Outsourcing theory
Outsourcing is the exercise of utilizing external service providers with the job of performing in-house endeavors. This has attracted a rising interest in recent years as managers consider whether it is in their best interest to perform activities in-house or externally. Outsourcing is a contractual agreement whereby an organization controls a part or all of the functions of the department within an organization to an external party. The organization pays a fee and the contractor delivers a level of service that is defined in a contractually binding service level agreement. The contractor provides the resources and expertise required to perform the agreed service. Outsourcing is becoming increasingly important in many organizations (Bartlett 2004).
According to this study, it was found that outsourcing causes increased performance and productivity Along the same vein although it has yielded positive outcomes there are some implications such as human costs and financial loss. This study looked at the financial and human aspects of outsourcing as well as the attitudinal view on outsourcing in which a theoretical framework was established.
Support of the theory
The specific objectives of human outsourcing vary from organization to organization. Typically, though, the goal is to achieve efficiency, commitment, and delivery in human resources through corporate restructuring to take advantage of a vendor’s competencies. Outsourcing of human resources is thus the theory that the study will use to access its effects on leadership performance and employee commitment.
The theory accesses the positive reasons for outsourcing in order to determine why it has an impact on leadership performance and employee commitment. There are different reasons why organizations outsource. However, the main reasons for embarking on outsourcing include a desire to focus on a business’s core activities, pressure on profit margins, and increasing competition that demands cost savings and flexibility with respect to both organization and structure. These reasons support outsourcing theories within organizations.
Despite the advantages highlighted, there are possible disadvantages associated with outsourcing. This includes costs exceeding customer expectations, loss of internal human resource experience, loss of control over hiring, and difficulty in reversing or ad changing outsourced arrangements (Corbett 1996).
Diagrammatic illustration of the theory
The attitudinal result of the study showed that outsourcing programs were found to have a negative perception of work participation. This in effect did affect the improvement of skills as well as accomplishment of work within the organization.
In addition, utilizing the outsourcing program had a negative relationship as regards communication within the organization, importance of work and its weaknesses, and individual responsibility (See Figure 1.1).
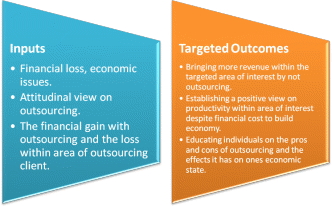
Figure 1.1. gives the inputs regarding the pros and cons of outsourcing. Although outsourcing yields positive outcomes to a degree, on the other hand, it causes economic downfall in the area of interest. It is necessary to educate companies/businesses and the managerial staff on both. Ultimately, each company/business is different in its views on outsourcing. On the other side, it can save one financially because the costs of goods within one’s own country are not affordable when it comes to purchasing in bulk. Education is vital so that one can weigh their options when it comes to outsourcing goods/materials, the effects it has on economic status, and current and/or potential employees.
The inputs of outsourcing should be able to reflect the output and the study should be able to compare the variables under the inputs to be able to ascertain whether indeed outsourcing positively affect leadership performance and employee commitment. This will entirely be based on the targeted outcomes of the study.
A theoretical proposition in the study
Understanding the risks associated with outsourcing is the key to determining the extent to which outsourcing affects leadership performance and employee commitment. Business risks associated with outsourcing are hidden costs; contract terms not being met, service costs not being competitive over the period of the entire contract, and the balance of power residing with the vendor. However, there are ways that these risks can be reduced including establishing measurable partnership enacted shared goals and rewards, utilization of multiple suppliers or withholding a piece of business as an incentive, formalization of a cross-functional contract management team, contract performance metrics, periodic competitive reviews and benchmarking and implementation of short-term contracts (Charara 2004).
According to this study, it was found that outsourcing caused increased performance and productivity and has yielded positive outcomes. Along the same vein, although it has yielded positive outcomes there are some implications such as human costs and financial loss. This study will be based on the practical nature of outsourcing of human resources that impact leadership performance and employee commitment. Outsourcing is the effective use of resources from outside the firm that has been seen to improve organizational planning as well as staff morale. Outsourcing is said to cause not only increased performance but also productivity which leads to good outcomes in the organization in terms of employee commitment and leadership performance (Bolumole 2007).
References
Bartlett, B. (2004). How outsourcing creates jobs for Americans. National Center for Policy Analysis.
Bolumole, Y., Frankel, R., & Nasland, D. (2007). Developing a theoretical framework for logistics outsourcing. Transportation Journal, 46(2), 35-54.
Charara, J. (2004). Impact of outsourcing ‘lasts years’. People Management, 2(4), 15-18.
Corbett, M. F. (1996). Redefining the corporation: Bringing order to a new industry. Outsourcing Leadership Forum, 1-7.