Introduction
Southwest Brooklyn in New York City is home to the 400-bed inner-city community teaching hospital known as Lutheran Medical Center. The hospital started an initiative to significantly enhance its emergency department in response to its main goal. However, the lack of improvement in patient satisfaction clearly saddened the staff, but it did not perplex them. Patients had to wait longer for the beds because transferring people from the emergency department to an inpatient bed took longer since the amount of readily available hospital beds remained unchanged while patient traffic grew.
Therefore, healthcare organizations should address the issue of improving patient satisfaction, given the increasing wait times for hospital beds, by implementing other quality improvement measures. These measures can help identify the root causes of accidents, develop preventive measures, and improve patient safety. The objective of this quality improvement program is to identify and analyze the patient care process, offering some alternatives to the current QI plan. To achieve this, relevant process optimization tools and approaches will be used.
Current State Analysis
The present state analysis aims to offer a thorough knowledge of the existing process or system contributing to the issue. This will make it easier to identify the issue’s root cause and improvement opportunities. Currently, the patient discharge procedure is mostly manual and uses little technology. The nurse in charge of a patient’s care must physically complete a paper discharge summary form, which is then verified by the attending physician for correctness. Following approval, the patient gets a physical copy of the discharge statement and any relevant medications and follow-up appointment information.
To detect the problematic area, many performance measures may be employed, including the number of days a patient is admitted to the hospital before being released. A longer period of stay may indicate inefficiencies in the discharge process. The readmission rate is the percentage of patients readmitted to the hospital within a certain period after being released. A high readmission rate might suggest an issue with the treatment delivered or the discharge protocol.
A root cause analysis (RCA) may be performed to discover the fundamental reasons for an issue. RCA is a problem-solving method that seeks to determine an issue’s root causes to prevent it from recurring (Balakrishnan et al., 2019). The patient discharge procedure’s RCA may uncover various contributing elements, such as inconsistencies and inefficiencies that occur from the lack of defined protocols or procedures for this discharging process. The latter does not seem to be automatized, with just a little technology to digitalize and speed it up. Communication breakdowns among nurses, doctors, and other healthcare personnel participating in the discharge process may result in delays, errors, or insufficient information.
Solution Development
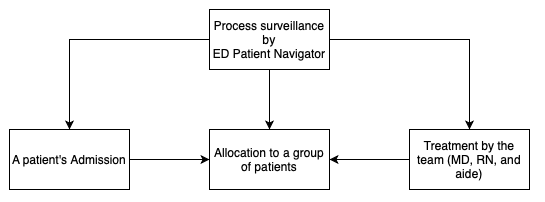
Potential solutions to the problem areas highlighted in the case study are to be created. To achieve this, it is essential to depict the organization’s current process of patient admission and treatment. As visible from the flowchart, the key position responsible for the whole process surveillance is the ED Patient Navigator (Diagram 1). They oversee the treatment measures conducted by the team consisting of an MD, RN, and aide. Moreover, the Navigator seems to control a number of other organizational aspects related to the mentioned process. Such an extent and amount of duties may lead to miscommunication and over-power of a single manager.
However, the indicators from the case show that through the years, patient flow and satisfaction have increased, although not reaching the desired level. Thus, the potential interventions are not to change the current system drastically but rather imply slight shifts within the scope of communication among the staff. It is essential to create treatments that are unique to the highlighted areas for development. These interventions should be evidence-based, realistic, and aligned with the aims and objectives of the organization.
To effectively address healthcare organization issues, it is crucial to prioritize the most suitable solutions based on predetermined evaluation criteria. The selected solutions must exhibit high levels of feasibility, impact, and sustainability. By selecting options that effectively address identified problem areas, the healthcare organization can enhance the quality of care they provide patients (Prato et al., 2019). To ensure the efficacy and longevity of the chosen solutions, it is essential to take a systematic approach that takes into account multiple factors.
Hence, referring to the root cause analysis, the following options for improvement may be identified. Firstly, it is to create standardized protocols and procedures for patient discharge, with clear roles and responsibilities for all parties involved. Secondly, it is important to increase the use of technology to automate and accelerate the discharge process, such as by using an electronic summary form and planning software. Thirdly, it is to improve communication and coordination among healthcare professionals involved in the discharge process, for example, via frequent team meetings or a communication tool.
Implementation Plan
A comprehensive set of actions must be developed to implement the selected solution successfully. The following steps can be taken to develop an implementation plan. Firstly, it is to compose the project team that will be responsible for the development of new communication tools and standards. This involves determining the project leaders, stakeholders, and subject matter experts accountable for implementing the solutions, as well as assigning duties and responsibilities to each team member.
Secondly, it is essential to define the implementation’s scope. This will ensure the project stays on track and the team works toward a common goal. Thirdly, it is determining the necessary assets, which implies specifying the personnel, instruments, and funding required for implementation. The team will ensure that all necessary resources are available before beginning the implementation procedure.
Fourth, the team will create an implementation schedule that includes significant milestones and due dates. This will guarantee that the team fulfills its objectives within the allotted time and that the project stays on course. Fifth, the stakeholders who must be kept informed about the implementation and develop a plan to do so will be determined. This should include routine progress reports and status updates. Sixth, it creates a training plan and identifies the individuals requiring training on the new system or procedure.
Finally, it is the determination of achievement metrics, which implies the definition of how the success of the implementation will be measured and develop success indicators. Moreover, prior to implementing the solutions on a large scale, they must be evaluated in a smaller setting (McDonald et al., 2018). Implementing the solutions on a larger scale will help identify any issues or problems.
Measurement and Reporting
Here, it seems reasonable to focus on determining and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented solutions in resolving the specified problem. The following aspects are to be covered: key performance indicators (KPIs) are precise measures used to assess the effectiveness of the suggested solutions. KPIs must be relevant, quantifiable, and linked to the project’s goals. Medication mistakes, patient satisfaction, and employee satisfaction are key performance indicators for the case study.
Furthermore, the strategy should state how often data will be gathered and who will be responsible for data analysis. Data for the intervention might be gathered via chart audits, questionnaires, and focus groups. Data should be gathered from various sources, including patient records, staff surveys, and patient satisfaction surveys. Based on data analysis, monitoring progress and modifying the implementation strategy are the required activities. The obtained information should be examined and utilized to track the success of the implementation strategy. If the statistics show that the implementation strategy is unsuccessful in resolving the stated problem, it should be changed.
The implementation outcomes should be communicated to stakeholders such as the healthcare organization’s leadership, staff, and patients. The data should be conveyed as soon as possible openly and straightforwardly. Following these processes will allow the healthcare organization to monitor and assess the effectiveness of the solutions and make appropriate modifications to improve patient care and management quality.
Any quality improvement effort requires strong leadership and change management. To guarantee the project’s success, a communication strategy must be established to keep stakeholders informed of the project’s goals and progress. This strategy should include what will be communicated, who will receive it, and how often progress will be reported, including key stakeholders to get their support and buy-in for the project. This may be achieved by including them in the project’s planning and execution, collecting their feedback and input, and resolving their concerns.
The teams of MDs, RNs, and aides should be responsible for collecting data related to the implementation of the project. Regular progress updates and a final report summarizing the project’s effect on the stated problem should be included. Any facts or statistics that support the project’s findings and conclusions should be provided as well.
Given the current HR structure of the hospital, the mentioned information should be provided to the ED Patient Navigator. They will track the progress and guide the teams for a reasonable and productive workflow. Leadership and change management methods may assist the healthcare organization’s quality improvement project in succeeding and promoting a culture of continuous improvement.
Conclusion and Possible Alterations
This quality improvement project aims to address the hospital’s issue of insignificant patient satisfaction. Such a state of affairs was due to inadequate and inconsistent communication among the personnel. Staff training, computerized reminders, and improved monitoring and responsibility were proposed answers. Based on feasibility, impact, and sustainability, staff training and greater monitoring and responsibility were the suggested options as well.
The implementation plan covers the aspects of staff interactions, equipment, and scheduling. Data gathering and analysis were planned to track the outlined KPIs. Data analysis should be used to monitor progress and adjust the implementation strategy. Leadership and change management tactics ensured solution acceptance.
Then, a communication strategy was created to educate stakeholders about the project’s goals and progress, and key stakeholders were engaged in gaining their support. Quality improvement. However, change resistance and accountability issues may plague the project. Hence, interventions should be reported and updated regularly to remain successful.
Nevertheless, if the indicators show the expected outcomes are not achieved, it will be necessary to arrange some alterations to the suggested measures. First, if patient satisfaction is not enhanced, the ED Patient Navigator should consider re-organizing the current nursing combined triage/fast-track model in terms of assigning a coordinator to each team. Second, if the communication is not improved, it will be reasonable to consider alternative tools used to resolve this issue.
References
Balakrishnan, K., Brenner, M. J., Gosbee, J. W., Schmalbach, C. E. (2019). Patient safety/quality improvement primer, part II: Prevention of harm through root cause analysis and action (RCA2). Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 161(6), 911–921.
McDonald, T. B., Van Niel, M., Gocke, H., Tarnow, D., Hatlie, M., Gallagher, T. H. (2018). Implementing communication and resolution programs: Lessons learned from the first 200 hospitals. Journal of Patient Safety and Risk Management, 23(2), 73–78.
Prato, L., Lindley, L., Boyles, M., Robinson, L., Abley, C. (2019). Empowerment, environment and person-centredcare: A qualitative study exploring the hospital experience for adults with cognitive impairment. Dementia. 2019;18(7-8), 2710–2730.