Overview
The assignment involves a description of three approximating approaches, namely analogous, bottom-up, and parametric techniques. It also gives a detailed discourse of the individual method and a highlight of the circumstances which may necessitate their preference for use. Additionally, there is an introduction of the triangular distribution and the Beta distribution, as the two common 3-point methods of estimating the duration and costs. Finally, the difference in the computed results and decisions on the preferable method to employ is given.
Estimating Techniques
Analogous Estimating Technique
The technique utilizes the information from the previous equivalent project or activity for projecting the budget or period of the undertaking. The parameters from the past tasks that are used include scope, project length, complexity, weight, and financial plan. The attributes serve as the baseline for measuring or approximating a similar item for a prospective venture. Subsequently, the method relies entirely on the actual measures of the earlier comparable tasks for the efficient computation of rough estimates of the particular parameter in a current venture. It is mostly employed in projects with the likelihood of impeding adjustments due to identified variances in project intricacy (Project Management Institute, 2017). Additionally, it is used in approximating project time-scale when there is scarce data regarding the project.
The method is dependent on the knowledge, expertise, and intelligence of the user in identifying the similarity and variability among the dual projects. In such instances, the attributes of one of the central parameters fit linearly with the costs of the item in the project of interest. The reference model can then be utilized in the cost approximation for an attribute of the current assignment. From the preceding, the technique is ideal for estimating when the available information about the project cost is scarce. Moreover, it can be preferred when the institution has a limited budget and require speedy results.
Bottom-up Estimating Technique
The approximation of the ultimate costs of the product is arrived at through summation of the entire costs for work, material, infrastructure, and other inherent costs in work phases. The technique calls for the availability of in-depth knowledge of the process. Additionally, it requires the interactions in the method and the plan information for the undertaking. The approach can be implemented on an operation, activity, or the foundation of a feature. In all instances, the individual component level costs are computed and summed up to achieve the overall venture costs. The expenses of a phase are connected to particular attributes of the project, like materials, human resource and equipment (Hueber et al., 2016). This is beneficial for the project planners, which is insightful to cost as it provides the designers with direct feedback on cost impression during the design exercise.
The principal shortcoming of the approach is the intensive requirement of efforts to undertake the estimation. It also faces drawbacks in that it demands inordinate project details for fine outcomes. Nevertheless, it offers a straightforward process with ease of understanding and is the only technique adaptable to advancement in technologies. The approach is best suited, where the timeframes of the project are spread, and the organization requires estimates that are accurate and reliable.
Parametric Estimating Technique
The methodology employs predetermined algorithms during the modeling of the project to approximate the inherent expected duration and cost. The approach is frequently utilized by construction and engineering fields due to its ability to simultaneously provide the estimate for the requisite resources, overheads, and time of a project. It also employs the available statistical information and the past data regarding a similar project to compute the ideal estimates for the undertaking. The specialists entrusted with the approximation process obtain the attributes from comparable tasks and uses them in the modeled algorithm of the prevailing project. For the effective application of the parametric technique, the project is broken down into sub-components, which are then matched with appropriate predefined correlations to deduce the estimations. Notably, despite the algorithms been obtainable from previous assignments, the definite conditions of the project get detached upon the establishment of the correlations.
The parametric evaluations are quick and easy to carry out and can be utilized during the initial planning phases. The major hitch of this approach is that it depends on a past directory; thus, it is unsafe for utilization outside the defined range of the database. It also suffers from the inability to delineate revamped requirements of a system or changes in technology (Hueber et al., 2016). However, the technique is desirable where the company is financially constrained but requires considerable accurate results, and more than a single dataset is available.
3-Point Cost & Duration Estimation Methods
From the given information, the computations for the duration estimations using the triangular and the Beta distribution methods are as follows.
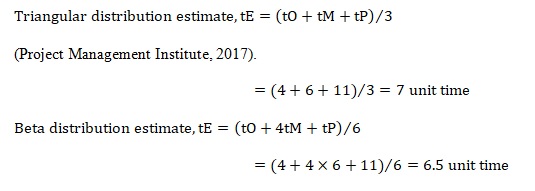
The estimated duration using the beta distribution is shorter than utilizing the triangular distribution method. This is because the Beta distribution method gives more precise value as a weighted approximated duration for the given case. In deciding the method to adopt, it will be essential to compare the computed durations with the worst-case phenomenon exhibited by the pessimistic duration (Sivaprasad & MacKenzie, 2018). The method with the greatest variance between the two is adopted.
References
Hueber, C., Horejsi, K., & Schledjewski, R. (2016). Review of cost estimation: Methods and models for aerospace composite manufacturing. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science, 2(1), 1-13.
Project Management Institute, H. (2017). A guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) (6th ed.). Project Management Institute, Inc.
Sivaprasad, S., & MacKenzie, C. (2018). The Hurwicz decision rule’s relationship to decision making with the triangle and beta distributions and exponential utility. Decision Analysis, 15(3), 139-153.