Executive Summary
Marketing audit has become a common practice among many businesses as they undertake strategic planning in their marketing process. The audit aids in measuring an organization’s marketing capability as well as environmental threats and opportunities. This type of audit report is made up of a structure with detailed diagnostic steps of an organization’s marketing activities, marketing systems and the operating environment. The success derived from the provision of products and services by a business is usually determined either indirectly or directly by forces in its macro-environment.
The environmental factors encompassing the marketing operations being conducted by Proctor and Gamble comprise of national factors and aspects which play roles that massively impact on its marketing processes. Besides, the same environment is made up of political, economic, socio-cultural and technological (PEST) factors. It is important to mention that the current operating business environment for Proctor and Gamble is strongly characterized by high level of competition from its competitors such as Unilever, Kimberly-Clark, Johnson and Johnson, Clorox and Colgate-Palmolive. Careful application of the 4Ps marketing mix (product, price, promotion and place) should be established for greater competitive advantage.
Introduction
Marketing audit has become a common practice in strategic planning among many firms since the audit aids in measuring an organization’s marketing capability. Studies reveal that marketing audit has numerous potential benefits since it provides a detailed analysis of a business’ internal situation and external environment, an opportunity to identify future threats and opportunities and an objective evaluation of present activities and past performance.
Streeter (2003, p. 70) indicates that a marketing audit report is made up of a structure with detailed diagnostic steps of an organization’s marketing activities, marketing systems and environment. This paper explores the marketing audit of Proctor and Gamble Company by evaluating its marketing environmental variables, operational variables, the macro-environment and micro environmental factors) are either out of control of the organization’s marketing strategists
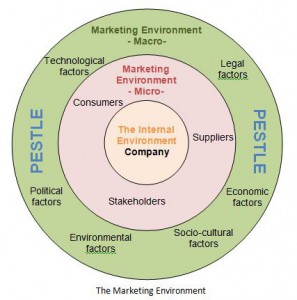
Marketing environment
Schumann (2001, p. 93) notes that the marketing environmental factors are divided into three significant levels which include the national environment (macro-environment), meso-environment and the internal or micro-environment. It is imperative to note that a marketing environment is crucial to marketers in building both internal and external relationships through value addition.
Geographical market
Markle (2011, p.287) defines a geographical market as an environment in which a business experiences similar conditions of competition like other businesses over same products. Multinational businesses such as Proctor and Gamble define their geographical market through product nature and characteristics, difference in market shares, barriers in market entry and transport cost levels. Markle indicates that among the aforementioned factors, competition in marketing focuses on the interesting aspect of transport cost as this determines whether or not regional or global trade is feasible.
The operations of Proctor and Gamble (PEST- G analysis and Macro-environmental analysis)
The success derived from provision of products and services by a business is usually determined indirectly or directly by forces in its macro-environment (Valentine 2012, p. 40). A marketing environment is normally controlled by both macro and micro-environmental factors. It is imperative to highlight that decision makers in marketing need to critically analyze and diagnose a business’ marketing environment. This can be achieved through environmental scanning whereby forces within a market environment are assessed and interpreted for diagnosis.
At Proctor and Gamble, environmental scanning is a process being conducted with the aim of gaining a deeper understanding of the elements within its environment, ensuring that the business develop effective strategies which fit well with the environment, analyzing market situations and observing the diverse changes within the market environment (Valentine 2012, p. 40). As such, its management has taken a keen interest in involving, controlling, coordinating, directing, organizing and planning of all its marketing processes. As such, it has been able to derive diverse and ample benefits from understanding its environment.
The environmental factors encompassing the marketing operations being conducted by Proctor and Gamble comprises of national factors and aspects which play roles that massively impact on its marketing processes. Palmer, Dunford and Akin (2009, p. 100) observe that an environment in which a business is operating plays a critical role by influencing competition, generating threats and colossal opportunities. The macro-environment of Proctor and Gamble comprises of political, economic, socio-cultural and technological (PEST) factors.

PEST analysis
Political environment
Leavy (2010, p. 13) indicates that governments of diverse nations normally intervene to a certain level in the economic activities carried out by businesses. Such areas of intervention include setting up of tariffs, trade restrictions, environmental laws, labor laws and tax policies. Besides, political stability and instabilities within a region impacts on the environment of a business.
At Proctor and Gamble, political factors have had massive impact on driving down consumer demand for its products, its marketing activities and provision of products and services to consumers.
Economic environment
One of the most affected industries during times of economic downturn is the trade industry since consumers can easily decline from purchasing products or shift to alternative and cheap goods. Schumann (2001, p. 93) posits that the ability of the US and global economy to remain stable is a great asset for Proctor and Gamble. Its management understands that it can do very little to change this environment. However, it supports good governance of the country since this would shield the economy from financial instabilities and consequently enhance resilience whenever such cases are inevitable.
Socio-cultural factors
The effectiveness of marketing is largely dependent on satisfaction of consumers and their consequent passage of the same information to others (Stuart 1998, 410). Proctor and Gamble strongly rely on people’s social ties to pass their product experiences to others who would equally seek to achieve the same. Though such ties work well for P&G, the organization faces stiff competition from emerging organizations that are offering similar products. As indicated earlier, it is critical that an organization strengthens its online communities and establishes essential follow-up mechanisms to ensure that its consumers obtain better product experience.
The ability of consumers to remain linked to an organization’s products either through marketing programs or community set up will strongly draw a line between current and future demand for P&G’s products. Notably, Markle (2011, p.287) narrates that the current US generation appears to lose the affinity for the already existing products especially with continued emergence of newer technologies (Winer 2009, p. 110).
Technological environment
In his publication, Streeter (2003, p. 70) expounds that technology will remain the greatest force that will determine the direction of activities and operations being conducted by a business. Proctor and Gamble has been strongly affected by the rapid technological developments that have seen enhancement of its manufacturing processes as well as boosting marketing activities. The company markets its products online and more people are able to access P&G’s product information online and make correct decisions on whether to visit the company physically of via its website.
Online communities are continually growing and more people are relying on technology to market, purchase and obtain relevant product information. The demand for P&G products as well as its marketing operations is expected to increase with the advent of technology even to the emerging market in the developing world. According to Sun and Wu (2011, p. 340), the technological environment will continue to create a better marketing niche for Proctor and Gamble
Competition
Main competitors
The current business environment which Proctor and Gamble operates is strongly characterized by high level of competition from its competitors such as Unilever, Kimberly-Clark, Johnson and Johnson, Clorox and Colgate-Palmolive. This has been lauded by many analysts as a factor which compels P&G to develop effective marketing practices. The role of developing effective marketing practices at Proctor and Gamble’s current business environment makes it one of the most important marketing factors in ensuring greater sustainability of product value.
Toegel and Barsoux (2012, p. 53) note in their publication that the industry in which P&G operates remains one of the most dynamic due to varied personal tastes and preferences which make consumers to easily shift from one organization to another. Indeed, P&G experiences stiff competition from other multinationals.
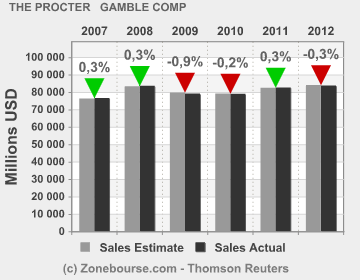
Sales and profit trends
While the company is yet to report its performance in the fourth quarter in August this year, its sales and profit trends like those of its competitors have continued to increase.
From the figure above, its revenue in terms of profits has continued to rise over the years due to its effective marketing and sales strategies. Its revenue is expected to have risen by $ 0.77% by the time the market opens (see appendix II). Compared to its competitors, P&G’s household and personal products have raised its revenue above that of its competitors. For instance, P&G’s revenue stands at 79,689.0 followed by Kimberly-Clark at 19,746.0 (Winer 2009, p. 110).
Market shares
Proctor and Gamble’s market share has continued to grow since it has increased its business units by 20 % since 2010 (Winer 2009, p. 110). It has also merged its products with Gillette to increase awareness of its brands and compete favorably with its competitors. Its stock price from marketing and corporate strategy has increased by about 50% in terms of growth (Winer 2009, p. 110).
Target markets
The target market for proctor and gamble’s products ranges from children, teenagers and adults (Valentine 2012, p. 40).

P&G has diversified its market to target new areas with its products. Johnson (2002, p.9) points out that the business has identified major opportunities in continent like Africa where there is large market for its products.
The company
Procter and Gamble (P&G) is one of the leading consumer goods multinational companies in America which manufactures a wide range of products such as Pampers, Always, Vicks, Crest and Tide among others and distributes to its consumers in markets across the globe (Valentine 2012, p. 40). The ‘company has its headquarters in Cincinnati, Ohio through which it plans its marketing activities and the distribution of its products to drug stores, membership club stores, grocery stores, and mass merchandisers across over 180 countries (Winer 2009, p. 110).
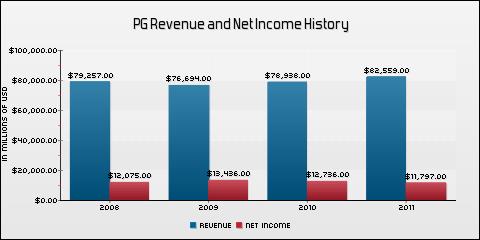
Sales and profit trend
In the year 2007, Procter and Gamble’s profit growth was marked at 12% minimum with a growth of 20 % in its earnings (Winer 2009, p. 110). Its growth in profit from its sales has considerably grown to $ 82.6 in the last year, a consideration that is reflected by high profits in 2011 (See appendix II). Procter and Gamble has been able to establish its competitive edge via differentiation of its offerings. It leadership has devoted finances and time to research and development (R&D) with an aim of creating new products needed by consumers.
Market share
The market share of Proctor and Gambles has continued to grow as it has increased its business units over the years. It has also merged its products with Gillette to increase awareness of its brands and compete favorably with its competitors. Its stock price from its marketing and corporate strategy has increased by about 50% growth (Winer 2009, p. 110).
Business sector and Project focus
Proctor and Gamble has cut a niche and built its brand on both products and services in the US and other parts of the globe (Winer 2009, p. 110). Its products include Pampers, Always, Vicks, Crest, Tide, paper towels, facial tissues, diapers and bath tissues, skin care products, prestige fragrances, personal cleansing, hair care, deodorants and cosmetic products.
SWOT analysis
Strengths
Since its inception, P&G has continuously grown its marketing activities and processes to become one of the leading providers of household and personal products. Analysts have pointed out that P&G’s products ranging from Pampers, Always, Vicks and paper towels have strongly attracted customers who have in turn developed preference and confidence to the company’s brands. Analysts indicate that the company through its packaging ideals has built a name through its brand gained competitive advantage over the competitors.
Weaknesses
Marketing analysts indicate that the availability of substitute products and increasing demand for cheaper products presents established and strong businesses such as P&G with difficulties of lowering cost and ensuring economies of scale. While many businesses have opted to lower their commodity prices to gain a competitive edge over others, P&G has been hesitant, a consideration that has seen many consumers shifting to alternative products. The nature and quality of its products cause its goods to assume high costs making many buyers who cannot afford them shy away. Its commodity prices are not reflective of the affordable prices necessary for capturing the ready market in many regions.
Opportunities
Modern sales and marketing operations for P&G products require better and quality products and demand the application of better technological considerations. The company has been known to ensure quality and uses technology to enhance the effectiveness and quality of its products. In return, this presents it with numerous opportunities to reach the market and introduce fresh products to new markets.
Threats
One of the major threats facing P&G is the nature of the highly competitive market environment it is operating in. The company is exposed to a stiff competition from its competitors like Unilever, Kimberly-Clark, Johnson and Johnson, Clorox and Colgate-Palmolive. It is worth mentioning that since its competitors are developing similar products and lowering the cost of their products, P&G faces a great threat of losing on its marketing strategy.
The company’s marketing strategy
Businesses that target raising maximum profits from the sale of their products and services develop effective marketing strategies. The need for profits propels them to identify the needs within a target market. Janicijevic (2010, p. 100) indicates that at P&G, one of its marketing strategies centres on building customer relations since this attract customers attention, retain them and can be used to obtain feedback on its products.
Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning (STP)
In his publication, Hopkins (2009, p. 27) point out that STP is an important component that boosts the competitive edge of a business, its products gets identified, market segments corrected and market mix applied to maximize profits. In the case of P&G, it has been able to select potential locations where a mixture of low class, middle class and upper class people are and can buy its products. In these segments, it markets and carries out promotions of its products. Market segmentation carried out by P&G is a practice that is being pursued with greater vitality. This according to analysts ensures that newer avenues for selling products are identified and the existing market is understood better.
Another marketing strategy is targeting in which the company considers individual groups’ behaviors to determine their exact preferences. In his discussion of targeting, Hopkins (2009, p. 27) indicates that P&G products target businesses and individuals.
Differentiation and growth strategy
P&G differentiation strategy has assisted it to separate and make unique its products especially similar goods being produced by close competitors in the market. Marketing managers find it easy to position specific products and enhance their sale when products are easily noticeable by consumers in the market. This factor has been a major platform towards the growth of P&G.
The marketing mix (4P’s)
Effective articulation of marketing mix at P&G forms the best platform upon the company understands its marketing environment, designs its products based on customer’s needs, and explores newer market niches. The emerging global effect driven by forces of demand and supply calls for more articulate market analysis aimed at outdoing competitors.
Product
Proctor and Gamble has built its brand on both products and services in the US and other parts of the globe. Its products include Pampers, Always, Vicks, Crest, Tide, paper towels, facial tissues, diapers and bath tissues, skin care products, prestige fragrances, personal cleansing, hair care, deodorants and cosmetics. It has continued to diversify and extend its production to other modern and unique children’s products. Notably, children’s products are highly sensitive and therefore call for careful design to suit the diverse market. Of particular importance is the emerging younger generation’s demand for fancy and appealing products.
Price
Pricing of the aforementioned products has always been a key consideration for the company because it determines their affordability. As a result, P&G has established a clear method of determining the prices of different products in a manner that more people are able to afford the products. To further promote accessibility, various products are priced differently depending on complexity of their production and design. At this point, the company seeks to ensure that all products are of high quality even those with lower prices on their tags. A good example is pampers which is mostly used for babies and sells at $ 23.99 a pack. The company often brings down the prices especially during promotions to increase sales and reach out more consumers to acquire its products.
Promotion
Ahenkora and Peasah (2011, p.280) elaborate that promotion is one of the most important aspects in P&G’s marketing practice because it informs consumers on what is available in the market and at what price. Therefore, promotion acts as part of an informative tool that is critical for assisting consumers to plan for their budgets with ease. P&G’s promotion includes advertising which is largely conducted in the media daily. With over 90% of US population having access to television and radio, advertising on them has been of great success because of the guaranteed large audience (Winer 2009, p. 110). Notably, the company has recently taken a great bias towards online advertisement due to wider availability of clients.
Place
Following the continued expansion of population across the globe, P&G’s products have been made more available in various geographical locations. Janicijevic (2010, p. 100) indicates that P&G maintains large stores in key states. Besides, the products are also available in major markets. As indicated earlier, these stores are crucial in the sense that they give a chance to consumers especially those who need smaller quantities.
Evaluation of companies strategies and tactics
Evaluation of companies current position and company success (growth in sales and profit)
The current leading position of P&G in terms of sales of products, revenue and income can only be attributed to its effective application of Porter’s five forces framework such as market rivalry, a consideration that has enabled it to compete favorably and establish a competitive edge (Winer 2009, p. 110). As already noted, P&G’s profit and market share are favorably stable. This is due to its marketing strategies that involve positioning, segmentation, diverse product differentiation and the ability to raise and lower commodity prices without incurring losses.
Prospects for future growth
Product lifecycle as explained by Ahenkora and Peasah (2011, p.280) is a process whereby products undergo a process from raw materials through growth, maturity, and final decline. The greatest task for P&G’s future growth is to ensure that the stage of growth and maturity is extended and lengthened. Using more aggressive promotional strategies would act as a renewing platform of products being received by consumers.
Promotional methods should be purposefully designed in a manner that more consumers are able to get the message on P&G’s products availability. For instance, intensification of online promotion and use of billboards to reach more consumers is indeed welcomed alongside the current methods. Notably, intensified online promotion would enable the company to reach out to more consumers even beyond its already established locations.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it is evident that effective articulation of marketing mix in organizations forms the best platform for understanding the market, designing products based on customers’ needs, and exploring newer market niches. Careful application of marketing mix, product, price, promotion and place are indeed crucial for P&G’s business portfolio. However, due to emerging competition and global economic forces, it is definite that P&G should enhance its marketing strategies.
References
Ahenkora, K. & Peasah, O 2011, ‘Crafting strategy that measures up’, International Journal of Business and Management vol.6 no. 10, pp. 278-283.
Hopkins, M 2009, ‘8 Reasons Sustainability Will Change Management (That You Never Thought of)’, MIT Sloan Management Review vol. 51 no. 1, pp. 27-30.
Janicijevic, N 2010, ‘Business processes in organizational diagnosis’, Management : Journal of Contemporary Management Issues vol. 15 no. 2, pp. 85-106.
Johnson, L 2002, ‘Issue selling in the organization,’ MIT Sloan Management Review vol. 43 no. 3, pp. 8-9.
Leavy, B 2010,’Design thinking – a new mental model of value innovation’, Strategy & Leadership, vol. 38 no. 3, pp. 5-14.
Markle, GL 2011, ‘Constructions of citizenship among multinational corporations’, International Journal of Business and Social Science: Special Issue, vol. 2 no. 24, pp. 283-293.
Palmer, I., Dunford, R.& Akin, G 2009, Managing organizational change a multiple perspective approach, McGraw Hill, Boston.
Schumann, P. 2001. A moral principles framework for human resource management ethics. Human Resource Management Review, vol. 11 no.2, pp. 93-111.
Streeter, B 2003, ‘Sweet deal’, American Bankers Association. ABA Banking Journal vol. 95 no. 11, pp. 69-74.
Stuart, L 1998, “Case study – the leveraging of brand equities to create a category champion: Nestle’s management of Crosse & Blackwell”, British Food Journal vol. 100 no. 9, pp. 405-412.
Sun, T. & Wu, G 2011, ‘Trait predictors of online impulsive buying tendency: a hierarchical approach,’ Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, vol. 19 no. 3, pp. 337-346.
Toegel, G. & Barsoux, J 2012, ‘How to become a better leader’. MIT Sloan Management Review vol.53 no. 3, pp. 51-60.
Valentine, L 2012, ‘Wealth management: revenue solution? American Bankers Association. ABA Banking Journal vol.104 no. 3, pp. 40-44.
Winer, RS 2009. “New communications approaches in marketing: issues and research directions”, Journal of Interactive Marketing, vol. 23 no. 2, pp. 108-117.
Appendices
Appendix I
Appendix II