Introduction
Project financing is an essential aspect of project success. A detailed and well-incorporated process should be applied in the planning, controlling, and managing records of a project. It is not easy to attain the goals and objectives of a project since the process is constrained by challenges in finance management and project costs. The goal of the study is to discuss the different project funding sources along with their success implications of a project. The benefits and limitations of joint ventures to business strategy and project funding will be expounded. The project planning processes and problems facing finance management and project costs will also be debated in the paper.
Define what you understand about project financing and explain the variety of funding sources available. What are the implications of the different sources towards the success of a project.
Project financing is a funding arrangement relying on the future cash flow of the project as a source of repayment. The arrangement uses project assets and interests as collateral security. The lenders and sponsors share joint-venture risks in funding the project. The process of financing can be present at any stage of a project based on the strategy of financial managers (Sharp & Peters, 2017). Project financing can occur at any given stage of the project as per the terms of the financial management team (Sharp & Peters, 2017). The generally applied sources of financing for projects are private finance, loans, overdrafts, or grants (Lock, 2017). Potential funding sources are detailed as follows.
Short-term project finance sources
Short-term project sources include overdrafts and loans. Overdrafts are useful since it’s normally due for refund in not more than one year. In overdrafts, interest payments are taxed and charged only when that facility is used. It is flexible since any amount can be borrowed at any given time. In the case of loans, there is less flexibility since payments are made on the basis of pre-agreed terms, including payment time. Loans, however, provide higher interests which are tax-deductible which means loan return can exceed interest payments. Internal rate of return can be used to derive the cost of money borrowing given the returns from the project.
Long-term project financing sources
Long-term sources include sales and leasing, loan capital, and share capital. Sales and leasing are where assets can be sold to a certain project development company and then leasing back for a mentioned term. These assets can be used to fund the project. Loan capital consists of three categories: venture capital, business angels, and debentures. Venture capital increases the value of shares so that they can be sold at a profit. Venture capitalists mostly consider those companies considered too risky by others. Business angels are private investors who seek equity in exchange for their investment (Harrison & Lock, 2017). Debentures loans are raised by the floating charge of a company’s assets. Interest payments here are made before shareholders received their dividends. Share capital is profits shared among company shareholders in direct exchange for their investments in projects.
Project Grants
Grants can be directly gifted to a specific project as free funds from the government, the European Union, and national lotteries.
Project success factors
Availability of free flow of funds improves the success of a project. The quality of sponsors helps in improving the chances of success. Insurance helps improve project success in case of defaults and losses.
List the benefits and risks of joint-ventures to the long-term business plan and funding of projects.
Firstly, joint ventures increase access to specialized technology and skillful personnel (James, 2016), thereby improving the quality of projects and increasing the likelihood of long-term success. Secondly, joint ventures share risks and costs where a project fails, allowing projects more of a safety net in long-term projects. Thirdly, joint ventures tend to have a larger customer database (James, 2016), increasing their profitability, which increases funding and chances of a successful project. Finally, joint ventures forge long-lasting business project relationships and improve lessons learned jointly over time.
Risks of joint-venture
Particular attention should be paid to projects in which two forces are participating because there is a chance that the resources and capabilities of the two will not be equal (Reuer, Klijn & Lioukas, 2014). Next, difficulties with communication are a common issue that can lead to misunderstandings that will result in poor outcomes (Yan & Luo, 2016). Finally, the difference in corporate cultures may affect the outcomes as well.
Project financial management requires very detailed processes concerning planning, control and administration and records. Briefly describe these processes with reference to PMBOK.
Planning of resources, estimation of costs, budgeting, and cost control are the essential elements of financial management in projects.
The PMBOK guidelines outline the specific elements of financial management and emphasize the importance of paying close attention to the process of planning, spending and monitoring them throughout the course of a project. It is critical for project managers to identify the required financial resources that will be used in a particular project, quantities of these components, and specify the undertakings (Larson & Gray, 2015). Additionally, financial managers have to estimate duration, prospective risks, chosen funding source, costs of construction, and tax benefits.
Project managers are required by PMBOK to ensure cost control is conducted such that it caters to variations in the plan caused by any change of cost baseline or other concerns. Aspects of being included are a financial plan, revenue benefits, request change, and contract requirements.
Meanwhile, the process for administration and records involves the storage of financial records in a standard format, preferably on the computer (Rose, 2013). The inputs included are the previously presented contract requirements, financial plan, and the financial report status. These records are further in the process of developing a plan of communication with stakeholders. The administration is necessary to ensure that the project meets the contractual requirement.
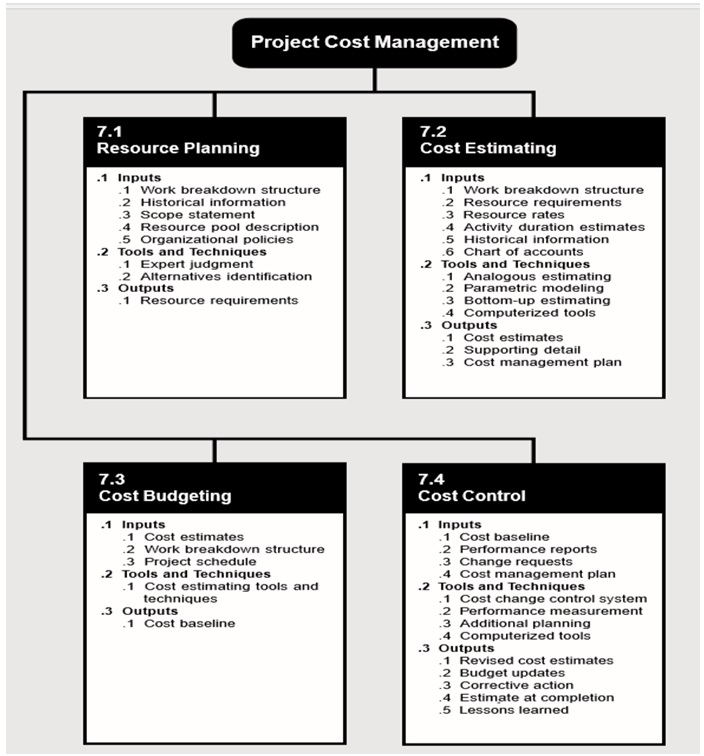
Define (with simple examples) the following aspects of a financial management plan; i) resource planning, ii) cost estimating, iii) cost budgeting and iv) cost control.
Resource planning is done at the beginning phase by defining the resources (people, equipment, and materials) needed. Resources are things like labor, equipment, and time required to accomplish a project. Work breakdown structure (WBS) is developed by the project manager. In it, project elements that are crucial for resource planning are specified. In addition, Harrison and Lock (2017) recommend incorporating and evaluating information from previous projects for efficient preparation. The scope statement is the final component of the resource planning in which the project is justified using set objectives.
Cost estimate involves the development of approximate costs of the resources that will be required to complete the identified scheme. This is the general price tag a project is required to be funded to achieve its goal. Methods that can be used for cost estimation are parametric models and analogous estimation. For instance, if more work than initially anticipated is required for the design stage of an assignment, the project manager is needed to carry out additional calculations and determine whether these alterations will offset the original plan and expected savings. Several tools are developed to facilitate similar estimations, for example, bottom-up and analogous estimating, parametric modeling, or computer-based solutions (Kerzner & Kerzner, 2017).
Cost budgeting is used to allocate costs over a time period and gives a periodic and project cost a task that helps in the effective establishment of cost baseline, which is necessary for evaluating project performance (Martinelli & Milosevic, 2016). A cost baseline is used to measure the actual performance progress, for example, where a project involves the construction of a plane. The first task would be to construct a WBS for the project. However, the WBS requires people to allocate costs at the different levels of WBS, thus accomplishing cost budgeting.
Cost control measures variance from cost baseline and assists in applying decent corrective measures to attain minimum costs. Cost control software is used to define effective cost control measures.
What you believe are the biggest challenges in project cost and finance management and why. Choose one of these areas: Resources planning i.e. people, equipment, materials etc.
Resource planning is arguably the biggest challenge to project cost and finance management. Other areas like cost control are reliant on proper resource planning. Any failure to effectively plan adequate resources forces managers to seek resources at short notice with potentially higher costs or lesser quality, thereby further compounding project costs. One can argue that The Millennium Dome project is one example that failed due to inadequate resource planning (Abbasi, Wajid, Iqbal & Zafar, 2014). Had the team contracted the right human resources for marketing and budgeting, the project may have succeeded.
Conclusion
Project financing can be sourced in a number of ways (loans, grants, investors, and private finance), each with its own associated risks and costs. It is the most significant asset in the success of a project development cycle. Joint ventures, whilst generating additional funding and technologies, can pose challenges that hasten project non-fulfillment. Financial management incorporates different elements, including estimating, monitoring, administering, and recording spending.
The development of an accurate estimation and baseline budget for the project is the primary method of resolving perspective issues. Additionally, control measures allow project managers to evaluate costs and funds to enable the fulfillment of set goals. Furthermore, it is critical to keep a record of spending and compare it with the planned budget to ensure adherence and proper execution. Finally, communication with stakeholders should update them on the status and advancement of the project, which is crucial for its success. Effective resource planning is arguably the biggest challenge to project costs since other challenges are triggered and compounded by it.
References
Abbasi, N., Wajid, I., Iqbal, Z., & Zafar, F. (2014). Project failure case studies and suggestion. International Journal of Computer Applications, 86(6).
Lock, D., (2017). The essentials of project management. 4th Ed. London: Routledge
Harrison, F., & Lock, D. (2017). Advanced Project Management. London: Routledge.
Kerzner, H., and Kerzner H. R., (2017). Project management: a systems approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling. 11th Ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Larson, E. W., & Gray, C. F. (2015). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge: PMBOK (®) Guide. Project Management Institute.
James, D. (2016). The benefits of a joint venture for pathology. The Health service journal, 126(6494), 24-25.
Martinelli, R. J., & Milosevic, D. Z. (2016). Project management toolbox: tools and techniques for the practicing project manager. New York, John Wiley & Sons.
Reuer, J. J., Klijn, E., & Lioukas, C. S. (2014). Board involvement in international joint ventures. Strategic Management Journal, 35(11), 1626-1644.
Rose, K. (2013). A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). e1-e1.
Sharp, J., & Peters, J. (2017). The Management of a Student Research Project. London: Routledge.
Yan, A., & Luo, Y. (2016). International Joint Ventures: Theory and Practice: Theory and Practice. 1st Ed. London. Routledge.