Introduction
Strategic management is considered to be one of the basic elements that allow a business company to achieve success in its operations in both domestic and international markets (Thompson, 2001, p. 24; Thompson, Strickland, Gamble, 2009, p. 37). However, even such giants of the global business as Pepsi Co. sometimes face diversification strategy issues in their developmental initiatives, and a comprehensive restructuring and strategy re-formulation become necessary to overcome the emerging consequences.
Pepsi Co’s Strategy
SWOT Analysis
Thus, to see the roots of the issues experienced by Pepsi Co. between 2007 and 2008, it is necessary to carry out the SWOT analysis for the company:
Fig.1 Pepsi Co. SWOT Analysis.
Acquisitions and Mergers
Thus, the strategy of Pepsi Co. regarding acquisitions and mergers is one of the strengths of the company according to the SWOT analysis. The examples of successful acquisitions of Pepsi Co. include:
- 1980s Mug root beer, 7UP International, and Smartfood ready-to-eat popcorn acquisitions;
- 1990s Walker’s and Smith’s Crisps, Gamesa, and SunChips acquisitions;
- 2001 Quaker Oats acquisition;
- 2000s Sandora Juice, Lucky Juice, Star Foods acquisitions;
Industry Driving Forces and Porter’s 5 Forces Model
Further on, to better understand Pepsi Co.’s industry positions, 5 forces Porter’s model can be quite helpful (Thompson, 2001, p. 289):
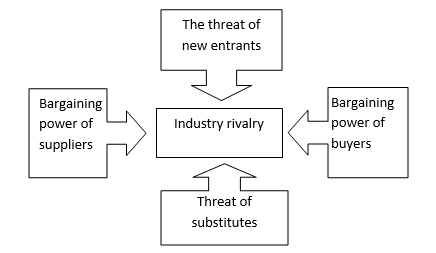
Thus, one can see that the rivalry among existing firms in the industry is the central driving force, and Pepsi Co. faces this rivalry at especially severe rates as far as it tries to catch up and exceed the Coca-Cola market share, while also trying not to stay far behind losing its positions to its other competitors, i. e. Cadbury Schweppes and Nestle. Further on, Pepsi Co. tries to cope with a high power of suppliers by establishing long-term relationships with the latter.
The power of buyers is crucial for the industry with such great competition, and this factor is one of the major threats for Pepsi Co., as well as the threat of substitute products provided by its competitors. At the same time, the threat of new entrants is rather low in the beverage industry as there are quite high operating margins and capital requirements.
Recommendations
So, Pepsi Co. faces major issues in the beverage industry, i. e. the rivalry within the industry and the strong buyer power both conditioned by the fierce industry competition. To cope with these issues, it is recommended that Pepsi Co. should:
- Continue diversification of products to cope with the competition and threat of substitutes in the market;
- Monitor buyer satisfaction levels;
- Implement customer-friendly programs to increase buyer satisfaction levels.
If properly implemented, these steps are expected to strengthen Pepsi Co.’s market position and enable the company to develop competitive advantages in the beverage and snack industries.
Works Cited
Thompson, Arthur, A. J. Strickland, and John E. Gamble. Crafting and Executing Strategy: The Quest for Competitive Advantage Concepts and Cases. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2009. Print.
Thompson, John. Understanding corporate strategy. Cengage Learning EMEA, 2001. Print.