Need an analysis of the marketing environment Hyundai Motor Company operates? Read this essay! Learn the secret of Hyundai business strategy that made the company so successful. The Hyundai strategy includes an environmental policy that meets modern sustainability and technological innovation challenges. Want to know more? Keep reading!
Overview of the Company
Hyundai Motor Company (2011) pointed out that the company was founded in 1967 and launched Pony in 1976 as the first automobile of Korea, which has exported to Ecuador in the same year. In 1983 and 1985, the company started its operation in Canada and the USA respectively, In 2009 the company has explored its entry all most all over the world with sales of 2 million units of vehicles and placed at 60th among the to hundred companies of the world.
The management philosophy of the company has aligned with a boundless sense of accountability to recognize all possibilities with respect to humanity and to uphold its core values pointed to the customer, challenges, partnership, and people and globalization to rank at the top of auto producers. Under the global financial crisis, the company has evidenced a remarkable growth of with a brand value of US$ 5 billion, from 2010; the company is going under serious challenge of sustainability for which the company needs to align with a new strategy.
Hyundai Business Strategy: Vision
Hyundai’s vision is to turn into an esteemed international corporation by achieving some short-term visions as shown below:
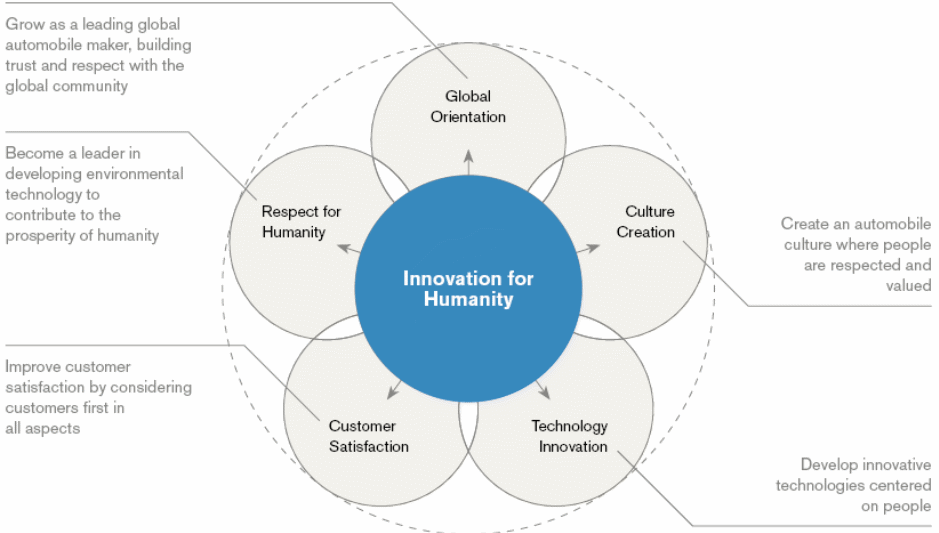
Marketing Environment: Hyundai Risks and Challenges
Hyundai Motor Company (2011) pointed out that the company identified 2010, as a year of new challenges to respond to the environmental sustainability and to produce eco-friendly vehicles, while in 2011; the company has aligned to it all plants to develop the company as an organic company with appropriate emphasis to the innovation of new environmental-friendly vehicles.
To address such challenges, the need to have competitive superiority of technological innovation, essential to strengthen management skills, and enhanced investment on green technology to encounter with the competitors both in-home and abroad. Meanwhile, in the domestic market, the company has been striving with competitors while the emerging market as India has serious risks of both eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions for automobiles. On the other hand, though it was spoken that the global financial crisis has already over, but the US market trend demonstrates that it is going to keep serious shocks in the overall market for which Hyundai Motor Company need to reengineer its strategies to gain a competitive advantage from the diversified strategy.
GLC (2009) identified that the company has been suffering from tremendous risk of accounting fraud and added that in 2007, the CEO Mr. Chung evidenced to engaged with a personal fraud of KRW 90 billion from the company and more KRW 360 billion cheating through earning management, for which the Seoul District Court has sentenced him for three years imprisonment. To overcome such risks the Hyundai Motor Company needed to have a particular accounting standard to protect the unholy alliance of the management and accountant and auditors.
Marketing Environment: Hyundai External Environment Analysis
PEST Analysis of Hyundai Motors
Political factors
Although the political environment in South Korea is quite business-friendly that do not cause any major problem to the company, the political instabilities and unfriendly governmental policies in other countries of its operations is a major problem for Hyundai Motors.
Foreign direct investment policies of foreign governments, unfriendly governmental attitude in foreign countries like India, and the recent unsteady atmosphere in the Middle East are putting pessimistic impact on the company; conversely, range of governmental incentives, e.g. tax-exclusion and tax-credit of automobile pool lanes, and so on are putting optimistic impact on the global automobile giant. However, the policymakers of Hyundai are continuously putting their efforts to cope up with the hostile global political environment.
Economic factors
The global automobile industry could be influenced by alterations in demand, increasing inflation rates, uneven interest rates, fluctuating exchange rates, rising taxation rates, and more significantly, by global financial crises, which has already contributed to lower expansion rates of the global automobile industry. According to a report of The Financial Times, the impact of the global financial crisis over Hyundai, however, was not as harsh as it was over the competitors like BMW or General Motors.
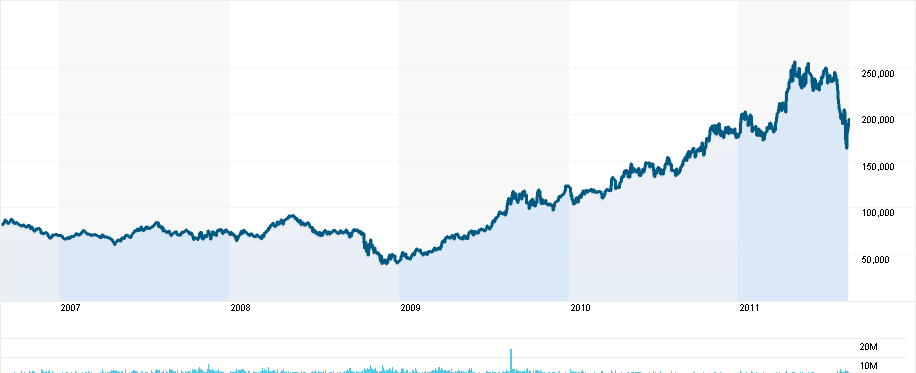
Most importantly, in that report, Simon (2010) went on to argue that the market share of this automobile company in the United States raised by 1.2 percent – whilst the growth of share was three percent in 2008, surprisingly, it rose to 4.2 percent in 2009.
Moreover, when most of its competitors were observing continuous falling profits and decrease in demand, which forced them to make job cuts and factory close-downs, its sales in the United States expanded by 8 percent; also, the North American squirt assisted Hyundai to observe $832 million profit in 3rd quarter of 2009 (Ihlwan, 2009). The basic chart of Hyundai motors shows that although there was a slight decrease in profits, it was not as extreme as other industry giants’ harsh experiences. Moreover, by the end of 2009, the company began to see a gradual rise in the share prices:
Socio-cultural factors
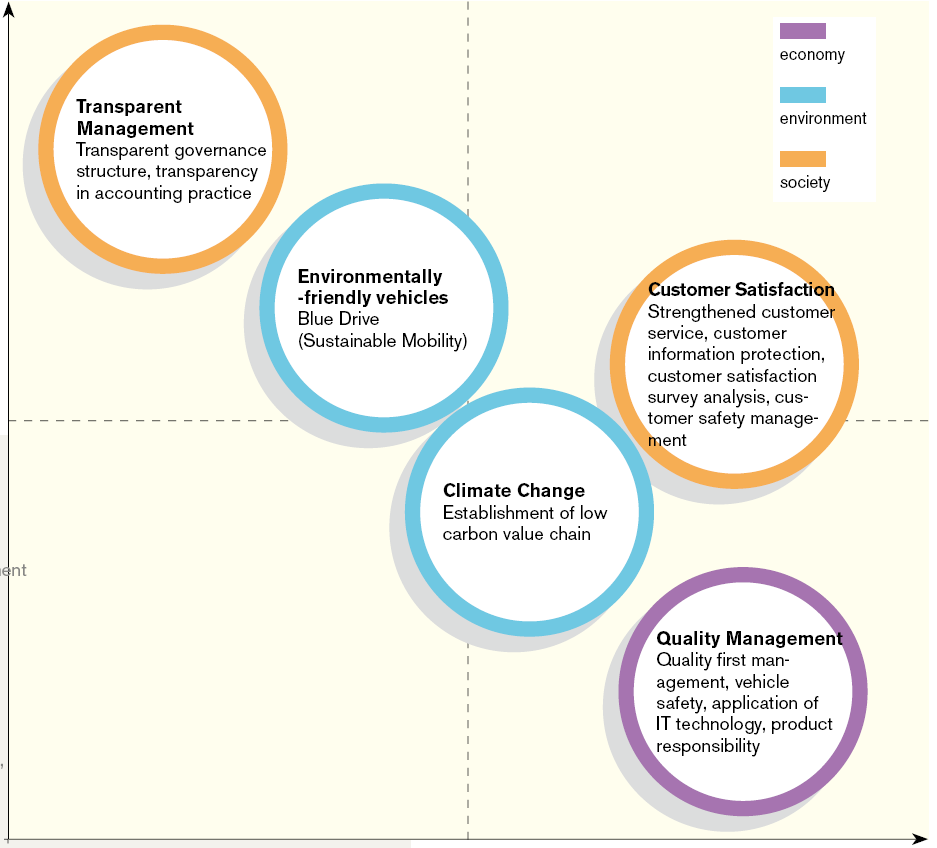
Hyundai is much concerned about its social responsibilities; its sustainability report suggests that it is endorsing moral management-practices as a vital way of boosting stakeholder value, permitting workers to take essential roles, and encouraging intelligibility amongst stakeholders; in 2001, it formed HMC Ethics-Charter, Employee Code of Conduct, and Guidelines for Ethical-Business Conduct to encouraging moral business-practices (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010). Hyundai is also undertaking environmentally sustainable projects. The figure below shows its socially responsible practices:
Hyundai also hopes to be socially responsible by lowering emissions:
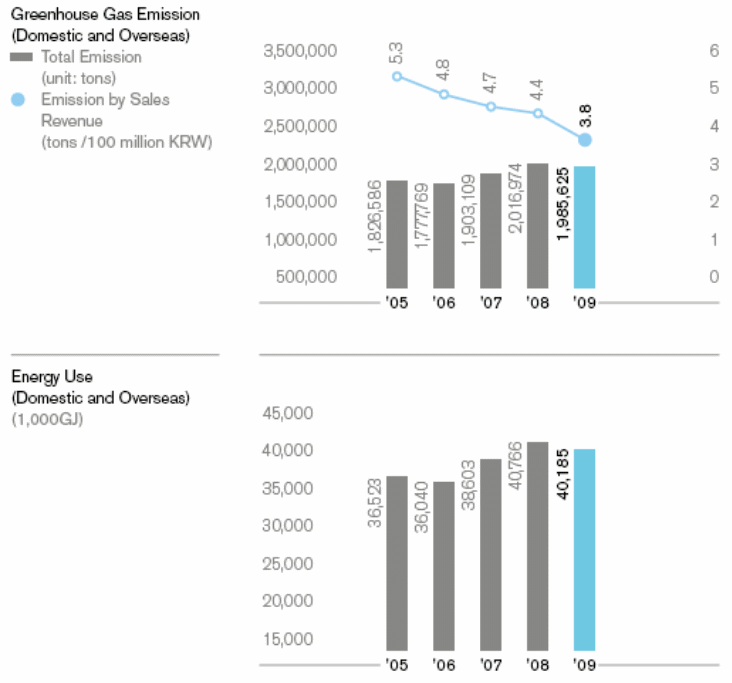
Technological factors
Hyundai carries out R&D with most modern technologies making vehicles that are low-emitting, unique, and globally competitive focusing on foremost technologies that address ecological concerns; it is developing ecologically friendly hybrid-cars, electric-automobiles, and hydrogen fuel-cell-vehicles; it launched the world’s first LPG-Hybrid-vehicle, Elantra LPI Hybrid, that has made with proprietary-technologies; in 2011 it will launch Sonata-Hybrid (Hyundai Motor Company, 2010). The figure below shows how Sonata Hybrid is technologically more advanced than previous models in terms of carbon emissions:
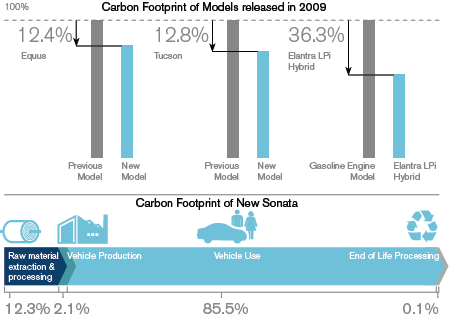
Hyundai Business Strategy Analysis: Porter’s Five Forces Model
Threats from new entrants
Threats from new entrants are quite low in the industry because of various barriers to enter the market. New entrants more often lack adequate finances, proficiency, satisfactory knowledge about specialized car manufacturing methods, and skilled personnel. Furthermore, once established, it gets hard for the new players to sustain in the highly competitive business environment and to join in price competitions with the industry giants. Besides, the legal barriers and regulations pose adverse impacts for newcomers as well. In recent times, Hyundai motors are facing very few threats from the emerging markets under its worldwide operations from some new entrants; this is especially from the densely populated markets like China and India – the company is facing this threat from those new foreign car producers because of governmental preferences to safeguard infant industries and the incentives provided to them.
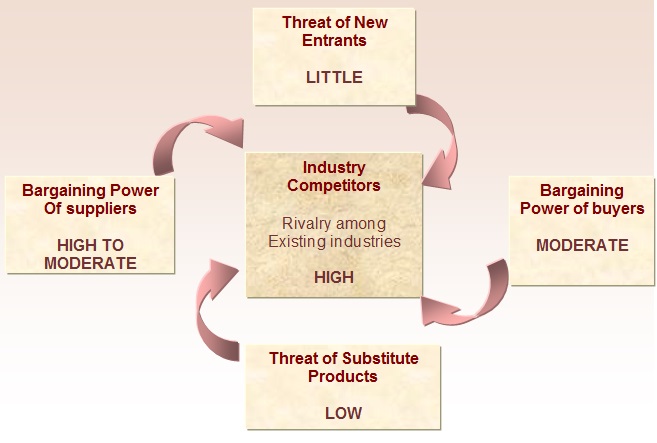
Bargaining power of suppliers
The bargaining powers of suppliers in this industry are generally low because many suppliers are present in the market. However, car manufacturing suppliers are generally raw materials companies delivering steel, aluminum, fuel, rubber, etc; in different regions, power of these suppliers varies, for example, in China, bargaining power of domestic vendors vary regarding quality and price; moreover, Lithium Lon Battery Manufacturers are major suppliers group of the company for delivering technical components for producing hybrid cars.
Bargaining power of buyers
Due to the presence of innumerable automobile producers, the switching costs of the buyers are relatively higher than any other industry sector; moreover, customer loyalty is also not significantly noticeable. Companies like Hyundai, Toyota, Nissan, Honda, Fiat, etc offer the cars comparatively at the same prices for which it gets easier for the customers to select their desired piece of product from any one of them. However, the bargaining power of the customers seem to diminish when it comes to price considerations of cars of companies like BMW or Mercedes as their prices are quite higher than others. Therefore, the preferences of the middle-income earners remain with companies like Hyundai.
Threats of substitute products
Threats of substitute products are extremely high. Apart from different motor vehicles from other direct competitors, Hyundai has to face stiff competition from some other alternative transportations like public transports, buses, railways, bicycles, etc; these types of substitutes are often chosen by people because of their easy accessibility and cheapness.
Rivalry among existing firms
As noted earlier, the global automotive industry is fully saturated featured by several manufacturers along with their numerous offerings; Hyundai has also to face many smaller and larger competitors at both domestic and global levels; the most potential competitors of the company are General Motors, Honda, Ford, Mitsubishi, Land Rover, and BMW, etc.
Hyundai Business Strategy: Competitive Analysis
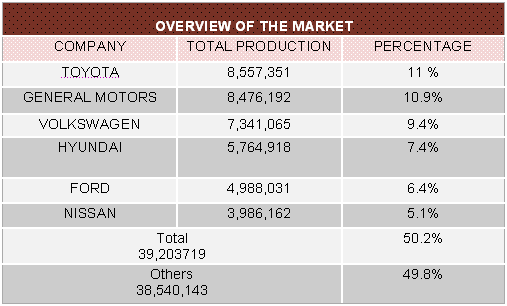
The global automotive industry has featured by numerous giant players causing Hyundai to face intense competitive pressures. The figure below outlines the major competitors of Hyundai in the global context:
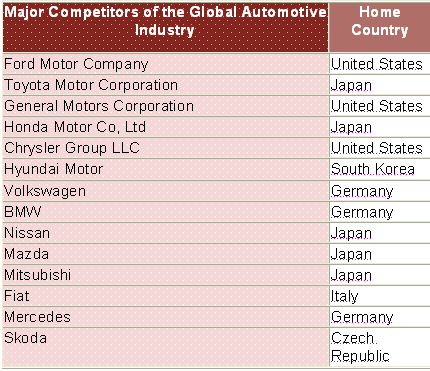
It is noticeable from the competitive analysis below that Toyota holds the first position in the global context with 11% market share whilst Hyundai is in the fourth position with a 7.4% share:
Marketing Environment: Hyundai Internal Environment Analysis
Resources and Capabilities
Following are the main resources and capabilities of the Hyundai Motor Company –
Figure 10: resources and capabilities of Hyundai. Source: Hyundai Motor Company (2011).

McKinsey’s 7s Framework for Hyundai
In the light of Thenmozhi (2011) and Lee et al. (2003) literature, McKenzies 7s model is an important approach to analysis internal environment of an organization and here Hyundai Motor Company is involved in the following issues.
Global Strategies of Hyundai: Organizational Structure, Policy, & Planning
- Organizational Structure
- Policy and Planning Systems
- Employee Skills
- Staff’s Profile
- Core Communication Style
- Shared Value
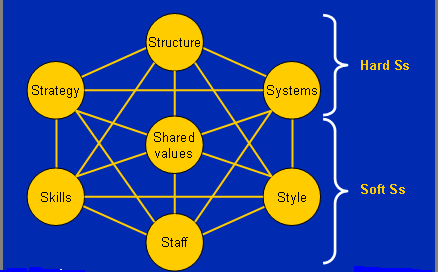
From previously mentioned model, first three Ss are referred as hard whereas rest of four Ss are soft though global market analysis revealed that, Hyundai is positioned in the niche market where their global strategies are considered three major facts namely –
- identify and analyze to penetrate in the global profitable markets
- crafting market penetration as well as market development strategies and
- Being a market follower key concentration on rapid product innovation
The organizational structure of Hyundai is principally involved in the bureaucratic approach where the entire organizational hierarchy positioned in numerous levels with diverse job responsibility and here chief limitation of the firm is slower decision-making trends in the automotive industry.
On the other hand, corporate skills of Hyundai are included multidimensional skills of aggregate employee that patronized enhance organizational performances through production, marketing, sales, and market development; however, staffs are featured with multidimensional skills, dynamic, loyal, well-motivated, proficient to teamwork as well as individual success plan. Style represents a downward communication approach that delivered diverse hierarchical influences according to managerial responsibility; however, through shared valued, Hyundai focuses on competitive spirits through diligence as well as thrust for climbing peak of the industry.
Hyundai Business Strategy Analysis: VIRO Framework
Another internal analysis tool that focuses on four aspects valuable, rarity, imitable and organized. All of the four attributes are coherently attached to the status of technology, human resource management (HRM) and the supply chain management (SCM).
Inconsistent with the Hyundai’s profile, with a severe crisis during 2010 the company has confirmed the sale of 3,610,000 vehicles attributed through environmentally friendly transmission technology or eco fondly technologies; thus, aggregate bends value of Hyundai is now USD 5.0 billion and ranked sixty-five among top hundred global automotive firms; moreover, with 80,000 multidimensional skilled and dedicated employees, in assessing cordial consumer service, positioned top of VDS (Vehicle Dependability Survey) for the third time in this year.
Meanwhile, SCM status revealed that Hyundai principally conducts cross-functional approach for manufacture and sale of cars, moreover, their distribution channel has paid key concentrate on B2B (Business to Business) rather than B2C (Business to Consumer) though in Asian region can’t structured competitive manufacturing price compare to China and India. For more details following is the table of VIRO status (Hyundai Motor Company 2011).
Table 1: Hyundai VIRO Status. Source: Self Generated.
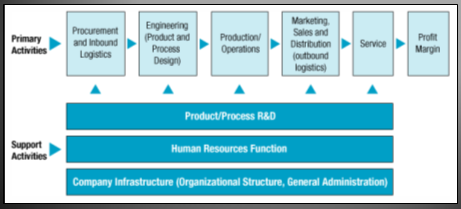
Value Chain
Hyundai formed their value chain system through assembling two activities as shown in following figure primary activities and secondary activities where primary acts are included production, marketing, sales, and distribution and after-sales service, whereas secondary acts performed procuring internal logistic support, managing financial resources, HRM, technology development through R&D (Research and Development). (Thomson and Strickland 2003)
Evaluation of strategic Fit
It would consider SWOT analysis and culture of the company –
Hyundai Business Strategy: SWOT Analysis

Strengths
- Hyundai was the major guarantor of US-Super-Bowl and it backed 2009-FIFA Confederations-Cup
- It is numerous reward winner including the Genesis-award
- It won the title of the “Best Corporation” for client-satisfaction in Chinese market
- Its overseas sells at Africa went over 1m vehicles
- It got the first position in New-Vehicle-Launch-Index.
Weaknesses
- It has not penetrated in some of the prospective and populated third world Asian countries
- It lacks sufficient production of trucks or other forms of transports.
Opportunities
- The strategy makers have decided to extend the product line to include various types of vehicles that can generate money
- The extension of the business in other prospective countries would contribute to higher profit margins.
Threats
- The rival firms could easily catch up with Hyundai’s strategies and beat the company if it fails to come up with something new
- Global trade laws and regulations is also a big threat to the business.
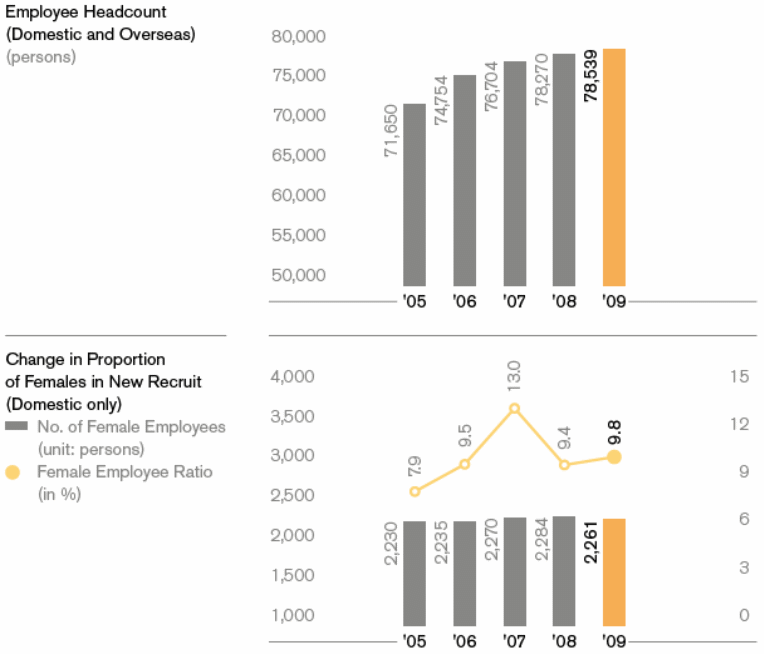
Culture
The organizational culture of Hyundai has based on the principle of establishing equal opportunities in every arena. Even in the case of recruiting workers, it tries to ensure equal opportunities for male and female:
Marketing Environment: Hyundai Strategic Directions
The purpose of this part is to find out a suitable strategic solution for the future implementation and recommend a strategy considering the score of suitability, acceptability, and feasibility. Explanation of Scale would be evaluated by giving a score between 1 and 5 for each condition, where 1 is very unfavorable and 5 being highly favorable –
Strategic Direction 1: Diversification Strategy
Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson (2001) argued that diversification means entering a new market with new products, which help to reduce risks, increase profitability with return on investment, and sustain in the competitive market. According to the sustainability report of Hyundai 2011, it has some commitment to the stakeholders to introduce new products to meet its strategic goal. Also, the company has to face risks in the US market due to the impact of the recent financial crisis and the business some existing market is not going well because of some external and internal factors. In this context, it is essential to consider diversification strategy to expand its business in a new market with new products and it can follow both related and unrelated diversification strategy considering market trends, the demand of this product in the new market, the response of the buyers, production cost, technologies facilities of new market and so on. However, this report would suggest introducing a Tyre manufacturing plant as Hyundai has enough financial resources and capabilities to diversify its business; however, the following table analyzes this issue considering some evaluation criteria –
Table 2: Strategic option 1. Source: Self-generated.
Strategic Direction 2: Restructuring Pricing Strategy
Kotler and Keller (2008) stated that the company should consider a market-oriented pricing strategy in the crisis period though there are different types of effective pricing strategies such as competition-based pricing and target pricing. However, Hyundai offers competitive and affordable prices for few models particularly environmentally friendly products but many luxury models have designed only considering the purchasing power of higher-class people. Here, it should important to mention that many large companies, such as General Motors and BMW have lost their market share in the global due to excessive price of the products; as a result, the marketer of Hyundai should restructure its pricing strategy considering the external business environment, global economic downturn, competitor’s position and buyer behavior of the national and international market.
Table 3: Strategic option 2. Source: Self-generated.
Strategic Direction 3: Joint Venture and Acquisition strategy
Hitt, Ireland & Hoskisson (2001) pointed out that joint venture is one of the most effective foreign entry strategies and expand the business in the global market; however, it would help to develop corporate strength, share management skills by the partners, influence government in legal issues, and so on. However, the Hyundai Group can achieve competitive advantages by using a merger or joint venture with large automobiles to share their assets and technologies to expand the business in the global market.
Table 4: Strategic option 3. Source: Self-generated.
Recommendation of One Specific Strategic Direction
This report recommended that Strategic Direction 1- Diversification Strategy is the best strategic solution by the evaluation criteria and appraisal methods. However, this report would help the management to take the future initiative as it scores the evaluating criteria such as builds brand awareness, aligns with the vision, competition, financial risks, market demand creating a loyal customer base and so on to find out most appropriate strategy and it suggest diversification into Tyre Manufacturing Plant as it gained highest score. At the same time, Mergers and acquisition is now a suitable and acceptable strategy but pricing strategy is also a good strategic direction for Hyundai as it achieved second-highest score but it is subject to huge financial risk, for instance, manufacturing and operating costs, economic downturn, price of raw materials and so on.
Hyundai Business Strategy: SFA Analysis
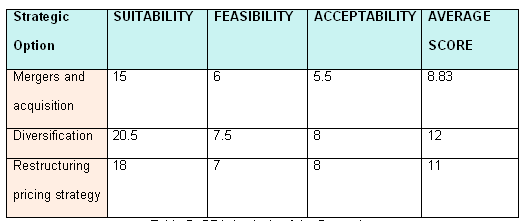
Suitability
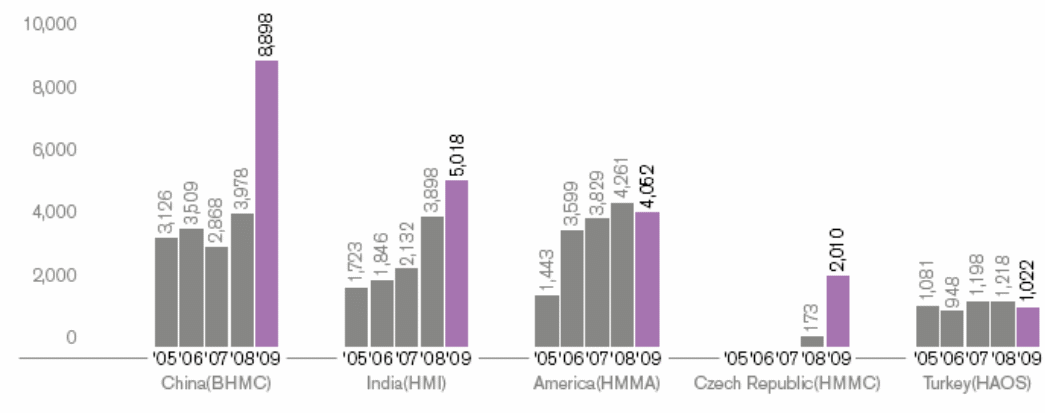
- According to the article “Dynamics of Strategy”, Hyundai holds the fourth position in the global market with a 7.4% market share, therefore, it should require to expand its operation in new markets due to achieve market-leading position. As a result, diversification into Tyre Manufacturing Plant is a perfect strategy for Hyundai Motor Company to penetrate new foreign markets; however, the following figure shows the sales position of four major global markets, which encourage the suggested strategy.
- Also, the direction matches with the long-term strategic goal and concentrated more on the core competencies, and existing resource and capabilities, particularly technology, HR and financial resource;
- It would assist the company to increase profits after two to three years.
Feasibility
- Short and long-term growth rate: The implementation of this project would help Hyundai to achieve a significant growth rate more in the long-term than that of the short-term. In the short-term, it would take some time for the business to mitigate the expenditure on the project. In a longer period, this project should contribute significantly to the expansion.
- Financial risk: It is unlikely that there will be failure in the project causing financial losses because Hyundai has enough finance to afford the project and cope up quickly; notably, its net profit in 2010 was about US $7b with $3.5b in 2009; also, it has large and experienced workforce internationally to accomplish the project efficiently. The R&D experts and most modern technologies will further ensure the project’s success.
Acceptability
The implementation of this project would gratify and reconcile the stakeholders’ altering demands making it quite acceptable to everyone.
Implementation and Control
The board of directors of Hyundai would have close observance over the successful accomplishment of the project by 2013. The ultimate control and management powers of the project would rest with the board of directors. They will oversee every single step before the organization of the project to ensure if proper quality criteria have maintained.
Financial Plan to establish Tire Manufacturing Plant
This purpose of this plan to gather an idea about total cost and profit to expand in the global market and it would consider the following factors –
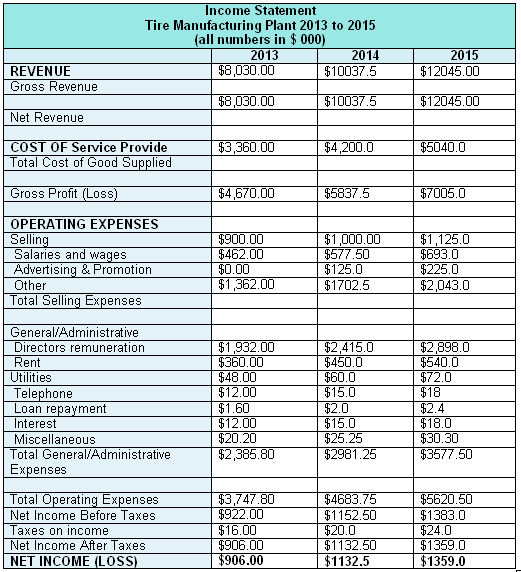
Projected Profit and Loss
This report would provide three Years Income Statement for Tire Manufacturing Plant to measure its prospect –
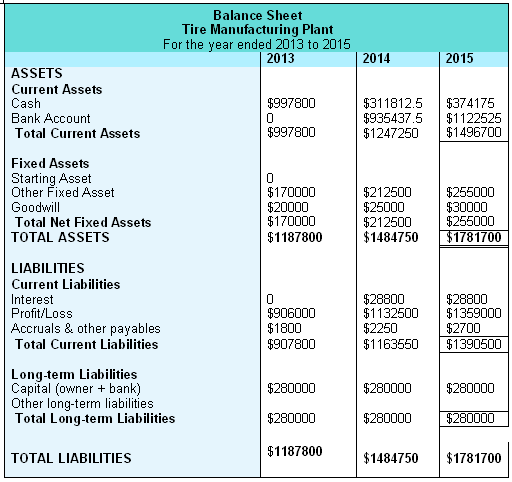
Projected Balance Sheet
The financial management team also provides a pro- forma balance sheet of XYZ New Store for the year 2011 to 2013.
Pro-forma Cash Flow
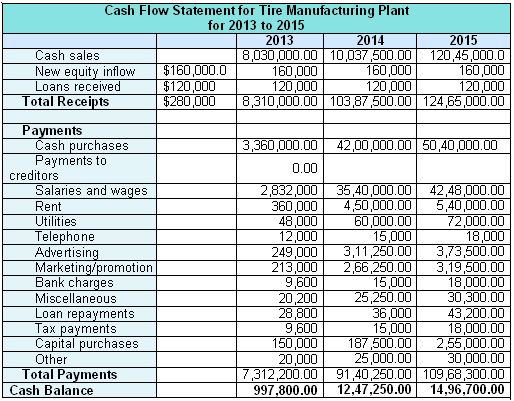
Gantt chart
The subsequent Gantt chart shows the milestone plan for next 5 years –
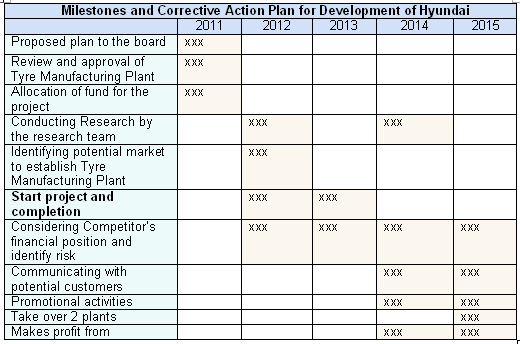
Reference List
Cable News Network (2011) Hyundai Motor.
David, F. (2008) Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. 12th ed. London: Prentice Hall.
GLC (2009) Hyundai Motor Company Ltd: Proxy Paper. Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. Singapore: South- Western Thosmson Learning.
Hyundai Motor Company (2010) The Road To Sustainability: Hyundai Motor Company 2010 Sustainability Report. Web.
Hyundai Motor Company (2010) Worldwide Hyundai Motor. Web.
Hyundai Motor Company (2011) Hyundai Corporate Message. Web.
Hyundai Motor Company (2011) Hyundai History. Web.
Hyundai Motor Company (2011) Hyundai Innovation – R&D Vision and Strategy. Web.
Ihlwan, M. (2009) Hyundai Posts Record Earnings amid Recession. Web.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2008) Marketing management. 13th ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Lee, R. et al. (2003) Hyundai Motor Company – Beijing Automotive Joint Venture. Web.
Reuters (2011) Chart: Hyundai Motor Co (005380.KS).
Simon, B. (2010) Hyundai benefits from US recession.
Thenmozhi, M. (2011) Organisational Capability Analysis. Web.