Abstract
Women form a very important part of Emirati society. The days when women were expected to sit and wait to be provided with basic needs by their husbands are long gone. Currently, women have asserted their authority in various sectors of the economy. They are part of the driving force in most of the companies around the country and in society in general. They form the largest percentage of shoppers in this country and they hold very influential position in various firms in the United Arabs Emirates. The world is first embracing technology and one of the best technological inventions in the business world is e-business. E-business is very important both to the customers and to the business units. As women are gainfully employed in various firms unlike before, many families find that they lack time to spend going to the shopping centers. The invention of e-markets, therefore, comes in handy in enabling them to get access to what they need with just a click of the button. To the business unit, e-commerce has broken the geographical barrier. It is now easy to trade in various locations without the need to have a physical facility in that area.
Despite the obvious advantages e-commerce promises to bring to firms willing to embrace it, some challenges are associated with this firm. Emirati women are associated with some of these challenges. Their role in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in this country is critically analyzed in this research. This research specifically focuses on the actions of women that may be seen as a hindrance to e-commerce. The research takes the quantitative approach to address this issue.
Introduction
Technology has completely transformed the face of the earth. The emerging technologies have brought new approaches to doing business. Communication has greatly been improved, following the invention of new communication tools. E-commerce came into existence, thanks to the improved technologies in the world. Many businesses have embraced e-commerce as a way of reaching out to their customers. The brick-and-mortar markets are still popular. However, the current trend indicates that this will change very soon. Electronic commerce is gaining popularity at a very rapid rate (Nelson, 2006). The current working class has very little time to spend shopping around. For this reason, they prefer shopping online in the comfort of their offices or at home. This saves their time and provides them with enough time to ‘visit various stores’ online and compare their prices. As such, many businesses have therefore gone online. E-commerce is growing at an unprecedented rate and as things stand currently, no business can afford to operate without it.
The United Arabs Emirates is one of the leading business hubs in the world. Dubai is one of the leading business cities and is very popular in the emerging economies. It has actually displaced the United States as the leading exporter of various manufactured goods to Africa and other emerging economies. Firms in this country have been keen to ensure that they embrace e-commerce in order to be in a position to manage market competition (Rodgers & Maryanne 2003). However, research shows that when implementing this technology, there is always a difference in the way men and women act. Women tend to be conservatives when it comes to the implementation of emerging technologies. They are slow to adapt the emerging technologies.
E-commerce has experienced some barriers in this country, some of which have been associated with women. It is therefore very important to analyze the role of Emirati women in perception of barriers to e-commerce in the United Arabs Emirates. The fact that women are slow to adopt new technologies plays a big role in creating challenges for smooth implementation of e-commerce in various businesses in the country. This is specifically so because there has been a consistent increase in the percentage of women in the corporate sector of the country. With their increased number, it becomes a big challenge if they cannot adopt technology at a rate that is required (Akhter, 2008). The cost associated with e-commerce is another factor that has made some firms not move with speed to embrace e-learning. However, this study will focus on the role of women in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in this country. The paper seeks to investigate the role of gender in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in the United Arabs Emirates.
Literature Review and Research Question
Introduction
In every research, the researcher needs to formulate questions that would help in guiding the steps towards data collection and analysis. In this research, literature review was very important in guiding the process of data collection. The research question was developed at this stage because it was important to guide the kind of literature that the researcher would be exploring. It would help the researchers determine which secondary sources were relevant and which were not. This is very important as it helps in eliminating irrelevant works of literature. The following question was formulated to help guide the research.
What is the general perception of women towards adoption of e-commerce in various firms within which they work?
“The association between e-commerce barriers and gender has not been explored in-depth, even though it has implications for the adoption of this technology” (Kolsaker & Payne, 2002). As evident from many developed nations, the role of women in issues that affect the economy cannot be ignored. The difference between the way men and women perceive issues needs to be addressed effectively to allow consistency.
A study carried out by MacGregor & Vrazalic (2008) reveals that men and women face different challenges as business managers and entrepreneurs. “Addition findings from the study reveal a greater differentiation of barriers within male owned/managed SMEs, which suggests the need for more customized e-commerce adoption program in these organizations” (MacGregor & Vrazalic, 2008). Differing levels of appreciation for e-commerce between men and women could slow down the level of growth in its application. It is important that women develop the same level of appreciation for e-commerce as men to allow its development.
Issues that concern men in business management further differ from those which women would be concerned about (Whitehead & Roy, 1999). While women are more concerned about details, men tend to pay attention to cumulative progress. Their management styles further differ as explained by Hersey, Kenneth, & Dewey (2008) who point out “female managers of small business are more comfortable with giving instructions to staff through informal conversation than are their male counterparts”. Communication and problem-solving strategies further differ. “While men will stress the role of power, female managers stressed the importance of interpersonal communications.”
Gender differences in the perception of e-commerce
Gender plays a significant role when it comes to adoption of new technologies and business practices. The differences arise from the way men and women perceive the importance of a certain technology, its benefits and challenges. A study conducted in Australia by (MacGregor & Vrazalic, 2008) reveals that there is no major difference between the way women and men view e-commerce, but reveals a difference in the way men and women react to technological problems facing their businesses. In a study conducted on small business owners, the results reveal that men are less concerned about new technologies for their businesses and felt they do not need them. Women on the other hand are more receptive as far as new technologies are concerned. They are keen on understanding how the technologies could benefit their businesses and how easily the technologies can be integrated into their businesses.
In the UEA, differences in gender arise from many other factors. The level of literacy among women is lower compared to that of men. This makes it more difficult for a larger number of women to appreciate and use new technologies in the market such as e-commerce. It may not be easy to shop online if one does not understand the technical language associated with some parameters of an online transaction.
Managerial differences between men and women
As Carter (2000) explains, “studies conducted in the past on the role of gender in business management have revealed that women and men have very different management approaches. Studies in Europe, Scandinavia, and the US show that females saw the small business sector as a means of circumventing the ‘glass ceiling’”. The studies further reveal that growth of females in the sector in Australia is over four times that of males (Rodgers & Maryanne, 2003). Even in this situation, the reality is still to catch up with an environment where men and women should enjoy equal chances in business management. “The successful managerial stereotype remains masculine-self confident, dominating, competitive, decisive, aggressive, and independent.”
Cultural conditioning and gender stereotyping further create big differences in the way women approach technical issues and solutions at work, as well as how they develop teams to manage challenges at work. Women are more likely to use their positions to create an environment where people are supported and nurtured. Men on the other hand use senior positions to create hierarchal environment where nothing short of obedience is expected. The environment supports issuing and receiving orders, as well as authority. Women grow up knowing how to be responsible and handle easy things that have well-defined futures. As a result, technical issues, which can be hard to predict, become hard to manage.
Further differences arise from the way men, women perceive issues, and at what level of priority they place them. According to Carlin (2009), “Females perceive technical issues to be a more important barrier than organizational issues.” Men on the other hand are more concerned with the development of a plan on how a new aspect will help develop the plan. MacGregor & Vrazalic (2007) explains, “By contrast, male SME owners/managers are more concerned with the sustainability and of e-commerce in the organization, implying the need for a different focus in e-commerce initiatives”, echo this.
Men and women adopt different strategies in the way they handle business-related issues. Furthermore, they have different preferences and strategies as consumers. These differences are widespread and revolve around adaptability, attitude regarding new business paradigms, and the perception of risks (Akhter, 2008).In the Middle East, there are few economic and political opportunities for women as compared to what is available for men. This has been the trend for long as men and women continue to assume different roles in the society. This trend is explained in the gender role theory which explains that boys and girls assumed roles that were assigned to them as they grew up, roles that they have to keep up with even as men and women. In the Middle East, women are considered homemakers while men are considered as the providers. This means that men are constantly involved in different economic activities to earn a living for themselves as well as for their families.
Because of their strong physical features, men are considered the stronger sex. The more economic responsibility is placed on them leaving them in a position where they are constantly interacting with social and economic activities. Women were and still are considered in some parts of societies as the weaker gender and are assigned less aggressive duties such as taking care of children. In the UAE, the situation is slowly changing and women have access to more economic activities. Women today have access to education, formal employment; they have rights to entitlement and have legal representation when need be. As a result, they are more involved in economic activities and can easily relate to different economic paradigms.
E-commerce and gender in the UAE
E-commerce is increasingly becoming a popular aspect of many businesses. This is so in both developing and developed worlds as businesses try to reach global markets. In the last decade, there has been increased rate at which businesses adopt e-commerce as a strategy in improving their level of performance in the contemporary competitive market. However, several barriers have delayed the adoption of e-commerce. One of the main barriers to e-commerce is gender.
However, it remains that the role of gender in the perception of issues affecting e-commerce has not been investigated comprehensively. This is despite the fact that gender influence is a formidable force in many aspects of life and even technology. This paper seeks to understand the differences between men’s and women’s perceptions of challenges facing e-commerce and significant barriers in UAE. The country is considered the pioneer of gender empowerment in the Middle East and therefore, a study carried out in the region can be used to come up with significant recommendations even for the other countries in the region. In the past, researchers have put more interest in the differences between men and women in social issues, making it difficult to access literature on gender differences where technical matters are concerned.
There is a significant difference in the perception of barriers to e-commerce between men and women. In order to eliminate the barriers to e-commerce, there is a need to have a clear understanding of various perceptions of these barriers in order to come up with necessary solutions. Gender has a major role in the perception of these barriers, which are encountered in the adoption of e-commerce in the UAE. This part of the paper will analyze the role of gender in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in the UAE. The research methodology will be designed in a way that allows men and women to share their views on different aspects of e-commerce. The differences in their views will then be used to formulate arguments, conclusions, and recommendations for the paper.
Since the introduction of the internet, e-commerce has become very common in conducting various business activities all over the world. E-commerce has brought significant changes in the community in various aspects. It has also brought changes in the social environment. Adoption of e-commerce has helped in elimination of various barriers in international trade. Organizations can now use various information and communication technologies in different business activities. However, e-commerce has not yet achieved its potential in the international market. In Arab countries, e-commerce is still far away from reaching its potential level. This is despite the significance of its impact on the global market.
A number of barriers have faced the adoption of e-commerce by many businesses in UAE. One of the main barriers is the cost. The adoption of the current technology usually requires a significant amount of capital in its implementation. Many organizations are however not ready to incur such expenses. Another barrier in adoption of e-commerce is complexity involved in its implementation. This kind of technology requires an organization to adopt several changes in its operations. For instance, it may face resistance in an attempt to implement these changes. When resistance takes place in an organization, it usually has a significant implication in various business operations. Some organizations may also not be in a position to access the necessary resources required for the adoption of this kind of technology. In addition, security concerns are also a major barrier in the adoption of e-commerce among others. As a result, adoption of e-commerce in the UAE has not been successful as expected.
As already noted, there are a number of barriers to E-commerce in the UAE. These barriers have obstructed the adoption of E-commerce. Although there have been several studies carried out on the possible barriers to E-commerce, there has not been adequate effort made to examine the association between e-commerce and gender in the UAE. This is despite the fact that it has a significant implication in adoption of technology in day-to-day operations in UAE.
As seen earlier, there is a significant difference in perception of the barriers to e-commerce from both men’s and women’s perspectives. According to previous studies, it has been revealed that women perceive technical issues to be more important than the organizational issues (Schniederjans & Cao, 2002). This implies that women take the technical problems with more seriousness than organizational issues. For instance, they perceived the compatibility of the technology to have a major impact on e-commerce and its application in an organization. On the other hand, men emphasize more the suitability as well as the fitness of the e-commerce in an organization. This calls for having a more modified approach in the adoption of e-commerce in an organization.
The issue of gender has many implications in today’s business world. A number of questions are raised because of gender-related differences. Several aspects in the workplace are to some extent affected by the gender differences. For instance, the ability to use mathematics as well as fight stress in the workplace is usually different across the gender. In the traditional way of production, the men (Marchall, Michael & Elnora, 2006) dominated the business. Things have however changed. Women are now actively involved in day-to-day business operations in the UAE. In the traditional economy, the main economic activities were manufacturing oriented which was more dominated by men (MacGregor & Vrazalic, 2007b). This has been modified to a more retail and service-based economy that has encouraged more participation of the female gender.
There are several reasons that can be the possible causes of the differences in perception of these barriers from different people of a different gender. For instance, females are seen to be more comfortable when giving instructions through informal instructions than their male counterparts (Schniederjans & Cao 2002) are. Most of the male managers for instance are seen to stress the use of power in management. On the other hand, the female managers are seen to stress the importance of interpersonal communication in day-to-day operations in an organization (Kolsaker & Payne, 2002). Because of these differences, varying perceptions have also emanated from these differences.
It has also been realized that women are more reluctant to accommodate social business networks than their male counterparts (Gebler, 2011) are. As a result, women are not in a better position to attract investment partners or even partners who will be in a position to use such networks to attract technical assistance. This is despite the importance of such partnerships in the contemporary business world. As already noted, women are more concerned with technical difficulties. They take technical difficulties with more weight. On the other hand, male managers do not consider technical difficulties as a major intricacy.
Despite these barriers, several attempts have been made in an effort to mitigate these barriers. For instance, the technical barriers involving compatibility are expected to be minimal after the adoption of extensive markup language (Carter, 2000). By adopting this strategy, the problem associated with interoperability setbacks, which have been a major barrier, will be eliminated. This will promote the adoption of e-commerce in an organization largely.
From the above discussion, it is clear that there are significant gender differences in perception of the barriers of e-commerce. Women are more concerned about the technical barriers to e-commerce. They view the factors that are related to technology to pose a significant barrier in the attempt to adapt to e-commerce. On the other hand, men are more concerned about the suitability of the e-commerce as well as its fitness in an organization. However, both perceptions are significant in promoting e-commerce.
This section of the research will address the following question: does gender play a role in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in the UAE?
Conclusion
“Modern economic roles and social status reflect both change continuity for women” (Powell, 2010). This is evident from the number of girls and women who have access to education today. As Rodgers & Maryanne (2003) observes “schools and universities are segregated, and levels of enrollment of girls and their performance are impressive.” Gender plays a significant role when it comes to the adoption of new technologies and business practices. The differences arise from the way men and women perceive the importance of a certain technology, its benefits and challenges. A study conducted in Australia by (MacGregor & Vrazalic, 2008) reveals that there is no major difference between the way women and men view e-commerce, but reveals a difference in the way men and women react to technological problems facing their businesses.
Furthermore, it is evident that women are more reluctant to accommodate social business networks than their male counterparts (Gebler, 2011) are. As a result, women are not in a better position to attract investment partners or even partners who will be in a position to use such networks to attract technical assistance. This is unfortunate considering the importance of such partnerships in the contemporary business world. The fact that women are more concerned with technical difficulties and take technical difficulties with more weight should be used to support them develop and adopting e-commerce as entrepreneurs and as consumers.
Despite all the challenges and issues arising, one of the biggest strengths possessed by women is the capacity to multitask. They are capable of managing various social and financial activities at the same time. Furthermore, women adapt to challenges easily and are able to move on. These strengths should be used for the development of e-commerce in the UAE. Previously, women were considered as homemakers with little involvement in matters that affect the economy of a country. The situation has changed in the UAE and women are increasingly finding themselves on the frontline on economical matters. As evident from developed nations such as the European region, it is evident that involving women equally had significant benefits to the development of business paradigms in a country.
Data Collection
Introduction
This chapter focuses on various aspects of research development. It includes methods of data collection, analysis and presentation procedures. Every research project applies a certain research method to achieve its objectives depending on its goals. The methods used to conduct research in this project are compared closely with the methods proposed in the project proposal (Anderson, 2004). This was so because the project proposal had been proven to be workable. In research, design deals primarily with aims, uses, purposes, intentions, and plans within the practical constraints of time, location, money, and availability of staff (Hakim, 2000).
In this study, the researcher randomly picked a sample population from various firms in Dubai. The respondents were briefed in advance. This was necessary to ensure that respondents were prepared psychologically for the task ahead. This would also help in ensuring that response was given in time to allow timely analysis. The study population was also amicably informed in order to get prepared for the study. Briefing was important because it could enhance reliability of the study. It is also ethical to inform people before researching them (Badenhorst, 2007). The findings were also made public to the researcher as one way of ensuring morality in the study.
Furthermore, the researcher observed researcher-researched ethics by keeping away from criticism. This chapter also focuses on the literature review as one of the methods used in collection of secondary sources of information. It gives the reason why literature review was used as a method to collect data. The chapter gives an overview of the purpose of collecting and analyzing data and the basic questions used to gather the desired responses.
The chapter brings back the research hypotheses. This is important because it is at this stage that the researcher goes into the field to gather information. It is therefore necessary that the research hypotheses are brought to focus because they would be the guiding light in the process of gathering data (Baily, 1996). The researcher would be trying to confirm the hypotheses. In order to eliminate criticism, this chapter clearly states the scope of the study. There are limits beyond which this research may not hold because of the method used in data collection and analysis. It is therefore important that limitations are clearly stated to make it clear to readers of this material how far this research reveals what it purports to.
Since the main method of data collection was primary source, the questionnaire was the main instrument used to collect data. This chapter brings out the questionnaire format, reasons for choosing this format, its advantages and disadvantages. In a research process, sampling is very important because a certain population can be too big to facilitate a study of the whole population (Bell, 2001). This chapter discusses research design and methods of sampling, giving their advantages and disadvantages, and the determination of the sample size. Also discussed in this chapter is the data analysis technique. In so doing, the researcher hopes to bring to focus the channel through which data would be collected. This is not only meant to bring clarity to this research but also help young researchers who will be interested in furthering research in this field to know the steps necessary to reach the desired results in a given research. The researcher has ensured that the methodology is not only important to the professionals in the financial sector, but also other related sectors such as insurance, marketing, and procurement.
Quantitative research method
Quantitative research is a kind of study that utilizes figures to arrive at certain conclusions (Hakim, 2000). In this regard, the research will take the form of a survey, whereby the researcher identifies the sample and posts questionnaires to them. In this research, there was need to compare the relationship between variables in order to establish cause and effect
The researcher was interested in knowing how different factors (independent variables) had effect on the role of Emirati women in the perception of barriers to e-commerce in the country (dependent variables). This demanded a method that would be objective and able statistically to generalize the findings. The quantitative method was found to be the most appropriate method to use in this research.
Quantitative research involves systematic empirical study of a phenomenon by use of statistical tools. Its main objective is always to employ mathematical theories and models in developing its generalization (Anderson, 2004). Therefore, the quantitative method would help in this research. It would enable the researcher to test the hypotheses put forth for validity and allow the use of a sample as a representation of the entire population. It would help the researcher to determine the role women play in various firms they are in within this country in enabling businesses to embrace e-commerce. The quantitative method would also help in knowing if there is any relationship between the performances of the two genders in embracing technology.
Although qualitative methods were traditionally used in social science and would have been appropriate in this research, it is not able to give empirical support for research hypothesis. Qualitative methods explain why a given pattern of events has taken place the way they have (Vogt, 2007). On the other hand, quantitative methods explain what and when of phenomena. Ethnographic research and phenomenology as approaches to qualitative research would have been appropriate.
Scope of Data Collection
Primary data for this research was collected from various customers and employees of various mid-sized firms within Dubai. This data was collected with the help of a questionnaire. The scope of data collection was limited to the two categories of individuals. This was because of the time that was available for the research. Because most of the employees and customers were Emirati nationals, they clearly understood the social structure of the Emirati society and therefore were in a position to respond appropriately to questions regarding the society of the United Arabs Emirates. The research model below shows the stages that the researcher followed in collection of data, its analysis, the discussion, and then conclusion.
Research Model
This research utilized quantitative research methods in conducting the study and collecting data. Quantitative research was used because it aims at summarizing data mathematically. In this regard, the research took the form of a survey, whereby the researcher identified some individuals and posted questionnaires to them. The sampled population was selected randomly in order to eliminate biases. The researcher made follow-ups by conducting respondents on phone. Interviewing is another method of data collection that was used in this research. The researcher extracted more information from respondents by calling them.
The researcher developed the model below to help demonstrate the relationship between the dependent variables and independent variables. The independent variables have impacts on the dependent variables. The four independent variables, though related to some extent, will finally influence the successful implementation of e-commerce.
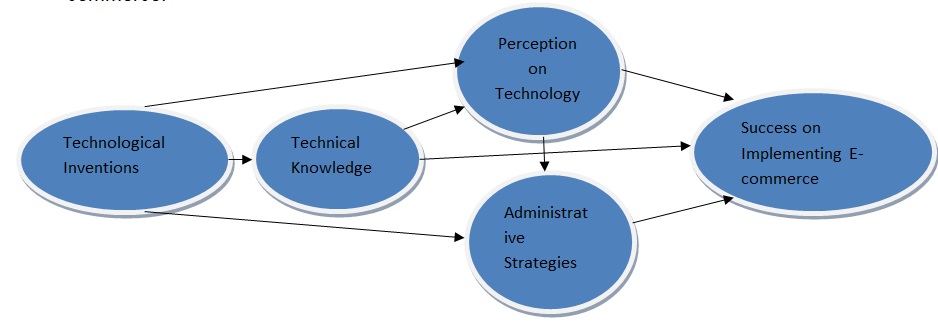
Technological inventions require technical knowledge for there to be compatibility. It also requires a good perception by the involved parties for it to be embraced in the firm. With a positive perception towards technological inventions and presence of technical knowledge in the firm, it would only require proper administrative strategies by the management to ensure success in the implementation of e-commerce. The variables are interrelated. For instance, technological invention will influence perception of the concerned individuals, but at the same time, it depends on the perception of this individual to prosper. The above variables help demonstrate factors that affect perception of women towards e-commerce, and how this perception would influence their managerial strategies. Finally, they would have an impact on how successful the firm would be in implementing e-commerce strategies. The research was done on a sample of the entire population. From this sample, the researcher generated data by formulating questions that would lead to the desired answers. To help focus this research, hypotheses were developed in order to create a vision of the research. Questions were therefore designed to respond to them. The questions were meant to generate answers that would either confirm or reject the hypotheses. The questionnaire was designed to reflect on this requirement.
Questionnaire design
There were two key methods used to gather information in this dissertation. The first one was through a questionnaire, which was electronically delivered to the sample population in Dubai. The questionnaire sought to capture various attitudes of the sample population regarding their opinions on the difference in perception of barriers to e-commerce between Emirati men and women. The second source of information used for the research was literature on various aspects of e-commerce in general, and the operational activities that take place within the selected firms in specific. The focus of the literature review was to find information on the application of motivation techniques within the workplace and also to determine the current state of research in relation to e-commerce. The questionnaire had four parts.
The first part sought to capture the background information of respondents. The second part dealt with the demography and gender of the respondents. This was to ascertain the prevalence of views in various categories in order to ensure that if any differences came about, then they would be captured in their demographic space. The third part dealt with academic credentials and work experience of the respondents. The motivation for this section came from the understanding that different sections of population respond differently to issues, based on age and academic credentials. The fourth part delved into the specific issues relating to the perception of Emirati men and women on barriers to e-commerce within the United Arabs Emirates.
The questionnaire also employed a mix of open and closed-ended questions to capture different aspects of issues studied. Open-ended questions were used because they give respondents more time to figure out their opinions, which would make them volunteer more information related to feelings, outlooks and comprehension of the subject (Murray, 2006). This would allow a researcher to understand the position of respondents as regards feelings. Open-ended questions minimize some errors that could have been created in the course of research. Respondents rarely forget answers if given an opportunity to respond freely. Furthermore, respondents cannot ignore some questions because they must go through all of them. Open-ended questions generate data that can be used in data analysis by other researchers. In other words, they allow secondary data analysis. On the other hand, closed-ended questions are analyzed easily. That is why they were used in this study (Taylor, 2005).
Each response can be coded for statistical interpretation. Nonetheless, closed-ended questions are compatible with computer analysis package. The technique is more specific meaning that its answers are consistent in all conditions. Finally, closed-ended questions take less time to administer unlike open-ended questions, which are detailed hence time-consuming.
The questionnaire was sent to respondents online. The researcher arrived at this decision after considering time and resources. The method is less time-consuming and very effective. Furthermore, the method allows respondents to reflect on the questions and answer them accurately (Andrzej, & Buchaman, 2007).
The literature collected provided information regarding various theories related to e-commerce, which is spread across the last ten years. The body of literature availed several theories dealing with sampling and sample designs in the business world and performance issues in the context of human resource development in various industries. Finally, the literature provided information on the state of research in the field. Various researchers have conducted studies on various elements of social differences between men and women and their effects on motivation (Kumar, 2004). This gave the study a sound academic backing and a strong basis for drawing comparisons and conclusions.
The use of the questionnaire made it possible to capture issues that are unique to e-commerce. This is because there was no accessible literature with required degree of relevance to the subject matter of the role of perception of women to the barriers of e-commerce in the UAE. The targeted sample population responded to the questionnaires, which were electronically delivered to them.
Sampling method was used for this survey.
Some factors should be put into consideration when choosing the right method of sampling in any given research project. In this research, precision was needed. The best method that would lead to the desired results was stratified sampling (Calabrese, 2006). As stated above, this method is simple to use and it is appropriate when one intends to use data quantitatively. The researcher settled on this method because the research population could be divided into subgroups for clarity purposes. The sample would then be divided into subgroups so that each group gets equal representation. Having identified the two strata as male and female members of the society, the females were given more weight because of the significance of their answers to this research.
Determination of the sample size
As stated above, in a study, there is always a need to have a sample population. This population will be representative of the entire population. The selection of this sample must therefore be designed in a way that would give the expected results. Generally, two constraints would help in the determination of the sample size: time and financial resources (Hughes, 1997). Time is very important in determining the sample size. If a researcher has a lot of time to conduct the research, it would be appropriate to consider using a larger sample size. However, in case the time available for the same is limited, then the researcher would be forced to limit the sample size to be in a position to conduct the entire research process successfully. Another constrain is the available finance for the research (Krathwohl, 2004). The process of collecting data and its subsequent analysis can be very expensive. For this reason, a researcher would determine the sample size based on the available finance. In the research, the sample size was chosen based on the two constraints given above and the five factors stated below.
- The variability of the population under study: There are instances where the items under study exhibit differences in characteristics, making it very difficult to choose a representative sample. Barzun (2004) explains that in cases where the study population does not exhibit serious differences in characteristics, it would be recommended that a researcher use a smaller sample as a representative of the entire population. However, if the study exhibits many differences, then it would be appropriate to use a larger sample as a representative. The researcher would be forced to look for all the varying attributes and include each of them in the sample (Taylor, 2005). In this research, it was noted that there was no big difference in character of the people under the study.
- Confidence level: In every research, there is a given level of confidence desired by any research. Hoyle (2002) asserts that this precision will determine the sample size to be used in the study. In most research, a confidence level of 95 percent is always recommended. Depending on the sensitivity of the issue under investigation, the percentage can be more or less than this standard value. In this research, it was necessary to produce a report that has standard level of precision. The sample population chosen was able to provide this.
- Margin of error: When a sample is taken to be representative of the population, the result would not always be an exact value. There will always be a variation between the actual value of the population, and the value given by the sample. The aim of every researcher is to ensure that the difference between the actual value of the population and the value is given by the sample taken is as close as possible. The larger the sample size, the smaller the gap between the value of the population and that of the sample (Baily, 1994). By taking into consideration constraints, a researcher would determine the sample size that would give a value close enough to the value of the population. The sample population gave closely related answers, depending on their gender. The researcher was therefore convinced that the sample size chosen would produce a value that has minimal difference with the value of the population.
- Population proportion: When a researcher sets to conduct a study in a given field, there are always characteristics that would be considered desirable for the research. According to Bak (2004), not all items in the population have the desirable characteristics that would enable success in the research. The researcher would hence be tasked with the duty of determining the proportion of the population that has characteristics that are desired in the study. This may not be easy because it may demand interaction between the researcher and the entire population of the study to determine the proportion with the desired attributes. It may be costly in terms of time and other resources. In this research, it was easier to determine the population proportion that would provide the desired results for the study.
- Population size: The total number of items in the study would always determine the sample size. Bouma (2000) says that it is always desirable to have a sample size that would properly represent the population. A large population would demand a larger sample size, and vice versa. In social science, it is always recommended that the sample size be about five percent of the population. This percentage would be higher if the population is smaller. Conversely, it would be smaller if the population were too large (Goddard, 2001). The researcher used a sampling formula by Ewens (1972) to calculate the sample size of employees for the study.
Description of Data and Analysis Techniques
Analysis of research questions
The following question was formulated to help guide the research. Having confirmed from the literature review that a difference in the rate at which men and women in the UAE perceive barriers to e-commerce exist, the researcher developed this question to bring to focus the effect this has on e-commerce within the country.
What is the general perception of women towards adoption of e-commerce in various firms within which they work?
The analysis of the research question will be done through SPSS. The data will be entered into the SPSS sheet and specific questions relating to the above research question will be run. The output will be found based on the percentage. The result would be based on the percentage rate of those who will be confirming or refuting the claim. The result will be given in tables and graphs.
To test whether there is a significant difference in the perception of men and women towards e-commerce by virtue of their gender, a chi-square of equal proportions will be applied using SPSS. The findings will be given in the form of a table.
From the result, the researcher will determine the chi-square value and compare it with the p-value. The p-value for this research is 0.05. Depending on the value that will be obtained, the researcher will get to determine the result of this question.
Testing the research hypotheses
According to Hoyle (2002), every research in social science sets forth to prove that a specific phenomenon occurred. Conducting a research is like a walk in the desert without a guiding map to show clear directions that should be taken in order to reach the desired destination. Hakim (2000), warns that care should be taken by every researcher when researching to ensure that he or she does not wander off the focus of the study just by the sheer wonder of the research in question. A path should clearly be set, upon which the research would take on reaching the desired solution.
Research hypotheses always provide solutions to this. Gupta (2002) defines hypothesis as a proposition made by the researcher about the research upon which the research would try to determine if it is true or otherwise. It is kind of a proposal or a guess that the findings of particular research would be in a particular way. As Hoffman (2001) notes, a research would always have two hypotheses for every single desired result. A research paper should always have null and alternative hypotheses. The null hypothesis would always refute the claim by saying that the proposition does not hold. On the other hand, alternative hypotheses would always try to affirm that the proposition set by the researcher holds. A test would always be conducted on the null hypothesis to reject it. When the null hypothesis is rejected, the alternative hypotheses will automatically hold, because the two are opposites. It is always every researcher’s desire to reject a null hypothesis because when a research accepts a null hypothesis, it would render the whole research unnecessary. It would be rejecting the proposition made by the researcher, a fact that would render the research null and void.
In analyzing the research hypotheses, the researcher would always set the significance level, always expressed as a percentage (Gusti, 2011). This percentage would be the limit within which the researcher would accept a null hypothesis. If the limit were surpassed, it would be said that there is significant difference and therefore a null hypothesis is rejected. Setting the percentage too high would be increasing the chances of confirming a given hypothesis, but it would reduce the accuracy of the research. Setting this percentage too low would increase chances of rejecting the hypothesis and increase chances of accuracy. In most the social sciences research, 5 percent is always acceptable as the standard significance level. As earlier stated in the assumptions above, this study takes 5 percent as its significance level. The researcher would test this hypothesis by analyzing the data gathered from both the employees and customers
Below are the three null hypotheses that the researcher wishes to test and reject in order to accept the alternative hypothesis, which would help in validating this research:
H1o. There is no difference in the perception of barriers of e-commerce between Emirati men and women.
This is the main hypothesis of this research whose rejection would validate the need for this research. By accepting this hypothesis, it would be a clear sign that the research confirms that there is no significant difference in the perception of barriers of e-commerce across the genders. The researcher wishes to reject this hypothesis.
The researcher will run the SPSS relevant to this hypothesis and determine whether the data collected confirms or rejects the hypothesis.
In order to test whether there is a significant difference in the perception of Emirati men and women towards e-commerce, chi-square for equal proportions will be applied using SPSS. By running the inferential statistics, the research findings can be generalized to the wider population within the sample drawn.
The next hypothesis was formulated to determine if there was difference in the way the two genders implemented strategies of e-commerce.
H2o. There is no difference in the implementation strategies of e-commerce between the two genders in the UAE.
The researcher wishes to reject this hypothesis from the data that will be collected. The significance level will still be maintained at 0.05, which translates to a 95 percent level of accuracy. The results will be put on tables and graphs to enhance understanding
If the above null research hypothesis is rejected, the alternate hypothesis would be accepted that there is a significant difference in the implementation strategies of e-commerce between the two genders in the UAE.
The hypothesis below was developed to ascertain the difference in the level of customers in the bank’s two branches.
H3o. No relationship between the perception of risks to e-commerce and the strategies that an individual would take in adopting e-commerce within an organization
The null research hypothesis above will be analyzed by running the data in the SPSS sheet to obtain the result. The researcher wishes to reject this hypothesis.
In order to test whether there is a significant relationship between strategies employed in adopting e-commerce and the perception of barriers to e-commerce; chi-square for equal proportions will be applied using SPSS.
If the null hypothesis were rejected, it would be concluded that a relationship between the perception of risks to e-commerce and the strategies that an individual would take in adopting e-commerce within an organization exists. This would mean that the alternative hypothesis below would be accepted.
H3a. There is relationship between the perception of risks to e-commerce and the strategies that an individual would take in adopting e-commerce within an organization.
Confirmation of this hypothesis will not only support the main hypothesis (the first hypothesis) of this research, but also give more clarification on the manifestation of this difference. It would point out some of the factors that have facilitated the difference stated in the first hypothesis.
Sensitivity Analysis
In every research finding, the correctness is always very important because an action may be taken upon the findings and recommendations of a given research. In case the result deviates from the truth by a considerable wide margin, it can result in serious consequences, especially if the action taken is of great impact (Barthe, 2010). However, it is worth appreciating that human being is prone to making errors on a number of occasions. This error can be in the process of input of the data or its analysis. Whichever point it may arise from, the consequences of such errors may be adverse if action were to be taken upon its recommendation. Sensitivity analysis is therefore important in mitigating such errors in a report. It helps in determining how robust a given research is.
In this study, the researcher appreciates the fact that such errors may occur. For this reason, there is need to develop measures that would help validate this research.
In this research, the main aim was to determine role of Emirati women in the perception of barriers of e-commerce in the United Arabs Emirates. However, this could only be done if there was a comparable difference between male and female branches of the bank. Reliability and Validity studies below help further explain how this research ensured that it maintained correctness of the findings.
Validity
The validity of a measurement instrument can be measured by the degree to which the instrument measures accurately what it is supposed to measure In this survey, content validity was measured where the representativeness, or sampling adequacy, of the content of the measurement instrument was checked with the help of experts in the field. In this study, the validity of the instruments was preserved ensuring the accuracy of the measurement where each variable’s indicators of existence were extracted solely from the literature of the work of previous researchers in well-established papers.
In this study, internal validity was ensured by checking the representativeness of the sample. The researcher ensured that the sample used, captured all-important characters at various sampled firms. External validity was ensured through triangulation that is, the researcher used more than one technique in collecting data. External validity was also guaranteed by asking respondents to give their views.
Reliability
Reliability means appropriateness, applicability, and truthfulness of a study. It refers to the ability of research instruments to produce results that are in agreement with theoretical and conceptual values (Proulx, 2011). The consistency of the measure, the probability of obtaining the same results again if the measure was to be replicated is referred to as reliability (Oppenheim, 1992). It is the relationship between the true underlying score and the observable score. Internal consistency is also important for the survey since it indicates the extent to which the items in the measurement are related to each other. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is very popular when determining internal consistency. This index ranges from zero to one, where a reliability of zero means no relationship, and reliability of one indicates a perfect and positive relationship. Since the reliability declines as the length of the question increases, the questions would be designed to be straight to the point. The idea behind internal consistency procedures is that questions measuring the same phenomenon should produce similar results. In internal consistency reliability estimation, single measurement instrument is administered to a group of people on one occasion to estimate reliability.
Summary
The United Arabs Emirates is one of the leading economic hubs in the world today. Carter (2000) says that this country, and especially the city of Dubai, has been a business attraction center for many of the developing countries in the world. This argument is supported by Carlin (2009) who holds that this is specifically so because of the fact that most of the products from this region are relatively cheap when compared to those coming from the west. This scholar reiterates the fact that Dubai has won the loyalty of the market in Africa and parts of Asia.
With this new development, there is every need to ensure that businesses in this country embrace the emerging technologies in order to be in a position to compete with firms from other countries. E-commerce, according to Hersey, Kenneth, and Dewey (2008), is one such new technology that a business cannot afford to assume. Many firms have gone online. This scholar states that one of the most important requirements of the middle-sized and large firms is the availability of a website. Most of the basic information of such firms would be found on the website. With the emergence of the social media, firms have considered e-commerce as the best way through which they can serve large markets with minimal number of stores. This scholar notes that every firm in this country has made considerable effort to embrace e-commerce, despite numerous challenges that it comes with.
Women have a role to play in breaking the barriers to e-commerce, just like their male counterparts. The barriers to e-commerce start from the perception of e-commerce among the concerned individuals. The biggest barrier to e-commerce has been a lack of acceptance among the relevant authorities. Many executives have not accepted the fact that e-commerce is a viable approach that can make a firm reach its goals at very faster rates. They have preferred to stay with their old ways of doing business, staying off such new approaches. Men have a different perception of technologies from women of this country.
It is observed that while men give emphasis on the suitability of e-commerce to an organization, women give emphasis on the compatibility of the relevant technologies and how they are applicable to the organization. Women have the perception that organizational issues are less important than technical issues. As such, they give lots of emphasis on the technical issues than they do on organizational issues. They have the belief that technical issues will define organizational issues.
While Powell (2010) agrees with this perception of women in part, this scholar warns that this is a dangerous approach to take. This is so because when organizational issues are sacrificed for technical issues, the firm would not be in control of the moves it will take. This scholar notes that it is important that a firm understands itself first before trying to bring in new approaches of operation. From this understanding, it will be possible for the firm to understand the approach that should be taken while implementing new technologies.
The two genders view barriers to e-commerce differently. Men are of the view that for e-commerce to be a success in an organization, conditions within the organization must be suitable enough. Moreover, e-commerce must fit in the context of the organization and not vice-versa. They therefore perceive barriers of e-commerce as organizational structures. As such, they give more emphasis on the organizational factors that would help eliminate barriers to e-commerce. On the other hand, women are of the view that barriers to e-commerce are technical in nature. They have the idea that the technical aspects of e-commerce are the real barriers to e-commerce. As such, they would consider giving more attention to understanding the technical issues as a way of breaking these barriers to e-commerce.
The next chapter focuses on the methodology used to collect data in this research. The researcher gathered data from a sample population in Dubai City. The sample was drawn from various individuals with varying backgrounds.
Conclusion
The United Arabs Emirates is one of the leading exporters of various manufactured products to the emerging economies in the world, especially in Africa and parts of Asia. The city of Dubai is particularly one of the largest business hubs in the world. With the emerging technologies, firms in this region are forced to adapt to various ways of conducting business that would enable them to manage the stiff competition posed by firms from the western countries and China and Japan.
E-commerce has emerged as one of the most relevant approaches to doing business. E-commerce enables businesses to operate easily in larger areas without the need to have physical stores in these areas. E-commerce is the new approach that most firms use to expand their market share. E-commerce is also very convenient for customers who may not have time to visit physical retail outlets, especially due to job-related commitments. E-markets enable them to shop in the comfort of their homes or offices.
E-commerce faces a number of challenges that may affect its successful implementation by various firms within the United Arabs Emirates. The perception of the concerned individuals towards these barriers will dictate the way they act towards addressing the issues. This research reveals that men have a different perception of barriers to e-commerce from that of women. Men believe that external forces should be manipulated to fit into the prevailing conditions of the firm. On the other hand, women believe that external forces should dictate the conditions of the firm. This difference in perception would affect the way individuals would act to eliminate the barriers to e-commerce.
The perceptions of women on the barriers to e-commerce have a big role to play in the successful implementation of e-commerce strategies in various firms within this country. As noted, people would always act based on their perception of various factors. Women believe that to eliminate barriers to e-commerce, it is important to adjust the internal factors of the organization to reflect on the prevailing external forces. They believe that an organization should always be flexible enough to adjust to technical forces relevant to the successful running of e-commerce. The Emirati women would always try to adjust the operational strategies of the firm as a way of the new technologies. This strategy might affect employees negatively.
References
Akhter, F. (2008). Gender and cultural differences in adoption of e-business infrastructure in the UAE. Computer and Information Technology, 8, 462-465.
Anderson, P. (2004). Research Methods in Human Resource Management. London: Chattered institute of Personell Management.
Andrzej, A. & Buchaman, A. (2007). Organizational Behavior. London: Prentice Hall.
Badenhorst, C. (2007). Research writing: breaking barriers. Pretoria: Van Schaik Publishers.
Baily, C. (1996). A guide to field research. Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press.
Baily, K. (1994). Methods of social research (4th Ed). New York: Free Press.
Bak, N. (2004). Completing your thesis: a practical guide. Pretoria: Van Schaik
Barthe, G. (2010). Verification, Model Checking, and Abstract Interpretation: 11th Ed. New York: Springer.
Barzun, J. (2004). The modern researcher (6th Ed). Belmont: Wadsworth.
based Concerns. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 20(4), 206-214.
Bell, P. (2001). Evaluating, doing and writing research in psychology: a step-by-step guide for students. London: Sage.
Bouma, G. (2000). The research process (4th Ed). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Calabrese, R. (2006). The elements of an effective dissertation and thesis: a step by step guide to getting it right the first time. Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.
Carlin, M. (2009). Cross-cultural e-commerce design guidelines for American and Chinese College student populations: Results from an empirical comparative study. University of Maryland.
Carter, S. (2000). Improving the numbers and performance of women-owned businesses: Some implications for training and advisory services. Education& Training, 42, 326-333.
Ewens, W. (1972). The sampling theory of selectively neutral alleles. Theoretical Population Biology, 3, 87–112.
Goddard, W. (2001). Research methodology: an introduction. Lansdowne: Juta.
Gupta, P. (2002). Statistical Methods (31rd Ed). New Delhi: Sultan Chand & Sons.
Gusti, N. (2011). Cross Section and Experimental Data Analysis Using E-views. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Hakim, C. (2000). Research Design: Successful Designs for Social and Economic Research. London: Routledge.
Hersey, P., Kenneth, B. & Dewey, E. (2008). Management of organizational behavior: Leading human resources. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Hoffman, E. (2001). Postgraduate research guidelines. Vanderbijlpark: Triangle Technikon.
Hoyle, R. (2002). Research methods in social relations. Fort Worth: Wadsworth.
Hughes, J. (1997). The philosophy of social research (3rd Ed). London: Longman.
Kolsaker, A. & Payne, C. (2002). Engendering trust in e-commerce: a study of gender-Krathwohl, D. (2004). Methods of educational and social science research: an integrated approach (2nd Ed). Long Grove, Waveland Press.
Kumar, R. (2004). Research methodology. A step-by-step guide for beginners (2nd Ed). London: Sage.
MacGregor, R. & Vrazalic, L. (2007). E-commerce in regional small to medium enterprises. Hershey: IGI Publishers.
MacGregor, R. & Vrazalic, L. (2008). The role of gender in the perception of barriers to e-commerce adoption in SMEs: An Australian study. Communications in the IBIMA, 4, 141-147.
Marchall, G.W., Michael, R.S. & Elnora, W.S. (2006). Marketing: Real people, real choices. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Murray, R. (2006). How to write a thesis (2nd Ed). Philadelphia: Open University Press.
Nelson, C. (2006) UAE National Women at Work in the Private Sector: Conditions and Constraints. Dubai: Trident Communications.
Oppenheim, N. (1992) Questionnaire Design, Interviewing and Attitude Measurement: New Edition. London, Pinter.
Powell, G. (2010). Women and men in management. London: SAGE.
Proulx, T. (2011). Modal Analysis Topics, Volume 3: Proceedings of the 29th IMac, a Conference. New York: Springer.
Rodgers, S. & Maryanne, H. (2003). Gender and E-commerce: An exploratory study. Journal of Advertising Research, 43, 322-329.
Schniederjans, M. & Cao, Q. (2002). E-Commerce operations management. Danvers: World Scientific.
Taylor, G. (2005). Integrating qualitative and quantitative methods in research. Lanham: University Press of America.
Taylor, G. (2005). Integrating qualitative and quantitative methods in research. Lanham: University Press of America.
Vogt, P. (2007). Quantitative Research Methods for Professionals Author. New York: Pearson.