Jacob’s Staff Design
Jacob’s staff, which is also referred to as a cross-staff, is the simplest tool used to make qualitative conclusions regarding the angle and height of an object concerning the observer. It was commonly used by navigators and astronomers before the telescope was invented (Winterburn). The simplest form of the tool is a calibrated pole with a crosspiece attached perpendicularly to it in such a way that it can slide up and down along the pole. Figure 1 shows a pictorial representation of Jacob’s staff.
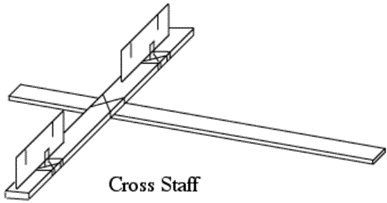
To make the device, the following items were required:
- A wooden yardstick
- A wooden 1-foot ruler to act as the crosspiece
- Thick manila paper or an empty cardboard box from packed food such as cereal
- 4-6 rubber bands
- A stapler
- Two paper clips and pieces of paper (Stern).
How to Use Jacob’s Staff
The first step is to slide the cross-piece to the center of the yardstick. The yardstick is sighted along the line midway between the stars whose distance is to be measured. The two sliders are then placed on the cross-piece such that the position of the slits coincides with the placement of the stars. The yardstick slider is then adjusted until both stars can be seen flashing simultaneously in the two slits.
The instrument was lowered and the distance between the two sliders was measured. Assuming that A was the angle between the yardstick and the direction of one star, the mathematical formula for tangent is then used to find angle A as follows:
Tan A = BC/AC
where BC is the distance between the slits and AC is the distance between the eye and the crosspiece.
Calibration of the Device
Calibration of the instrument was done by measuring the largest angle between the Big Dipper (based on “How to use Jacob’s Staff” instructions above). The angle was expected to be 25o. This estimate was chosen because it was likely to minimize the chances of error. However, the observed measurement was 27o. Therefore, the estimated precision of the instrument was ±2o.
Works Cited
Stern, P. David. “The Cross Staff.” NASA. Web.
Winterburn, Emily. “Astronomy and Navigation.” The Encyclopedia of Empire, 2016. Web.