Using appropriate analytical tools (such as PESTEL and five forces); analyze the external business environment about the analyzed cases. Conclude the main opportunities and threats derived from the above external analysis.
Introduction
Hewlett Packard operates within the Diversified Computer Systems industry in the United States. Over the years it has been in operation, HP has managed to diversify its product and services offering (Packard, 2006, p.33).
The US diversified computer industry is monopolistic. Salvatore (2006, p.400) defines a monopolistic market to include a market with a large number of firms that produce similar but differentiated products (Hewlett-Packard, 2009). Over the past decade, the diversified computer systems industry in the US has experienced a rise in the intensity of competition (Mobile Tech News, 2009). One of the factors contributing to the rise in the intensity of competition is the large number of investors venturing into the industry.
Also, firms in this industry are diversifying their operation by venturing into new market segments. One of the markets which are considered being very lucrative is the Smartphone market. Even though large firms such as Dell, IBM, Apple, and HP hold the largest proportion of the total market share, an increase in the number of new entrants is culminating in a decline in their market share.
This report is aimed at analyzing Hewlett-Packard.
PESTLE Analysis
Political environment
According to Mouncey, the political environment presents both opportunities and threats (2007, p.34). Currently, HP operates as a multinational company. It has established its outlets in 170 countries. As a result, it is affected by the political differences in the countries in which it operates. For example, some issues may be legal in one country but illegal in another.
The US has been politically stable. This has culminated in the creation of an environment suitable for business operations (Marchand, 2000). As a result, the firms have been able to conduct their operations effectively.
To enhance the country’s economic development, the US government has formulated several policies that promote business operations. For example, the US government has developed comprehensive Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) such as patents and copyright laws (Sekhar, 2009). As a result, firms which develop Smartphone’s can undertake their research and development successfully.
The US government has also entered into trade agreements with several countries through the formation of trading blocs such as NAFTA and MERCOSUR (Hornbeck, 2007, p. 23). This has significantly promoted bilateral trade between member countries.
Economic environment
The 2008/2009 global recession affected firms in different sectors. This is because there was a decline in the level of consumption by individual and institutional customers. Customers reduced their spending on IT products and services (Shreshtha, 2010). Their consumption was inclined towards necessities. This led to a decline in sales for mobile phones which affected the firm’s profitability. For example, during the first quarter of 2009, mobile phone sales declined by 15.8% (Mobile Tech News, 2009, para. 1).
Social-cultural environment
The US has a relatively high population. Also, the US is a pluralistic society which means that the country’s population is composed of individuals of different races, religions, cultures, and nationalities. Additionally, the country is characterized by a high rate of immigration which increases the demand for smartphones. According to Shreshtha (2010, para. 5), a significant proportion of the US population uses computer technology in executing the tasks. By 2006, a significant proportion of US citizens were using internet technology to do their work and paying bills. The integration of internet technology with the smartphone indicates that there is a high probability of an increase in demand for smartphones.
The firm’s operation may be affected by differences in culture within its markets. For example, some cultures may be against some of the new technologies invented by HP.
Other social issues affecting HP relate to increased pressure by civil rights activists on firms dealing with IT to reduce uncontrolled technological growth. Before venturing into some markets across the world, HP has to address these issues.
Technological environment
The US is one of the countries which adopted computer and internet technology early. As a result, many companies have ventured into the US IT industry. HP is amongst the trendsetters in the introduction of new information technologies. In the 21st century, the IT industry has increasingly become technical (Marchand, 2000, p. 54). Firms in this industry are undertaking intense research and development to position themselves in the market by attaining a high competitive advantage.
Legal environment
Most countries are increasingly being concerned about attaining sustainability in addition to environmental sustainability (Johnson, Scholes& Whittington, 2008, p.34). To achieve this, different countries are formulating environmental protection laws. Some of these laws relate to the disposal of used smartphones. As a result, firms are required to operate in a socially responsible manner to protect the environment (Shreshtha, 2010, para. 8).
In its operation, HP is required to adhere to rules and regulations governing certain issues such as pollution, health, and safety in addition to other laws that fit the host country’s interests. To survive in these markets, HP is required to adjust to these business laws.
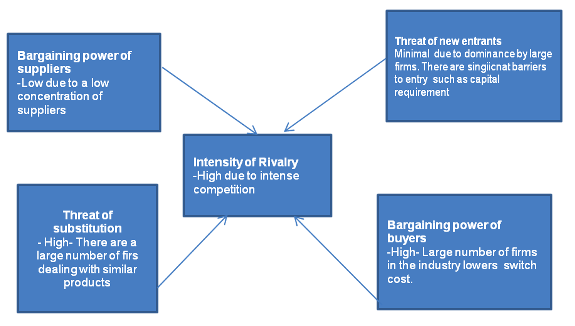
Porter’s five forces
Buyers
Because there are a large number of players in the industry, buyer power is relatively high. This arises from the fact that consumers can switch from one competitor to another at a relatively low cost.
Suppliers
The concentration of suppliers of electronic products and accessories is low. As a result, their bargaining power ranges from low to fair. Because HP has an international reach, suppliers are very keen on offering to supply to HP. To ensure that only high-quality products and services are supplied to the firm, HP has developed comprehensive selection criteria.
Substitutes
HP is faced with a relatively high threat of substitutes from other handheld devices.
Market rivalry amongst competitors
Threat from competitors is one of the most challenging issues which businesses face in their operation. The diversified computer systems industry is characterized by a hyper-competition. This arises from the fact that there are many competitors in the industry (Ungson & Wong, 2007). These competitors range from large enterprises such as IBM, Apple, and Dell to small and medium-sized enterprises. As a result, the degree of rivalry is relatively high.
The threat of new entrant
Due to the competitive nature of the industry, the threat of entry is minimal. Also, large players such as HP have dominated the industry making it challenging for new entrants (Wit & Meyer, 2004). Also, venturing into the industry requires firms to have a substantial amount of capital and survivor capacity. These requirements act as barriers to entry.
Main opportunities and threats
The political stability in the US means that HP can be able to undertake its investment in smartphones more effectively. Also, the fact that the US is entering into trade agreements with different countries means that there is a high probability of HP accessing new markets more cost-effectively (Hornbeck, 2007). On the other hand, the institution of IPRs by the government presents an opportunity for HP to undertake new product development successfully through research and development. This is because HP’s innovations are protected from exploitation.
The high population in the US presents an opportunity for HP to increase its customer base by attracting new customers. This is further enhanced by the current social change whereby most consumers are incorporating internet technology in their consumption patterns. Changes in the global economy, for example, the occurrence of a global economic recession, may affect the firm’s operation. This arises from the fact that demand for smart technology may decline as consumers shift their consumption to necessities (Hyers, Spooner & Gottheil, 2010). This may culminate in HP experiencing a decline in its profitability.
The high rate of technological innovation being undertaken by firms in the Smartphone industry presents a threat to the firm. This is because competing firms may develop new products which act as substitutes for the firm’s products.
HP faces intense competition from other firms such as Dell and IBM. As a result, it has to be continuously enterprising to survive the competition. Political instabilities in some of the countries where HP operates may lead the firm to incur substantial losses.
Using relevant frameworks, conduct an internal analysis of HP. Conclude the main strengths and weaknesses of HP derived from the above analysis.
To understand the operations of HP, value chain analysis is used.
Value chain analyses
Value chain analysis was developed by Michael Porter (Wit & Meyer, 2004, para. 4). It entails the evaluation of all the activities undertaken by a firm to ensure that it offers its customers high-quality products and services (Sekhar, 2009, p.115). Through the utilization of a value chain analysis, a firm’s management team can be able to identify internal areas which can contribute towards the firm attaining a sustainable competitive advantage. In its operation, the activities of HP can be subdivided into two main categories which include primary and support activities. The primary activities are mainly related to production. On the other hand, the support activities provide the firm with the background necessary for the operation of a firm.
Inbound activities
To ensure that its products and services are of high quality, HP has developed a comprehensive criterion for procuring its raw materials. This has been achieved through the development of an inventory control mechanism (Johnson, Scholes & Whittington, 2008). By automating its inventory process, HP can control its material usage. For example, the firm can be able to replenish its stock in time.
Operations
To ensure that the firm attains a high competitive advantage, HP has a research and development department whose role is to ensure that the firm produces products that are in line with the market demand. This arises from the fact that the research and development department can undertake effective product innovation.
Outbound logistics
These entail the various activities which are undertaken in the process of ensuring that the finished products are effectively distributed. To be effective in distributing its products and services to the market, HP has established several outlets in its market. Also, the firm has entered into a contract with firms that deal with computer products to ensure that they carry HP’s products. In line with this distribution strategy, HP enhanced its distribution strategy by ensuring that its partners access its entire product portfolio (ITP.net, 2008, para. 1). Considering the growth in information communication technology, HP has incorporated the concept of e-commerce. As a result, it is possible to order HP products and services online.
Marketing and sales
These include the various activities undertaken to generate sales and to ensure that the customer is satisfied. To achieve this, HP has incorporated continuous product improvement. As a result, the firm can integrate new features to its products hence being able to meet changes in customer product requirements. Also, HP has developed a comprehensive portfolio of products and services to meet the customer’s demands. For example, the firm has ventured into the manufacture of smartphones (Hitt, Ireland &Hoskisson, 2009, p.90).
In its marketing efforts, HP has adopted the concept of Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC) (Plummer, 2007, p.23). This entails the use of traditional and emerging marketing communication methods (Clow & Baack, 2007, p. 21). For example, the firm undertakes advertising via various mediums such as television, radio, and outdoor advertising such as the use of billboards. Also, HP has integrated online advertising through various social networking tools such as Facebook, Twitter, MySpace, and YouTube (Puscas, 2010, para. 1).
Services
To ensure that its customers are satisfied, HP has incorporated the concept of after-sale service on its products and services. For example, the firm has instituted a 24hour online and phone service (Hewlett-Packard, 2009, p.2). These services are toll-free. Through the provision of these services, HP has been effective at providing technical support to its customers. Also, HP sells its products accompanied by a portfolio of warranty services.
Support services
In its operation, HP has an experienced human capital. The firm has a human resource base of 324, 600. The large size of the firm enables the firm to be effective in executing its tasks. HP ensures that its employees are satisfied to improve their productivity. The management team has developed a good rapport with the employees. This is achieved through the adoption of the ‘Management By Walking Around’ (MBWA) style ( Fombrun, Tichy & Devanna, 1999, p.224).HP has also instituted a quality assurance department to ensure effective procurement and production of high-quality products.
Main strengths and weaknesses
The firm has efficient research and development which enables it to undertake product development successfully. Its global presence contributes to its profitability by accessing a wide market. The firm has a highly talented workforce which enables HP to be efficient.
The firm’s financial stability depends on the global market and not only its domestic market. The firm depends on 3rd party suppliers. As a result, its revenue can be affected in the event of failing to manage its suppliers.
Based on the internal and external analysis, and synthesis of the SWOT summary derived from it, identify two key strategic issues that HP faced before acquiring Palm and explain thoroughly why you define them as the key issues.
For several years, HP had tried to venture into the telephone market without success. The firm’s management team intended to diversify its operation by manufacturing mobile phones. In its initial phase, HP introduced its mobile handset which was marketed under the brand name iPaq (Levy, 2010, para. 1). The product was purchased from Compaq. However, this brand did not succeed since a large number of consumers adhered to the Microsoft Windows Mobile Operating System.
Secondly, the consumers were not appealed by the new product. The resultant effect is that the product was not adopted by any carrier. According to Becker and Arnold (2010, p.40), the success of a mobile phone company is dependent on the wireless carriers who offer support services through the provision of a network. The ineffectiveness of iPaq made wireless carriers not to adopt the new mobile handset. The effectiveness of a product is vital in ensuring that it succeeds in the market. This is because it results in the customers experiencing a high level of satisfaction upon consuming the product which culminates in the development of brand loyalty.
Upon acquiring Palm, HP was able to venture into the mobile market segment successfully. This is because Palm was successful in innovating the mobile operating system. According to Levy (2010, para. 3), Palm’s webOS is regarded as a successful mobile handset.
Considering the intensity of competition in the diversified computer system industry, it is vital for a firm’s in this industry to develop a highly competitive advantage. One of the ways through which they can achieve this is by venturing into new market segments. According to Gholson and Schloegel (2006, p.13), venturing into new market segments can enable a firm to attain the desired growth. HP’s inability to venture into the mobile market segment before it acquires Palm means that its growth potential was limited.
Using relevant frameworks (e.g. Ansoff) identify which development strategy HP used in the action of acquiring Palm and evaluate it using the SFA tool. Suggest another alternative option you think that HP can adopt to deal with its key strategic issues and again use SFA to evaluate it.
Several generic strategies can be used to understand development strategies. In its operation, HP is committed to becoming the leader in computer technologies. To achieve this, the HP management team decided to acquire Palm to develop its mobile handset.
Development strategy in the case of HP
By acquiring Palm, HP adopted a diversification strategy. Diversification strategy is considered to be a high-risk high-return development strategy (Raynor & Bower, 2001, p.93). This arises from the fact that the firm may not have the core competencies necessary to succeed in the new market segment. As illustrated in the Ansoff matrix below, the diversification strategy entails a firm expanding its operation by venturing into new market segments. This is achieved through the development of a new product. The product is intended to be marketed to new customers. By acquiring Palm, HP was able to diversify its operations by entering into the mobile telephony market. Initially, HP did not have experience in the mobile telephone market.
Suitability
The decision to acquire Palm was suitable considering the changes in the external business environment. The intensity of competition within the industry requires firms in this industry to develop their competitive edge. One of the ways through which this can be achieved is by diversifying their product and services offering.
Feasibility
Also, the decision is feasible since HP has a high competitive advantage in computer technology. Over the years, HP has been effective in developing computer technology. By acquiring Palm, HP will be able to integrate its computer technologies in the mobile phone thus enabling the consumers to attain a unique experience.
Acceptability
There is a high probability of the decision to acquire HP being accepted by the firm’s shareholders. This is because the acquisition will boost the firm’s effort to introduce a mobile phone. Also, the shareholders will accept the decision since there is a high probability of the firm increasing its profitability.
Currently, society is undergoing a social change in consumption. Most individuals are integrating e-commerce into their consumption patterns (Kazmi, 2008, p.34). By acquiring Palm, HP will be able to offer its customers ease of access to the internet through their mobile phones (Information Gatekeepers, n.d, p.8). This indicates a high probability of the firm’s product being accepted in the market.
Alternative suggestions
HP could have undertaken a joint venture with Palm. A joint venture entails a contractual agreement between two parties to undertake a certain project (Lorange & Contractor, 2002). The venture between Palm and HP would aim to develop the new mobile handset. In their new partnership, both Palm and HP would have to contribute towards the development of the new product according to their capabilities.
According to Reuer (2004), a successful joint venture can lead to a firm achieving its intended growth. The joint venture would contribute towards HP succeeding in its effort to venture into the mobile market. This is because Palm has developed sufficient knowledge about the mobile market. On the other hand, Palm would benefit by utilizing HP’s effectiveness in marketing. This means that both firms would benefit from sharing skills and experience.
Suitability
The suitability of the joint venture lies in the fact that both firms have developed their core competencies. For example, HP can enhance the development of mobile handsets by improving its features through the incorporation of computer technology. This will enable the firm to benefit from the increase in demand for smartphones.
Feasibility
HP has a certain amount of knowledge regarding the development of mobile handsets. This means that it can enhance its skills by acquiring Palm. Over the years, Palm has developed its competence in the development of mobile phone software. The acquisition will lead to the attainment of the intended synergy.
Acceptability
The decision would be endorsed by the stakeholders since there are associated benefits. For example, shareholders would benefit through an increment in the firm’s profitability which translates into higher returns. Also, the degree of risk involved is minimal. This is because both firms will contribute their technological skills.
Identify the key external and internal stakeholders of HP. Discuss how the power of the key stakeholders might influence the implementation of HP’s acquisition strategy.
Internal and external stakeholders
According to Hill and Jones (2010, p. 347), a firm has a wide range of stakeholders who include individuals and groups which have an interest in the operation of the firm. HP is composed of several internal stakeholders who include the employees, managers, board members, and shareholders. Similarly, the firm has a wide range of external shareholders. These include the general public, customers, unions, suppliers, creditors, the government, and other regulatory agencies.
To understand the stakeholders’ impact on the implementation strategy, the power/interest matrix has been used.
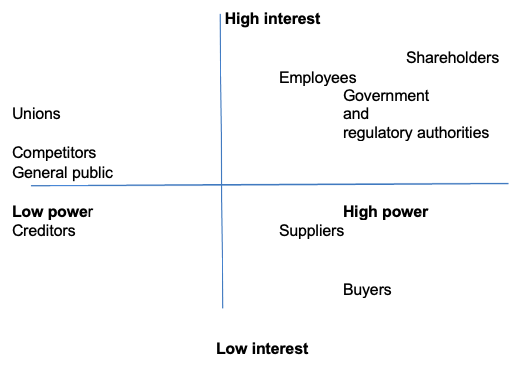
From the position map above, shareholders, employees, the government, and regulatory agencies are categorized as the stakeholders who have the most interest and power over the operation of the firm. Unions, competitors, and the general public are categorized to have low power but high interests. Creditors such as capital providers are categorized to have low power and low interest. On the other hand, suppliers and buyers have high power over the operation of the firm but low interest.
Ways in which key stakeholders may influence the implementation of HP’s acquisition strategy
HP may face a challenge in its effort to implement its acquisition strategy. One of the major sources of the challenge is the employees. The employees may perceive the acquisition as a threat to their job security (O’Leornard, 2004, p.3). For example, some of them may have a perception that the firm will downsize by laying off some of its employees. Also, HP may face a challenge in implementing the strategy due to the existence of cultural differences between Palm and HP. According to Ungson and Wong (2007), cultural differences may culminate in internal conflicts between the employees leading to a decline in their productivity.
HP creditors may demand that the firm pay off its debts before acquiring Palm. This is because they understand that acquisition involves a substantial amount of money. Also, the government may restrict the acquisition process until both parties have fulfilled stipulated requirements.
Despite these challenges, the shareholders and customers may support HP’s acquisition process. Through the acquisition, the firm will be able to achieve its wealth maximization objective which is the shareholders’ desire. On the other hand, the acquisition will result in the firm being more efficient. This will further enhance its ability to offer diverse and high-quality products and services. Also, the acquisition may result in the firm being more cost-effective. The resultant effect is that the firm will be effective in its pricing.
Conclusion and recommendation
From the analysis, HP has been successful in its domestic and international markets. However, its operation is affected by changes in the external environment. Some of the main challenges which the firm faces include political and social-cultural differences, changes in the global economy, and the high rate of technological innovation. Considering these changes, it is paramount for HP to undertake continuous market research to identify the changes in the external environment. As a result, it will be possible for the firm to formulate effective strategies to deal with environmental changes. The firm has also developed internal strengths through effective organization of its operations. HP should use these strengths to enhance its competitive advantage.
Reference List
Becker, M. & Arnold, J., 2010. Mobile marketing dummies. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Clow, K. & Baack, D., 2007. Integrated advertising, promotion, and marketing communication. New York: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Fombrun, C., Tichy, N. & Devanna, M., 1999. Strategic human resource management. New York: Wiley.
Gholson, N. & Schloegel, M., 2006. Driving growth and shareholder value: the distribution value map. London: Oxford Press.
Hewlett-Packard. 2009. HP post warranty care pack services for imaging and printing. New York: Hewlett-Packard.
Hill, C. & Jones, G., 2010. Strategic management theory: an integrated approach. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Hitt, M., Ireland, & Hoskisson, R., 2009. Strategic management: competitiveness and globalization; concepts and cases. Mason, OH: South-Western.
Hornbeck, J., 2007. Mercosur: evolution and implication for US trade policy. New York: CRS Report for Congress.
Hyers, J., Spooner, J. & Gottheil, E., 2010. Palm gives HP an edge in smartphones, tablets. Web.
Johnson, G, Scholes, K. & Whittington, R., 2008. Exploring corporate strategy. text and cases. London: Prentice Hall.
Information Gatekeepers.n.d. The mobile internet. New York: Mobile Internet.
ITP.net. 2008. HP enhances distribution power with broadline strategy. Web.
Kazmi, A., 2008. Strategic management and business policy. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill Education.
Levy, C., 2010. Actual analysis: HP buys Palm and the earth does move. Web.
Lorange, P. & Contractor, F., 2002. Cooperative strategies and alliances in international business. New York: Pergamon.
Mobile Tech News. 2009. Worldwide mobile shipment decline 15.8% in first quarter. Web.
Marchand, D., 2000. Competing with information. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Mouncey, P., 2007. Market research best practice: 30 vision for the future. New York: Wiley.
O’Leornard, K., 2004. HP case study: flexible solutions for multicultural learners. Web.
Packard, D., 2006. The HP way; how bill Hewlett and I built our company. New York: Collins Business.
Plummer, J., 2007. The online advertising playbook: proven strategies and tested tactics from the advertising research foundation. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Puscas, O., 2010. IMC case study Hewlett-Packard and integrated marketing communication. Web.
Raynor, M.E. & Bower, J., 2001. Lead from the Centre: How to Manager Diverse Businesses. Harvard Business Review. Vol. 80, No 5, pp: 93-100. New York: Harvard University.
Reuer, J., 2004. Strategic alliances: theory and evidence. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Salvatore, D., 2006. Managerial economics in a global economy. New York: Oxford University Press.
Sekhar, S., 2009. Business policy and strategic management. London: IK international Publisher.
Shreshtha, A., 2010. Pest analysis on Hewlett-Packard. Web.
Ungson, G. & Wong, Y., 2007. Global strategic management. Armonk, N.Y: M.E Sharpe.
Wit, B. & Meyer., 2004. Strategy: process, content, context; an international perspective. New York: South-Western College.