Introduction
PepsiCo is a corporation that includes a number of brands selling processed foods and beverages. The most famous products of the company include Pepsi-Cola, Mountain Dew, Cheetos, Doritos, and Lay’s. Other recognizable names are Tropicana, 7 Up, Lipton tea, and Mirinda (The Street 2017). The current state of the corporation shows that is has a diverse portfolio of internationally recognized businesses with strong representation and brand loyalty. The Street (2017) lists PepsiCo as the best variant for people who want to invest in the market for beverages as it has the best quality-revenue ratio.
Company Description
PepsiCo is a private business, traded as NYSE: PEP, S&P 100, and S&P 500 Components. Its primary product types are beverages (non-alcoholic) and processed foods. Soft drinks represent the main sub-industry of the company. The CEO and chairperson of PepsiCo are Indra Nooyi, and Ramon Laguarta is the current president. As of 2016, the company’s revenue amounted to almost US$62.8 billion. The net income of PepsiCo was approximately US$6.3 billion, and its total assets were around US$74.1 billion.
The corporation employs more than 260000 people and has about 100 different subsidiaries. Some of them are focused on local markets, while others are marketed globally. The loyalty of the company’s customers allows it to remain one of the most influential competitors in multiple markets. Furthermore, the stock of the business has the potential for growth according to the latest statistics. The continuous rise of the prices suggests that the company does not plan on giving up its main products (Figure 1).
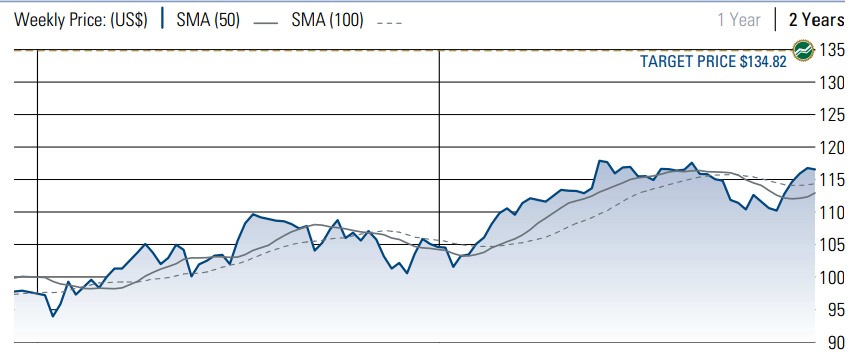
Although the company’s main products are perceived as ‘junk food,’ it has various brands that are not directly connected to this particular market. PepsiCo was founded in 1965, after two companies, Pepsi-Cola and Frito-Lay, merged together. However, the main branch of the corporation was established in 1898. The companies’ headquarters are situated in Purchase, New York. The structure of PepsiCo has its representatives in many parts of the world, including North and South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and the Middle East (The Street 2017).
The company is recognized as the second most influential food and beverage seller after Coca-Cola, but its current net growth is superior. Although many people are choosing to abstain from foods and products that contain a high amount of calories and sugar, PepsiCo’s signature brands continue to dominate the market.
Sector Outlook
The leading sector that can be researched in more detail in the industry of non-alcoholic beverages, where PepsiCo has the longest history of business operations. This segment usually includes soft drinks such as carbonated soda drinks (CSDs), non-carbonated drinks, and hot beverages with tea and coffee. Soft drinks take up the most prominent part of the industry as they are represented by various CSDs, juices, cold tea and coffee, sports and energy drinks, and bottled water. According to Bailey (2014), CSDs lead the market, with approximately 30% of all sales (Figure 2). These products are followed by bottled water.
However, the prevalence of carbonated drinks and their significance to the company is apparent. The author mentions PepsiCo and the Coca-Cola Company as the main rivals of this market. According to Bailey (2014), the companies share about 70% of all profits for CSDs between each other, while smaller competitors are far behind.
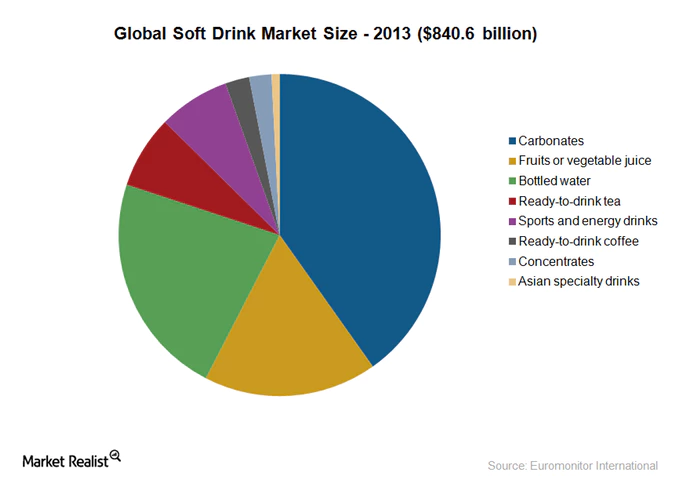
Such popularity of the brand reveals its strong standing as the industry is being continuously pushed by government regulations and social concerns. The connection between health-related problems and CSDs negatively impacted the market and led to a number of restrictions. The increasing attention to the consumption of sugar – the main ingredient of any CSD – allowed the US government to implement a Soda tax, which increased spending for companies. This alteration did not damage PepsiCo’s brand of CSDs significantly, and it continues to bring profits (The New York Times 2017). Nevertheless, the policies of PepsiCo and its main rival, the Coca-Cola Company, are changing as the corporations try to reduce the consumption of sugar.
Furthermore, one should note that by investing in PepsiCo, the person will benefit even if the CSD market suffers significant losses as the industries for bottled water and energy drinks, which are also represented in the assortment of PepsiCo, are growing. Furthermore, while the internal market for CSDs may be declining, PepsiCo can rely on other countries to keep the business stable. Currently, PepsiCo is tracking the state of developing markets in order to maintain its place on the global scene. The abundance of competition in the industry of carbonated drinks does not allow other brands to repeat PepsiCo’s success, which only raises its profitability and attractiveness to any investor.
Comparative Analysis
The industry of soft beverages is highly competitive despite its being controlled by a small number of corporations. Certain large businesses are rivals in terms of pricing, marketing, and innovation. The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo have to continuously develop new ways of attracting customers as their market positions are relatively the same. However, PepsiCo manages to have a net income higher than any other company in the industry (Figure 3). Its net sales are the biggest as well. Thus, an investment in this corporation may provide a person with a stable income, which does not fear the changes in the market. Developed markets do not see many changes from all companies as they do not provide volume growth. Emerging markets, on the other hand, allow companies to earn more.
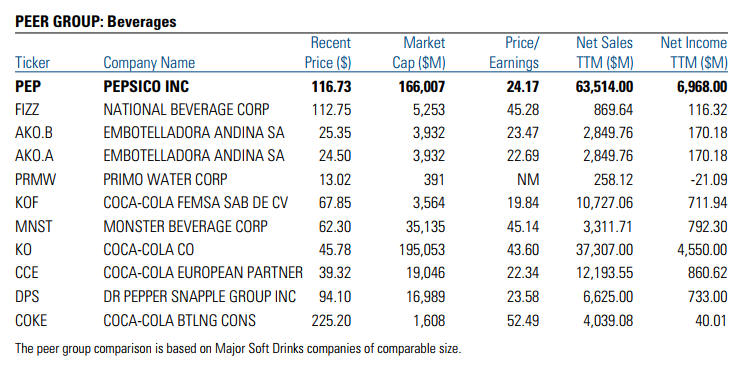
It is interesting to note that the company now focuses on its other branches as much as CSDs, as 52% of net revenue does not come from beverages but food (PepsiCo 2017). It is possible that the company centers on other types of products due to the fact that soda consumption is decreasing because of health concerns. However, the state of the market for snack foods resembles the industry described above as it is also highly competitive and represented by a small number of companies.
Fundamental Analysis
Although its revenues were falling at the end of 2016, PepsiCo improved its earnings per share in 2017 by more than 8% (The Street 2017). Overall, the corporation continues to increase its profits and has a positive rate of growth in stocks. In fact, in the last two years, PepsiCo saw an improvement in earnings, which may extend to the following year. According to the official report by PepsiCo (2017), the company almost met its goal of net growth in 2016. Most of the revenue comes from beverages sold in North America. Then, it is followed by the sales of Frito-Lay products in North America.
The revenue that comes from outside the US includes around 40 % of all profits. The company’s products are available in more than 200 states, and the company values its global approach as much as local ingredients and tastes. The region of Europe and Sub-Saharan Africa take up the third place of areas with the highest net revenue. Next, Latin America, Asia, Middle East, and North Africa follow with their income amounting to around 20% total (Figure 4). Thus, if an individual seeks to fund a business with a strong local presence and a well-established international system, he or she can invest in PepsiCo.
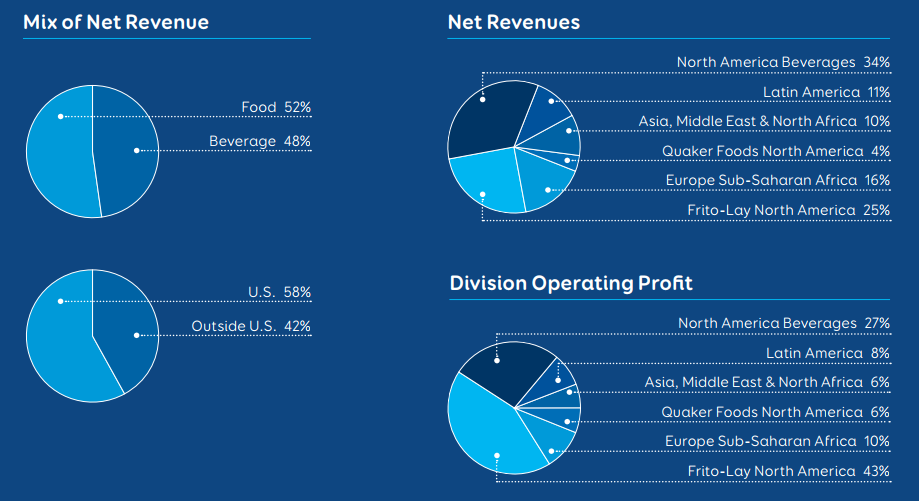
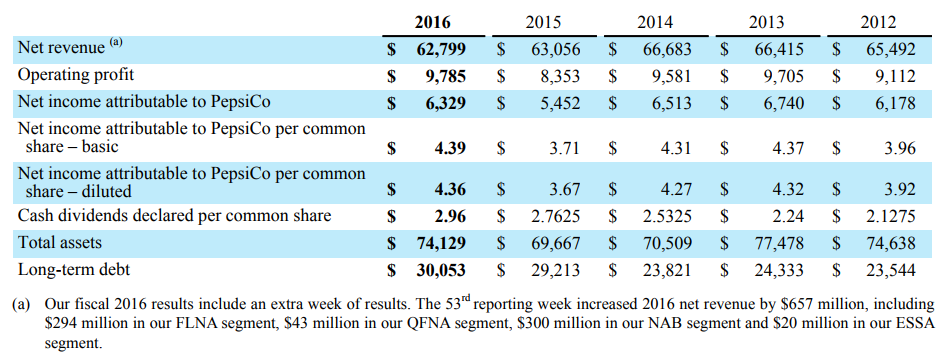
Looking at a five-year summary of the company’s fiscal results, one can see a case of stable growth and little decline (Figure 5). The main measurements, such as net revenue, fluctuate but stay in the same range. However, the overall assets of the business continue to grow. The company’s slow and fluctuating improvement can be explained by its extended presence on the market. PepsiCo is a strong competitor who dominates the industry dividing it with another influential company. The operating profit of the company grows, and the revenue from shares becomes higher as well.
Risk Analysis
Possible Risks
It is necessary to outline a number of risks that are linked to investing in PepsiCo:
- Capital resources – Although the company has stable profits, its total debt is growing every year (The Street 2017). PepsiCo (2017) admits that the situation of the company may be adversely impacted if credit markets and global capital cannot meet the business’ demands. The company has long-term financing, commercial paper borrowing, and debt financing to prevent any financial problems. However, PepsiCo’s debt management risk remains high.
- Consumer preferences – The financial situation of the company can be affected by the continuously changing tastes of their clients. The industry of food and beverage distribution is highly competitive as it depends on customer demand. Shifting trends in the food industry may quickly alter the position of the company and its profitability. For instance, the interest of clients in their health may lead to a decline in demand for CSDs due to their high level of sugar. The presence of saturated fat and sodium in snack foods is also a part of this issue. Consumed preferences always change, and the industry should be able to respond quickly to new challenges. If the company fails to appeal to the clients, it may lose a substantial amount of money.
- Laws and regulations – The food and drink industry of the US has many rules for companies to follow. Improper labeling and advertising, for instance, may lead to a number of legal problems and following financial losses. Ingredients have to be disclosed, and appropriate tags have to be used. It is also possible that new scholarly research may find some ingredients that the company currently uses unsuitable for consumption.
- Total return – The performance of the company that is linked to the stock’s price movement is not outstanding. Although it is not weak, PepsiCo can increase the rate of total return to compete with other companies.
- Growth – The company’s cash flow is growing steadily. It is highly unlikely that the company will encounter any financial problems in the near future.
- Stock volatility –The price of shares of PepsiCo has changed insignificantly during the last year (Figure 1). Thus, the company’s stock is not volatile as it does not show any substantial problems. In fact, it grows slowly and predictably, which allows investors to be sure of their benefits. The prediction for the next year can be based on these results as they are quite showing.
- Taxation – New and increased taxes may negatively impact the financial state of the company. Products with sugar and caloric sweeteners may be eligible for additional taxation in some markets. Some states in the US already have special regulations that limit the possibilities of the business on that territory. However, the company is dealing with these issues through innovation.
- Economic conditions – The company’s international presence exposes it to a number of countries with unstable economies. Therefore, PepsiCo may encounter such problems as high inflation, devaluation, and demonetization. These environments may bring more financial issues and make the company vulnerable to change.
SWOT Analysis: Strengths
- The company’s branding is easily recognizable due to its long history and popularity. PepsiCo incorporates a number of incredibly famous names from many industries. Thus, brand recognition is a valuable resource for the company to use in marketing and customer service.
- The company forged a strong bond with its clients over the years. Customer loyalty may help PepsiCo to mitigate the problems that can arise from changing customer demands.
- PepsiCo is one of the leading corporations in the food and beverage markets. Its current position can be considered one of its strengths as it distinguishes this company from the rest and gives it even more exposure.
- The broad market reach of the corporation ensures its high profits as PepsiCo can focus on different trends and products from various markets without the need to diversify further. It can rely on food products if the popularity of CSDs declines, for instance.
- The international presence of the company also gives it more ways to gain a profit and remain stable. The saturation of the US markets can negatively affect the sales, but PepsiCo has local and unique brands in different countries on which it can rely.
- The company has its own bottlers, which simplifies the process of negotiation for prices.
SWOT Analysis: Weaknesses
- The range of products can also be considered as a weak point of the company, as most products that PepsiCo sells are often linked to unhealthy eating habits. Sugary drinks and snack foods that are high in sodium may become less demanded in the following years due to peoples’ rising interest in health. To resolve this issue, PepsiCo added a number of healthy alternatives to its previous assortment, such as bottled water, juice, and oatmeal.
- The growing financial debt of the company may significantly damage its current state. The risk of PepsiCo being unable to manage its existing debt may lead to more economic issues in the future.
- The slow growth of the profits can also discourage some investors as it may not offer a high return.
- Inconsistent client base – diverse groups of clients may be hard to appeal to as they all have different preferences and tastes.
SWOT Analysis: Opportunities
- As the shift towards healthy foods is becoming more apparent, PepsiCo can use this opportunity to rebrand its businesses. While it will not be able to avoid its strong connection with processed foods and CSDs, it can concentrate on its other purchased brands. According to George and Lorsch (2014), the corporation is using this strategy already as it is focusing on healthier products and rebranding its current flagship beverages.
- The reach of PepsiCo in emerging markets may give the company an opportunity to create a sustainable approach to manufacturing. Torkornoo and Dzigbede (2017) state that PepsiCo uses a number of socially responsible practices to promote sustainability. For instance, it promotes recycling and helps poor communities to prevent malnutrition and obesity of children. More efforts in this area of operations may give PepsiCo more positive exposure.
- The company has enough resources to support continuous innovation for its manufacturing and distribution and education for staff.
SWOT Analysis: Threats
- Growing health concerns of people may create some liabilities for PepsiCo and endanger its branding. Customer loyalty may decline with time if the company fails to change with the central trends.
- Strong competition may put the company in a challenging position and expose it to financial problems. The Coca-Cola Company is one of the main rivals of PepsiCo, and it can start outperforming the latter in such a way that PepsiCo may not be able to recover.
Conclusion
Upon analyzing past and current data about PepsiCo, one can recommend investing in this corporation. Although the growth of the company’s profits may seem too slow, it is impossible to deny the stability of the business and its strong desire to grow even more. Furthermore, the process of diversification of PepsiCo leaves no doubt that the corporation has many long-term plans that will ensure its success. The risk of investing in one of the most critical players on the beverage and snack foods market is very low. The established and loyal customer base, along with a wide range of products and desire for further change, point to the fact that one should consider PepsiCo as a valuable investment.
Reference List
Bailey, S 2014, A guide to the non-alcoholic beverage industry.
George, B & Lorsch, JW 2014, ‘How to outsmart activist investors’, Harvard Business Review, vol. 92, no. 5, pp. 88-95.
PepsiCo 2017, Stock price & information. Web.
The New York Times 2017, ‘Beverages non-alcoholic industry snapshot’. Web.
The Street 2017, PepsiCo Inc.
Torkornoo, HK & Dzigbede, KD 2017, ‘Sustainability practices of multinational enterprises in developing countries: a comparative analysis of Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo Inc’, Journal of Global Initiatives: Policy, Pedagogy, Perspective, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 19-30.