General description of the Marking Information System
Title
Marking Information System (MIS)
General description
The purpose of the MIS or Marking Information System is to help the firm to extract data specifications from the databases. For example, customer managers can create lists of customers giving preference to certain kinds of products or services. This MIS uses customers’ characteristics as primary or optional identifiers and extracts the corresponding entries from the databases, including them into the marked lists (Laurikaitis 2010, 11). The software will ease the managers’ work with different groups of customers, allowing them to use an individual approach to clients, predicting and satisfying their needs. Furthermore, it assists the firm in analyzing the outcomes, detecting weaknesses in the programs and creating effective solutions to them.
Users
- Customer information. This data covers personal information provided by the customers, including their contact information, personal preferences, overall purchases and the average price of the chosen products.
- Specification criteria. To extract the target information from the database, users need to choose the identifiers attributed to a particular category of entries. For instance, users may want to extract the information for users who have not made a single purchase for the chosen period of time or those who buy only discount and budget products or services.
- Analysis of the data. The extracted data should be systematized and arranged appropriately so that the users could draw certain conclusions and create effective solutions.
- Customer order. After the data is analyzed and certain measures are taken to eliminate the weaknesses, customers are expected to make more purchases, and the firm’s revenues are expected to grow.
- Customer satisfaction. This information is provided by customers. It can warn the customer managers on how often they can contact particular customers for them not to become too intrusive and annoying.
- Customer history. The information dealing with the customers’ reactions and purchases (or rejections to purchase) should be recorded and added to the customers’ purchase history so that the managers could take them into account when contacting the same customers next time.
Instance
One of the important advantages of using MIS at Domino’s Pizza is an opportunity to differentiate between different groups of customers and implement an individual approach to them. Informing customers on available special offers, managers can encourage them to make unplanned purchases. By extracting particular groups of customers from the database, managers would be able to make informed decisions and achieve customers’ satisfaction with the quality of provided services.
External Description of the information system
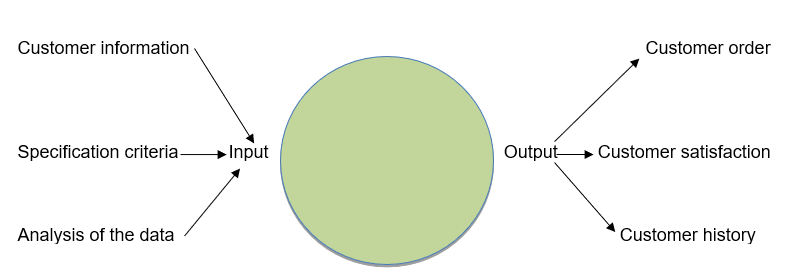
Inputs
- Customer information
- Specification criteria
- Analysis of the data
Output
- Customer order
- Customer satisfaction
- Customer history
Information processing
The system divides customer population into a number of groups, depending upon the variety of identifiers. Thus, the users of MIS can extract the information on a target group of customers and make informed decisions after analyzing this data.
Information stored
The information on the interaction outcomes is stored in the database. The customers’ responses and possible orders are recorded and can be used for future cooperation.
External view of the Order Entry System
An internal description of the Marking Information System
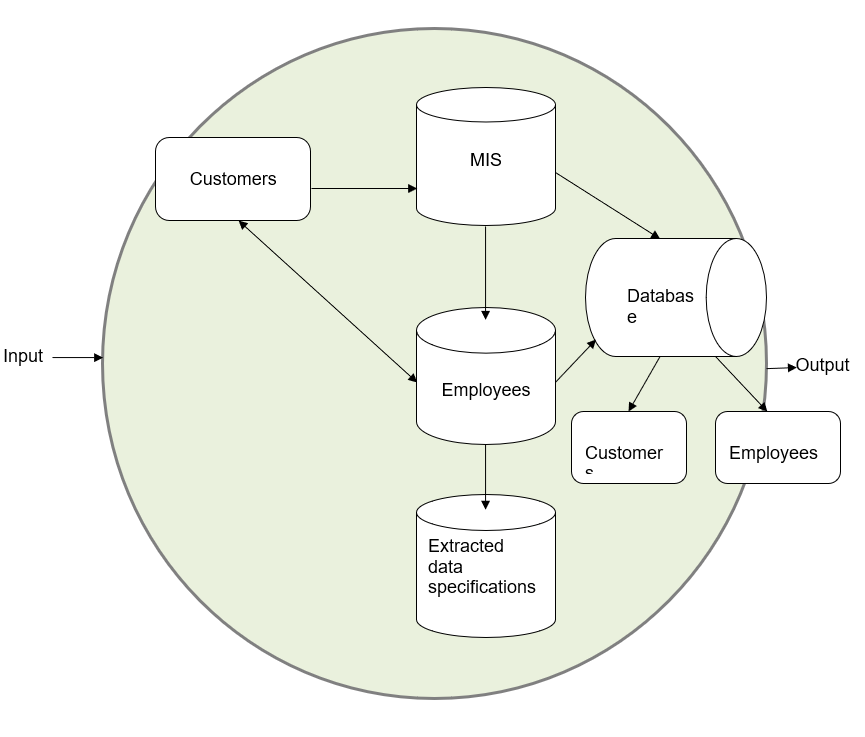
Information processors computerised
Customers: provide their contact information and personal preferences in their personal profiles when visiting the website of the firm. They can place an order and choose the payment method online. The information from customers’ personal profiles is stored in the firm’s database.
Employees: can access the information from this database and extract certain specifications, such as information for different groups of customers and their overall purchases. This would allow the employees to plan effective interaction and develop relevant special offers appealing to the interests of the target groups of customers.
The computer processes are run by the various software programs to:
- Save the data inputs and consolidate them into a general database.
- Attribute identifiers to different units of information and differentiate the entries.
- Extract information specifications are satisfying the chosen requirements.
- Save the data for the results of manager-customer interaction.
Information processors non-computerized
- The employees need to set the goals and select the identifiers for extracting particular units of information from the database.
- The employees analyze the extracted data specifications, identify the problems if any and develop effective solutions or improvements.
Information store computerized
Customer information: contact information, personal preferences, the overall amount of purchases, readiness for contact with employees (how often and via what channels – email, telephone, etc.)
The firm’s information: available offers and the time required for extracting the information specifications from the database.
Information store non-computerized
The employees register new customers who contact the firm without visiting the website and record the results of their cooperation with all groups of customers.
Networks
The database includes information entries made by customers and employees. When navigating the website and placing orders, customers access the database using their names and contact information. The employees, who extract the information specifications from the database, use their IDs and passwords and keep records of the reports they extract from the database.
Internal view of the information system
Reference
Laurikaitis, Aurimas. “Extracting Conceptual Data Specifications from Legacy Information Systems.” Doctoral dissertation, Kaunas University of Technology, 2010. Web.