, Walgreen should invest in continuous product and market innovation. The two strategies will improve the firm’s competitive effort.
US drugstore; strategic group map
The chart below illustrates the US drug store strategic group map.
Financial condition
Walgreen has managed to establish over 8300 drugstores in the US hence making it the largest drugstore. The firm has a strong history with regard to profitability and market expansion. Despite the changes in the external business environment, Walgreen has continued to increase the amount of dividend issued to shareholders. In 2012, the firm issued $787 million as dividends compared to $647 million issued in 2011. The firm shareholders’ equity increased from $ 14,847 in 2011 to $18,236 in 2012, which represents a growth with a margin of 22% (Holsted, Jones & Levin, 2012).
Profitability and growth
During the period ranging between 2010 and 2011, the firm’s net earnings increased by 29.8 % (Holsted, Jones & Levin, 2012). The increase emanated from the sale of some of its PBMs businesses. The firm also experienced an increment in its sales revenue because of acquiring other firms and increase in the number of organically grown drug stores. However, in 2012, the net earnings decreased with a margin of 21.6%. The chart below illustrates Walgreen’s operating statistics over the past four years.
The chart below illustrates Walgreens trend with regarad to net earnings
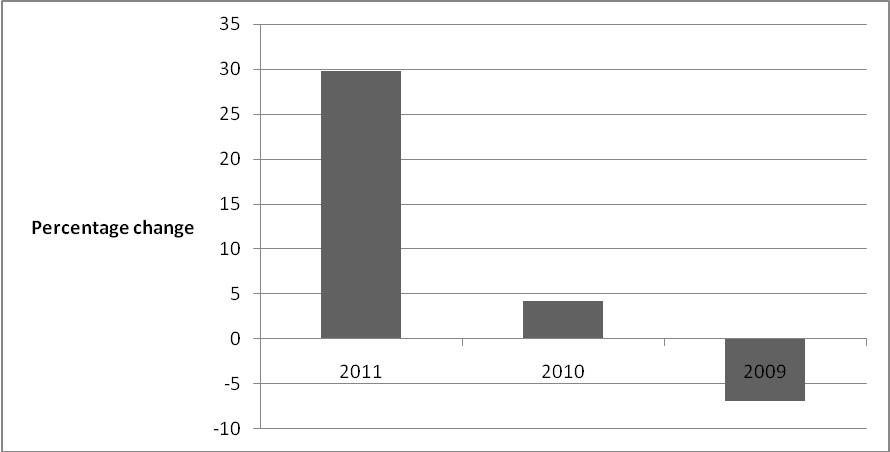
The firm has continued to enjoy positive financial performance over the past five years. The decline in the firm’s level of profitability in 2009 is because of the 2008 global economic recession. However, the firm managed to reverse the trend. It is expected that the firm will continue to experience high profitability and growth because of acquisitions and new store openings.
Liquidity
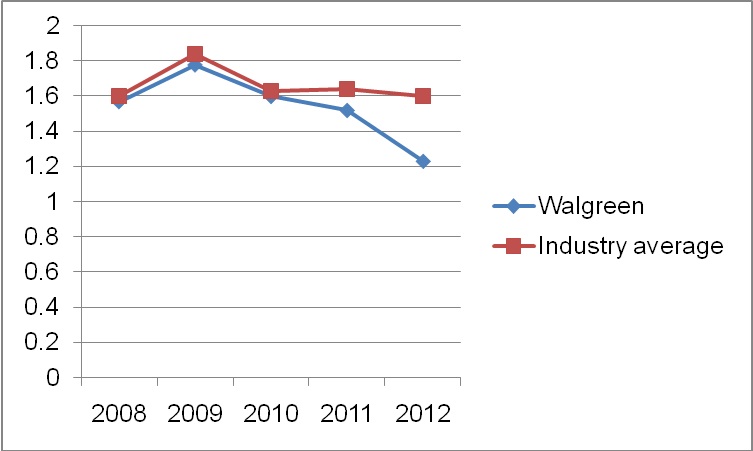
Liquidity ratios enable an organization to determine the effectiveness with which it can cover its current liabilities using the liquid current assets. The chart below illustrates Walgreen Company current ratio in comparison to the industry average. The chart shows that Walgreen has been effective in managing its current assets and liabilities.
The firm’s current ratio has been relatively below to the prevailing industry average from 2008 to 2012. However, in 2013, current ratio increased to 1.34 which is higher than the industry average. This illustrates Walgreen’s efficiency in managing current assets and liabilities.
Solvency
These ratios are used to determine an organization’s effectiveness in satisfying its long-term and short-term financial obligations. Total debt to equity is one of the solvency ratios that are determined by organizations. The chart below shows the company’s trend with regard to debt to equity from 2008 to 2012.
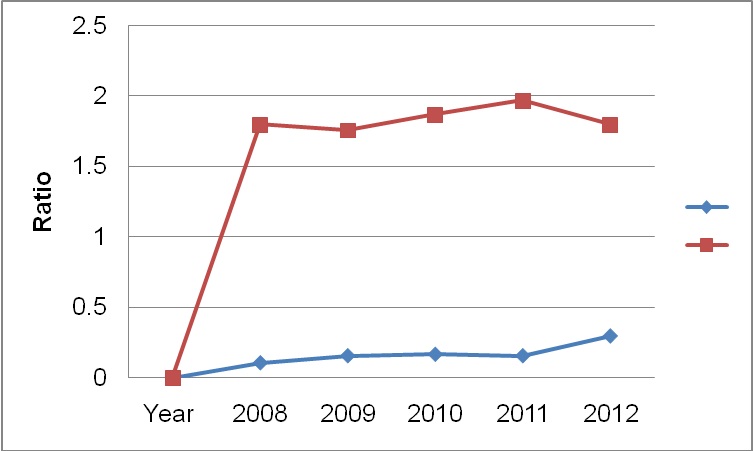
The chart shows that Walgreen Co has not been utilizing debt finance to sustain its operation. The company’s debt to equity ratio is below the prevailing industry average.
Activity ratio
The table below shows Walgreen’s total asset turnover. The firms’ total asset turnover is higher than the industry average. This shows that the firm has been effective in generating sales.
Core competencies
According to Samson and Daft (2011), a company’s core competence is used to describe organizations areas of competence compared to its competitors. The core competences improve an organizations’ level of competitiveness. Organizations base their core competence on diverse areas. Walgreens’ core competence is based on three main components, which include its size, location and distribution. These core competences are in line with the firm’s strategic objective of investing in high-tech stores and efficient distribution systems. Consequently, the firm has managed to improve its level of customer service and to minimize the cost of operation. The firm’s core competences have also played a significant role in differentiating the firm from its competitors. The firm’s likelihood of sustaining its core competences is high considering the firm’s commitment with regard to market and product innovation.
Competitive Strength Matrix
Walgreen faces intense competition from Rite Aid and Express Scripts. The matrix below illustrates a comparison the three firms’ competitiveness. The firms’ competitiveness is determined on a 5 point scale.
From the chart above, Walgreen has a high overall strength rating compared to Rite Aid and Express Scripts. This shows that the firm is more competitive.
Value chain
According to Schermerhorn (2010), value chain analysis enables an organization to develop a comprehensive understanding of its internal environment. The value chain is comprised of two main activities, which include the primary, and the inbound activities. Walgreens has developed an effective value chain that is comprised of both inbound and primary activities. The chart below illustrates the firm’s value chain.
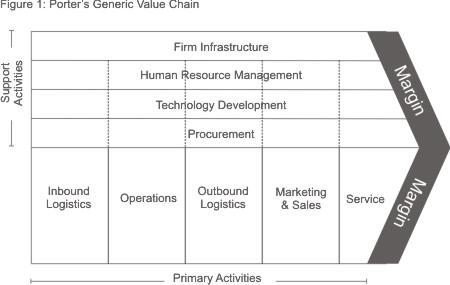
The inbound logistics relate to how the firm process of receiving, storing and distributing its products (Stone, 2008).
- Operations: Walgreens has managed to develop an efficient supplier relationship. The firm has integrated effective operation mechanisms in order to produce and offer high quality products and services.
- Outbound logistics: Walgreens has developed effective distribution mechanisms by establishing drugstores. The firm also distributes its products through the mail and telephone ordering system.
- Marketing and sales: The firm has adopted both conventional and modern methods of marketing by adopting integrated marketing communication.
- Service: The firm is committed towards customer satisfaction. Consequently, it has established a call center through which it interacts and supports customers.
With regard to support activities, the firm has established a comprehensive support system by integrating effective product procurement, technological development, infrastructure and human resource management. As a result, the firm is able to deliver value to its customers.
SWOT analysis
In order to survive in the long-term, it is essential for Walgreens’ management team to develop a comprehensive understanding of its internal and external environments, which can be achieved by using the SWOT model. The matrix below illustrates a summary of Walgreens’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Recommend strategies
In order to deal with the market changes, Walgreens management team should consider the following strategies.
- The firm should enhance its product differentiation strategy. One of the ways through which it can achieve this goal is by investing in continuous product improvement. Consequently, the firm will be able to meet the customers’ product needs. Moreover, the firm should differentiate itself by investing in market innovation.
- The firm should also consider adopting the focus competitive strategy. This move will improve the firm’s effectiveness in achieving market dominance.
- The firm should also consider venturing into the global market. However, the firm should evaluate the most effective globalization strategy to adopt, which will increase its competitive advantage.
Reference List
Chain Drug Review. (2013). Walgreens report robust results for fiscal 2013. Web.
Lai, K., & Cheng, T. (2009). Just in time logistics. Farnham, UK: Ashgate.
Market Watch. (2013). Walgreen Co. Web.
Mouncey, P. (2007). Market research best practice: 30 vision for the future. New York, NY: Wiley.
Samson, D., & Daft, R. (2011). Management. South Melbourne, VIC: Cengage.
Schermerhorn, J. (2010). Exploring management. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Stock Analysis on Net. (2013). Walgreen Company liquidity analysis. Web.
Stone, P. (2008). Make marketing work for you: Boost your profits with proven marketing techniques. London, UK: How To Books Limited.
Walgreens. (2013). Walgreens Presents Growth Strategy at 2013 Annual Shareholders Meeting. Web.