Abstract
The report provides a connection between the IMF and the World Bank in controlling global finance. The IMF and the World bank use several instruments to regulate the balance of payments problems and other financial crisis that countries might have faced. The report reviews several works of literature related to IMF and World bank, and from the pieces of literature, it is revealed that the IMF provides short and medium-term loans.
The world bank offers long-term loans to countries in financial difficulties. Meanwhile, the platform laid down by IMF provides criteria for a country to be qualified for the World bank loan. For effective control of global finance, the World and IMF need to ensure that the countries they offer loans implement the loans in the right direction.
Overview of International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank
International Monetary Fund (IMF) was created in 1946 aftermath of the Second War, and the major objective for the creation of IMF was to normalize international financial chaos that was the precedent of the Second World War.
Technically, IMF has been one of the specialized agencies of the United Nations, and since the formation IMF in 1946 until the present date, IMF has been at the forefront in ensuring international financial flows. (Sanford, Weiss, 2009).
However, the World Bank was formed at Bretton Woods in 1947 to rebuild Europe due to the devastating effects of the Second World War. Presently, the World Bank has provided multi-functions for countries around the world, and part of its function is to ensure global financial stability.
To achieve this aim, the World Bank has created international financial institutions such as International Finance Corporation (IFC), International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA), and the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). (World Bank Group, 2009). After the formation of the IMF and World bank, these two international institutions have used several instruments to control international global finance.
The objective of this report is to examine connections between the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in controlling global finance.
The report limits its inquiry to only the instruments the World and IMF use to control global finance.
Finally, the methods of inquiry will be a review of the literature on the World Bank and IMF in order to examine the instruments, both IMF and World bank used to control global finance.
Introduction to the connection of IMF and World Bank in controlling global finance
To control global finance, IMF and World bank use structural adjustment programs such as privatization and liberalization of the countries economy with the intention to reduce inflation and government expenditures.
It should be noted that there are conditions that the IMF and the World bank provide to the loans receiving countries, and the conditions depend on the number of credits that are offered to demanding countries. (Boockmann, Dreher, 2002).
Recently, the IMF and the World bank used some measures to control global finance. For example, in April 2009, the IMF announced its new Flexible Credit Line (FCL). The main objectives of FCL are to offer the credit line of Fund’s normal access for countries with good economic records of accomplishment for periods of 6 to 12 months. ( Sanford, Weiss, 2009).
IMF instruments to control global finance
As is indicated from the previous section, IMF is an international financial institution that serves the purpose of solving monetary problems through international cooperation. In addition, the IMF sees the stability of exchange rates in order to avoid exchange rates depreciation.
IMF also sees to the maladjustment of the balance of payment in order to ensure international prosperity. Typically, to help member countries to overcome the balance of payment (BOF) problems, the IMF offers short-term loans on the condition that they agree to make improvement on the macroeconomic performances. (Sanford, Weiss, 2009).
The short-term loans offered by the IMF are used to regulate the balance of payments problems between 2 and 4 years. It should be noted that the short-term loan offered by the IMF is to induce the capital outflow of the struggling economy of some countries in African, Asian, and Latin American. Apart from the short-term loan that has to be paid within 2 to 4 years, IMF also offers low-interest finance for poorer countries to be repayable within ten years.
The World Bank instruments to control global finance
Apart from the IMF, the World Bank also offers long-term loans to damaged countries due to the devastating effect of the Second World War. It should be noted that the core objective of the World Bank is to stimulate economic development and growth, and the World Bank controls the domestic institutional issues and microeconomic issues.
Typically, funds disbursed by the World Bank to the needy countries are effective for the exchange rate policies and macroeconomic issues. (Sanford, Weiss, 2009).
Connections between the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in controlling global
Typically, the overlapping functions IMF and the World bank to control global finance is to ensure that the two international financial organizations provide sufficient supports for countries facing financial crisis. It should be noted that the occurrence of the global financial crisis is a result of recessions and unemployment in the economy, and this leads to the collapse of financial markets.
Thus, the strategies that the IMF and the World Bank use ameliorate this financial crisis are to invest in the market of the countries experiences financial problems. As being indicated previously, the IMF provides short and medium-term loans for countries experiencing financial crises to regain its economy.
Meanwhile, the IMF provides a platform under which countries can demand sufficient funds from the World bank to regain their economy. This is one of the processes through which the World Bank and International Monetary Fund control global finance. ( Doebbler, 2009).
For example, with the response to the recent global financial crisis, there was an economic summit by 192 member states of World bank recently in 2009, and the summit was led by a Nobel Prize-winning, Joseph Stieglitz, former Chief Economist of the World Bank. The major objective of the summit to find a way of solving the global financial crisis that currently affects the world economy.
From the consensus of the summit all the members agreed, “It goes on to describe the need to take actions to reduce the impact of the crisis on employment, to ensure liquidity and capital needs of banks, and to ensure reliance on the IMF and World Bank as the institutions that will lead us out of this crisis”. ( Doebbler, 2009).
The tone of the summit shows that the IMF and the World bank can bail countries from financial problems, and this proves that the World and IMF have the necessary instruments to control global finance. However, the main contribution reform of IMF is to ensure that the economic policy of IMF and World bank programs strictly adhere. (Boockmann, Dreher, 2002).
IMF Stabilisation Programmes and World Bank Structural Adjustment program
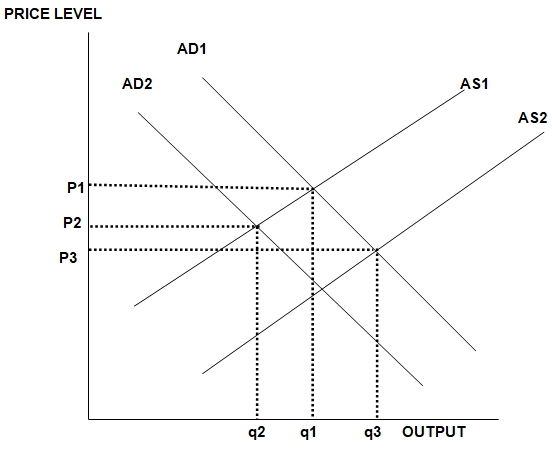
As illustrated in fig 1, the instruments IMF and World bank used to control global finance lead to an increase in output and lower prices. For example, the shift in the demand curve to left from AD1 to AD2 show that IMF programs are deflationary, and this shift lower the price as well as output.
However, in the World Bank programs, the demand curve shift from AS1 to AS2 points to the efficient programs of the World Bank, which lead to industrial restructuring. The effect is to increase the output and lowers the prices.
The direct impacts of the IMF and the World bank to global finance
The direct impacts of IMF and the World Bank have shown that the structural adjustment programs provided by the two international financial organizations can help countries in financial crisis to come out from their credit problems if they adhered to the conditions laid down for them by the IMF and World bank.
Thus, by adhering to these conditions, some countries have been able to come out from economic crises such as inflation, unemployment, unfavorable balance of payments, and other financial crisis that affects the global finance. For example, many countries in Asia that had serious economic problems in the 1970s have come out to be among the newly industrialized countries’ 2000s. (Boockmann, Dreher, 2002).
Despite the relationship between the IMF and the World Bank in controlling global finance, opinion still revealed that the World Bank has more technical instruments to control global finance than the IMF. As indicated by Boockmann and Dreher (2002), “the number of projects increases economic freedom, while the volume of credits reduces freedom.
This finding applies not only to the composite freedom index, but also to the individual index components, in spite of the fact that the index components cover very different areas of economic policy, such as monetary or fiscal policy, the quality of the legal system, or barriers to trade.
World Bank projects are more likely to improve economic freedom than do IMF programs. Programs of the latter institution have, according to our estimates, not led to changes in structural, growth-oriented policies”. (Boockmann, Dreher, 2002).
Conclusion
The report has revealed that the IMF and the World bank are interrelated in controlling global finance. While the IMF offers short – term and medium-term loans to countries with financial problems in order to come out from the problems, the World Bank offers a long-term loan for countries in order to ensure economic reforms.
Typically, the IMF offers a strict platform under which a country can obtain long-term loans from the World bank. The interrelationship of the IMF and World bank enhances the control of global finance.
Recommendations
There is some criticism levied on IMF and World bank because leaders of some countries in Africa and Asia often divert IMF and World Bank’s loans in their private accounts. This has made the loans provided by the IMF and World to be ineffective.
Thus, for the effective implementation of the World Bank and IMF loans, the two international financial organizations must provide the necessary supervision, advice, staff, and support for the countries in financial crisis in order to ensure that the loans provided are implemented in the right directions.
References
Boockmann , B, Dreher, A, (2002), The Contribution of the IMF and the World Bank to Economic Freedom, Social Science Electronic Publishing, Inc.
Doebbler, C, F, J, (2009), The UN Responds to the Global Financial Crisis? Opinion Editorial.
Sanford, J, E, Weiss, M, A, (2009), The Global Financial Crisis: Increasing IMF Resources and the Role of Congress, CRS Report for Congress, USA.
Loughborough University (2009), Lecture 7 International Institutions, GAAT, WTO, IMF (World Bank), Department of Economics.
Loughborough University, (2009) Lecture Note on Economics, Department of Economics.
World Bank Group, (2009), World Bank History, World Bank Archive.