The unprecedented outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic has been long-lasting and has caused substantial economic recovery challenges. Due to this, the U.S. government has to actively design and enforce policies that will handle different issues that cannot be addressed by pure market forces, like the unavailability of market risks and externalities (Stiglitz, 2021). In addition, covid-19 has caused disruptions in the current market arrangement and inabilities of expansion of businesses. Therefore, the government is crucial because it will ensure the restoration of economic growth.
Previous weak government intervention has made the United States economic system fragile when affected by the prolonged pandemic. Under equilibrium conditions for a competitive economy, the market can efficiently handle any economic issues (Stiglitz, 2021). However, the effects of covid-19 disrupted this condition, and the markets could not operate well, which could only be resolved by government intervention. In addition, the covid-19 was contagious, and it created an externality that made it impossible to deal with the pricing system. There was also unavailability of the market for risk because there were no excellent insurances markets, businesses, and individuals to purchase against the ravages of the pandemic.
The government should impose regulations on all businesses in the U.S. The main goal of private companies is to make money, but they usually take advantage of their employees. For instance, in the U.S., some insurance companies took advantage of their employees during the pandemic by either laying them off or reducing their salaries (Stiglitz, 2021). The government should develop regulations that will prevent these types of rules. In return, these regulations will affect unemployment in the country and public expenditure since the government will protect the population. Figures 1 and 2 below show the unemployment rate and the public expenditure rate in 2019 when the pandemic was at its peak across the world.
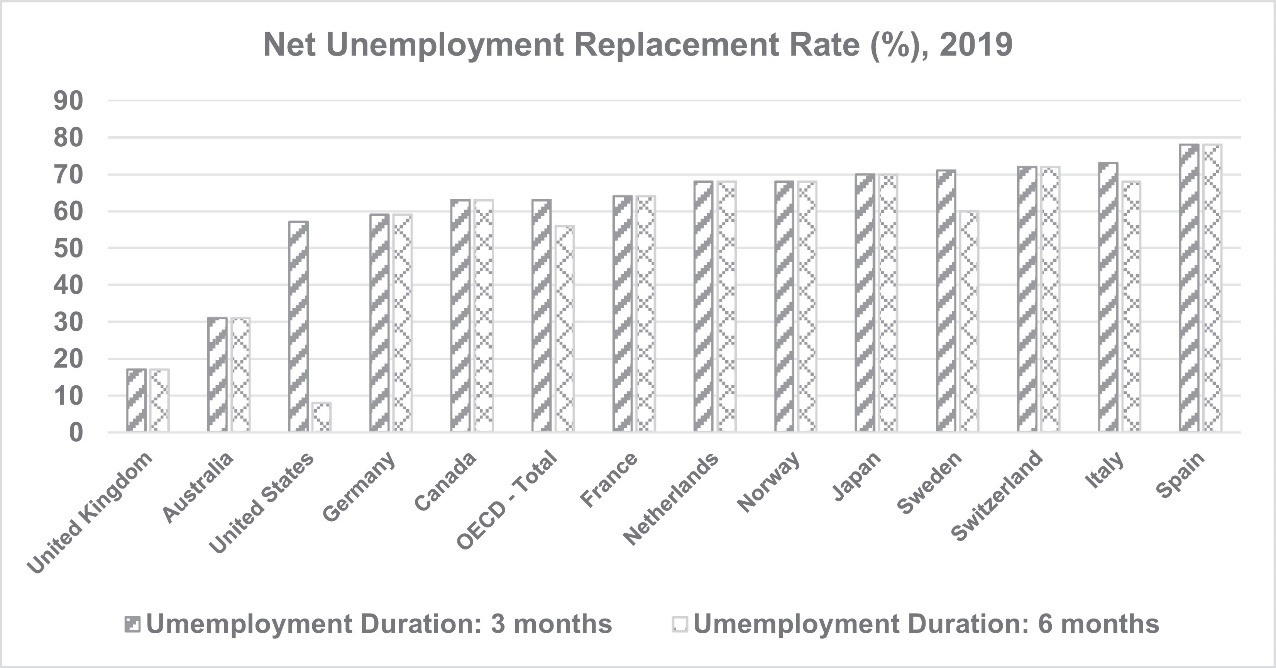
Figure 1 shows that the United States unemployment replacement rate was significantly affected in the first three months of being hit by the pandemic (Stiglitz, 2021). As the pandemic continued, the effect on the unemployment replacement rate reduced. In addition, compared with other countries, the U.S. was the third affected in terms of net unemployment replacement rate.
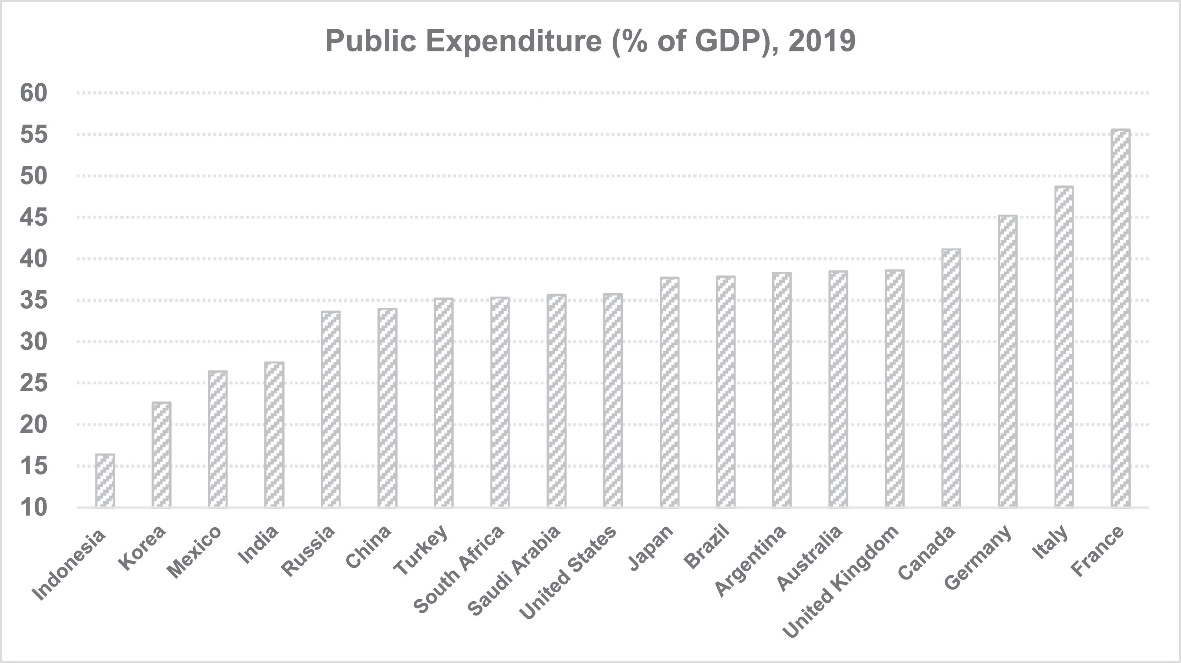
Figure 2 compares public expenditure (% of GDP) in 2019 between countries, and the U.S. was 10th in public spending globally.
Although government intervention through imposing regulation will protect employees, it will affect existing and entrant companies. The existing companies will be affected in a way that it will be difficult for them to expand or open new branches (Stiglitz, 2021). Opening new units will be expensive because the government will have regulations on salaries of employees to be posted in the new branch. On the other hand, it will be hard for new entrants due to expensive wages. Therefore, government regulations will have long-term effects that will lead to future increased unemployment.
In conclusion, the global pandemic outbreak has severely affected the overall economy of the U.S. In addition, the pandemic has taught the government the interventions it should actively participate in to prevent markets from being affected severely. The government should also be careful with the interventions it is involved in because it might have a long-term impact that might cause some consequences. Therefore, post-pandemic recovery of the U.S. economy is dependent on government intervention that should be favorable for both employers and employees.
References
Stiglitz, J. (2021). The proper role of government in the market economy: The case of the post-COVID recovery. Journal of Government and Economics, 1, 100004.