Introduction
Hilton, a multinational hospitality company, was chosen as a specific example of a company and its policies and strategies to promote the welfare of employees. Ensuring staff satisfaction and well-being is the basis of its effective operation and functioning.
Particular focus in this work will be given to well-being management and its integration with other areas of people practice – including health promotion initiatives, alignment with organizational performance and employee outcomes, and downsides of well-being policies. Based on the information received, several recommendations will be provided that will be aimed at a more comprehensive and sophisticated approach to ensure the well-being of workers in the workplace.
First, before proceeding to the analysis of employee welfare management, it is necessary to gain an understanding of what the selected company is. Henceforth, Hilton is an international hospitality organization with many hotels and resorts. The company was founded in May 1925 by Conrad Hilton and, throughout its long history, has gained popularity and a respected name (“The Story of Hilton,” n.d.). Thus, the company is the second largest in the hospitality business after Marriott. The working staff of the company is 159 thousand people. It requires effective and productive measures that will help care for such a large number of personnel.
When considering Hilton, paying attention to how employees see it is necessary. Research showed that “97% of employees at Hilton say it is a great place to work compared to 57% of employees at a typical U.S.-based company” (“Company overview,” n.d., para. 3). In addition, the same study showed that when applying for the individuals felt welcomed, proud of their workplace, the management in the company and the ethics and practices that were applied at the Hilton. Therefore, this kind of feedback from the company’s employees arouses increased interest in the study of policies to ensure the welfare of individuals in the workplace.
Management of Well-Being
The first aspect that will be considered when analyzing Hilton is the management of employee well-being and its integration with other practices. This aspect includes ensuring a favorable workplace and following all necessary norms, requirements, and rules of ethics (Peccei & Van de Voorde, 2019). In addition, well-being should be linked to practices that relate to health promotion initiatives (Foster, 2018). Within this aspect, the role of well-being champions, which are an integral part of ensuring the well-being of workers in the workplace, will also be explored.
A study of literary sources has shown that Hilton is a reasonably successful company in the field of caring for its employees. This is due not only to positive feedback about the work from the company’s staff but also to articles confirming this fact. Thus, research showed that “Hilton has developed a strong reputation as a purpose-driven company with a great workplace culture, driven by its team members” (“Hilton expands wellness platform and benefits,” 2022, para. 10). Moreover, it was noted that the hospitality giant is making a lot of efforts to create a unique and resilient workplace culture and team member benefits.
This aspect corresponds to such a criterion as a cooperative culture, which was highlighted as valuable in ensuring the welfare of employees. The company’s website provides a large amount of information that can be used for its analysis. So, the company annually conducts surveys among its employees regarding their feedback work and what they like most about their work. This measure has value and effectiveness as it provides a direct vision of the organization by employees who perform various functions and can accurately determine its advantages and disadvantages. On the company’s part, acquiring this kind of feedback helps to understand what needs to be changed (Mertens et al., 2021). This step is being implemented to improve the quality of Hilton’s work and customer service and to maintain high satisfaction among the company’s employees.
One of the initiatives within the company, which includes integrating several practices, is Thrive at Hilton. This innovation “umbrellas the many ways we support and empower our Team Members personally and professionally” (“What is thrive at Hilton?” 2022, para. 1). Thus, Thrive at Hilton positions itself as practices and policies that are based on providing benefits to employees in three main areas of mind, body, and soul. At the heart of this concept is providing health initiatives that will help individuals cope with health complications. For example, Hilton has its own healthcare pop-ups, wellness days, flu clinics, yoga, and mindfulness practices that are provided to each team member.
In addition to initiatives that focus exclusively on physical health, Hilton has those that provide spiritual and mental development. Thus, the company provides team members with the opportunity to take various self-guided e-learning courses that will contribute to improving and increasing staff skills. The list of these skills includes leadership, management, interpersonal communication, and other characteristics that help employees succeed in the workplace (Coffelt et al., 2019; He et al., 2019).
In addition, Thrive at Hilton pays attention to such an aspect as mindfulness and emphasizes the importance of the mental health of its employees, which is crucial to their well-being (Aboobaker et al., 2019). Thus, for example, the initiative focuses on providing employees with rest days during which they can relax at a reduced price in Hilton hotels and resorts. Moreover, the Thrive at Hilton online platform itself has various resources that will assist in acquiring knowledge, such as dealing with stress in the workplace or meditative practices for relaxation.
Well-being champions play a unique role in ensuring well-being in the workplace. These specialists are “employees who volunteer to focus on improving the well-being of their colleagues, as part of the company well-being initiatives” (“5 benefits of well-being champions in the workplace,” n.d., para. 10). In other words, this employee represents a leader in ensuring the most satisfactory working conditions and compliance with norms and ethics (Wieneke et al., 2019; Wieneke et al., 2019b). When analyzing the Hilton company, there was no information about the presence of well-being champions. It can be assumed that the performance of these duties is within the authority of managers and group leaders who report and monitor the welfare of employees.
Therefore, Hilton’s welfare management analysis showed that the hospitality company has a highly effective policy for taking care of its employees. One of the most beneficial initiatives for the staff was Thrive at Hilton, which provides resources and opportunities for employees in such areas as body, mind, and soul. This platform contains various useful practices for dealing with stress, information about benefits for team members, and data on healthcare pop-ups.
In addition, Thrive at Hilton also plays the role of an educational platform where individuals can improve their skills. However, it is also important to point out that the well-being champion plays a valuable role in the study of staff welfare, the main task of which is to monitor the implementation of this aspect among employees, information about which has not been observed at Hilton.
Alignment of Well-Being with Organizational Performance and Employee Outcomes
The next step is to analyze the relationship between employee well-being, organizational performance, and employee outcomes. This aspect includes several components: employee retention, absenteeism, employee satisfaction, and engagement. For a company that wants to achieve the most successful results, it is critically important to devote many resources to its employees. In addition, it is necessary to conduct research and analysis of performance, which will directly show how effective the strategies used are and which areas suffer the most.
Conducting an assessment of the workplace for the welfare of employees is one of the most effective tools. It allows managers to understand accurately what aspects require changes and how the company’s policy affects the staff (Hesketh & Cooper, 2019). Regarding Hilton, the value of conducting an employee welfare assessment is represented in the evidence-based approach. In other words, carrying out this procedure will contribute to acquiring evidence to make a decision regarding the staff and their level of satisfaction.
Several studies have focused on assessing the well-being of Hilton employees. An investigation by Mishra et al. (2021) may be valuable in the framework of this study. It examines one of the Hilton hotels for employees’ safety and health status. During a survey of workers, the authors received data that “the safety and health status of workers is good as most of the respondents revealed that there are no major and fatal accident cases recorded at the site since construction.” (p. 1). Thus, we can say that as for the physical safety of health, Hilton takes significant measures to ensure the well-being of employees, which contributes to the productive activities of the hotel.
However, often, psychological impact and constant stress become the causes of such undesirable consequences as burnout, absenteeism, and, in the most critical cases, dismissal. Reidhead (2020) pointed out that “a strong and healthy culture of hotel companies improves self-confidence among its employees and reduces work stress” (p. 433). Hilton is characterized by a high organizational and corporate culture, which are the basis for implementing any initiative or policy in the company. Therefore, the productivity of the company’s employees is at a high level because they have an increased level of satisfaction with the workplace and their well-being.
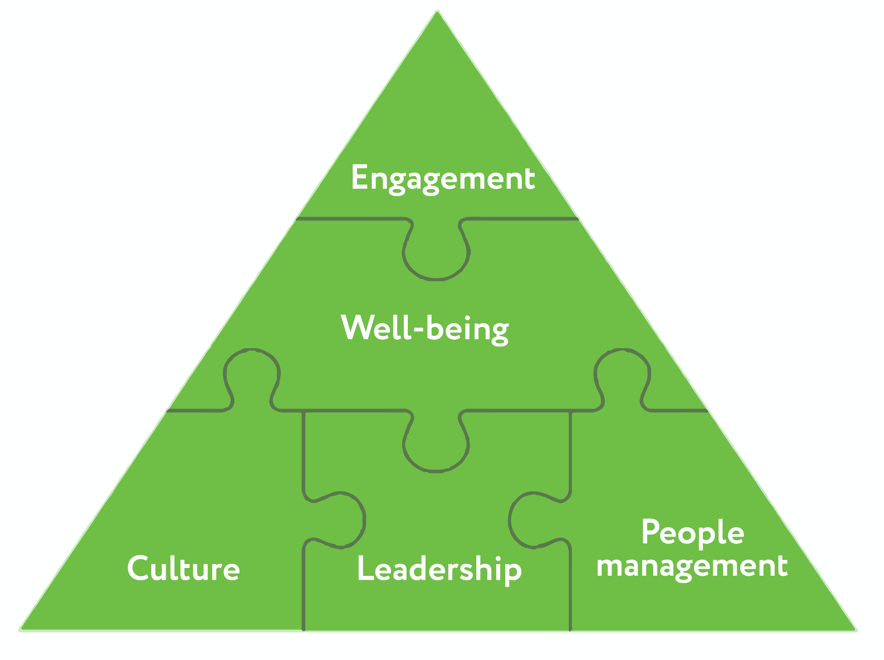
When creating and maintaining a strategy for ensuring well-being in the workplace, several aspects must be taken into account. These domains should guide the organization in determining which methods and tools it will adhere to. CIPD’s well-being pyramid model points to four main components: culture, engagement, people management, and leadership (Fig.1).
Combining and developing these aspects allows companies to improve the quality of staff work and their satisfaction. However, the most important aspect is understanding that these components should become an obligatory part of the company’s strategy. Only with the observance and equal development of each of these domains can the company achieve the desired outcomes regarding the welfare and work of the team.
In addition to performance, employee well-being greatly impacts aspects such as employee experiences and outcomes. This connection is due to the fact that in order to achieve the greatest productivity, employees must be motivated and have a desire to make the company as good as possible. The findings of the scientific literature have shown rather ambiguous data regarding the level of involvement of the staff of Hilton hotels.
On the one hand, “the survey showed that the majority of employees have been leaving Hilton Park Lane for two main reasons: these reasons were not being valued as a person and lack of career development” (Toksöz, 2021, p. 8). On the other hand, Reidhead (2020) showed “strong employee engagement with the organization” (p. 434). Based on this information, it can be concluded that such an indicator as engagement directly depends on the practices that are applied by individual parts of the organization (Sutton, 2020). This is because they may not follow the general strategy and policies of the company, which directly affects this criterion of well-being.
Satisfaction and commitment are equally valuable aspects of well-being. In the field of hospitality, this is of high importance since the level of customer satisfaction depends on how employees perform their activities. Thus, to ensure this aspect, the employer must constantly monitor how employee satisfaction levels change. When considering hotel employees, studies have shown that “the level of quality perceived by the customer depends on employee job satisfaction” (Baquero, 2022, p. 76). This information is a confirmation of the previously cited claims regarding satisfaction. It is worth noting that commitment and satisfaction are at the same level. Thus, when the first aspect falls, the second one falls. This, in its case, significantly worsens the service employees provide due to the loss of motivation.
Down-Sides of Well-Being Policies
Policies to create and maintain well-being in the workplace have a large number of advantages that necessitate their implementation in the workplace. However, like any strategy, there are also several negative sides, such as the study and prediction of which will contribute to their fastest limitation (Cooper & Leiter, 2017). One of the most serious issues is the lack of support from line managers and the transfer of responsibility to individuals in well-being management.
Policies to promote and ensure the well-being of employees must be supported at all organizational levels. In other words, all stakeholders involved in this process should participate in the development of the strategy and its implementation and perform their functions (George et al., 2019). However, there may be cases when line managers receive a low level of support from the heads of the organization. This fact is especially dangerous for a company like Hilton since the hospitality giant has many employees who need to be managed. Therefore, there are situations in which, due to the lack of support for managers, there may be a decrease in the productivity and efficiency of the company.
In addition, cases when employees do not receive support from line managers can cause a big problem. There may be several reasons for this problem, one of which is the overload of workers (Stone et al., 2020). Hence, when appointing this type of manager to manage and navigate the staff, it is necessary to properly distribute them in the organization. This is due to the fact that for companies like Hilton, which have a large staff of employees, it is important to provide support for everyone. With a lack of this aspect, problems and stressful situations may arise in the workplace, which will lead to burnout, anxiety, and layoffs.
Another problem that needs to be considered when studying welfare management is the transfer of responsibility. This issue consists of the transfer of certain powers to other individuals, which may occur due to the lack of professionalism of managers or work overload. For Hilton, this problem also poses a threat, especially during the high season, when hotels have a large number of guests. Due to the possible occurrence of various issues, some employees and managers may transfer their responsibilities to others. One of the critical consequences of this circumstance is the feeling of neglect and lack of support from the company for the staff. Moreover, individuals may feel overwhelmed, leading to increased stress and tension in the workplace and absenteeism.
When solving the discussed problems in the organization, it is necessary to establish organizational culture and control, which will contribute to the improvement and clear formation of well-being at work. This measure should, first of all, be carried out through the construction of organizational and corporate culture.
The next step is to spread awareness about this aspect among all employees. It is critically important to emphasize the importance of compliance with the set rules and responsibilities that the staff faces (Guest, 2017). In addition, it is valuable to establish communication channels that will not only solve emerging problems but also get answers to emerging questions (Verčič & Špoljarić, 2020). After that, an important part becomes monitoring how the corporate and organizational culture in the workplace is carried out and observed. Data collection can be carried out both through surveys and performance analysis.
People management functions can contribute to appropriate corporate cultures and strategies to support well-being. Focusing on and developing this area of staff activity contributes to improving communication and channels of interaction between employees. Thus, the possibility of problems such as the absence of guidance from supervisors and delegation of duties, which contribute to a decrease in the quality of work and an increase in stress, is limited. Additionally, people management has a special role in supporting sustainable well-being policies (Schermerhorn & Bachrach, 2020). Thus, they are responsible not only for providing the most comfortable working conditions but also for taking into account possible issues such as absenteeism, performance, and efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the welfare of employees is a rather complex and complex task that the employer faces. Using the example of Hilton, which is one of the leaders in the hospitality industry, you can see how the right policies and practices are reflected in this aspect. Therefore, the organization is characterized as one of the best employers in this business.
However, there are still studies that show that not all Hilton organizations have an equal level of employee well-being and satisfaction. Thus, it becomes critically important for the company to investigate the causes of this inequality and possibly pay attention to issues such as the lack of employees for personnel management. Another recommendation is to pay attention to how the organizational and corporate culture is implemented in the subordinate parts of the company. In addition to these aspects, Hilton Company conducts quite successful activities to maintain the well-being, satisfaction, and engagement of its staff.
References
Aboobaker, N., Edward, M., & KA, Z. (2019). Workplace spirituality, employee wellbeing and intention to stay: A multi-group analysis of teachers’ career choice. International Journal of Educational Management, 33(1), 28-44. Web.
Baquero, A. (2022). Customer and Employee Satisfaction in Hotels. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Issues, 4(2), 69-83. Web.
Coffelt, T. A., Grauman, D., & Smith, F. L. (2019). Employers’ perspectives on workplace communication skills: The meaning of communication skills. Business and Professional Communication Quarterly, 82(4), 418-439. Web.
Company overview. (n.d.). Great place to work. Web.
Cooper, C.L. & Leiter, M.P. (2017). The Routledge companion to wellbeing at work. Routledge.
Foster, D. (2018). The health and well- being at work agenda: good news for (disabled) workers or just a capital idea? Work, Employment and Society, 32(1), 186-197.
George, B., Walker, R. M., & Monster, J. (2019). Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta‐analysis. Public Administration Review, 79(6), 810-819. Web.
Guest, D.E. (2017). Human resource management and employee well‐being: towards a new analytic framework. Human Resource Management Journal, 27(1), 22–38. Web.
Hesketh, I. & Cooper, C. (2019). Wellbeing at work: how to design, implement and evaluate an effective strategy. CIPD Kogan Page.
Hilton expands wellness platform and benefits to launch new offerings supporting team member caregiving responsibilities. (2022). Hospitalitynet. Web.
Mertens, S., Schollaert, E., & Anseel, F. (2021). How much feedback do employees need? A field study of absolute feedback frequency reports and performance. International Journal of Selection and Assessment, 29(3-4), 326-335. Web.
Mishra, D., Mishra, A. K., Sah, D. P., Joshi, B. R., & Aryal, B. (2021). Assessment of workers safety and health status in high rise building: A case project of “Double Tree by Hilton Commercial Hotel at Naxal, Kathmandu”. Efflatounia-Multidisciplinary Journal, 5(2). Web.
Peccei, R. & Van de Voorde, K. (2019). Human resource management-well-being- performance research revisited: past, present and future. Human Resource Management Journal, 29(4), 539-63. Web.
Reidhead, C. (2020). Impact of organizational culture on employee satisfaction: A case of Hilton hotel, United Kingdom. Journal of Economics and Business, 3(1). Web.
Schermerhorn Jr, J. R., & Bachrach, D. G. (2020). Exploring management. John Wiley & Sons.
Stone, R. J., Cox, A., & Gavin, M. (2020). Human resource management. John Wiley & Sons.
Sutton, A. (2020). Living the good life: A meta-analysis of authenticity, well-being and engagement. Personality and Individual Differences, 153. Web.
The story of Hilton. (n.d.). Hilton. Web.
Toksöz, S. (2021). Impact of engagement exist in organizations’ internal environment on employees’ motivation, satisfaction, commitment and turnover intention. In E3S Web of Conferences (vol. 258, p. 10010). EDP Sciences.
Verčič, A. T., & Špoljarić, A. (2020). Managing internal communication: How the choice of channels affects internal communication satisfaction. Public Relations Review, 46(3). Web.
Wellbeing at work. (n.d.). CIPD. Web.
What is thrive at Hilton? Q&A with Hilton benefits leader. (2022). Hilton. Web.
Wieneke, K. C., Egginton, J. S., Jenkins, S. M., Kruse, G. C., Lopez-Jimenez, F., Mungo, M. M., Riley, B. A., & Limburg, P. J. (2019). Well-being champion impact on employee engagement, staff satisfaction, and employee well-being. Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes, 3(2), 106-115. Web.
Wieneke, K. C., Schaepe, K. S., Egginton, J. S., Jenkins, S. M., Block, N. C., Riley, B. A., Sifuentes, L. E., & Clark, M. M. (2019b). The supervisor’s perceived role in employee well-being: Results from Mayo Clinic. American Journal of Health Promotion, 33(2), 300-311. Web.